|
Lincoln Mark VIII
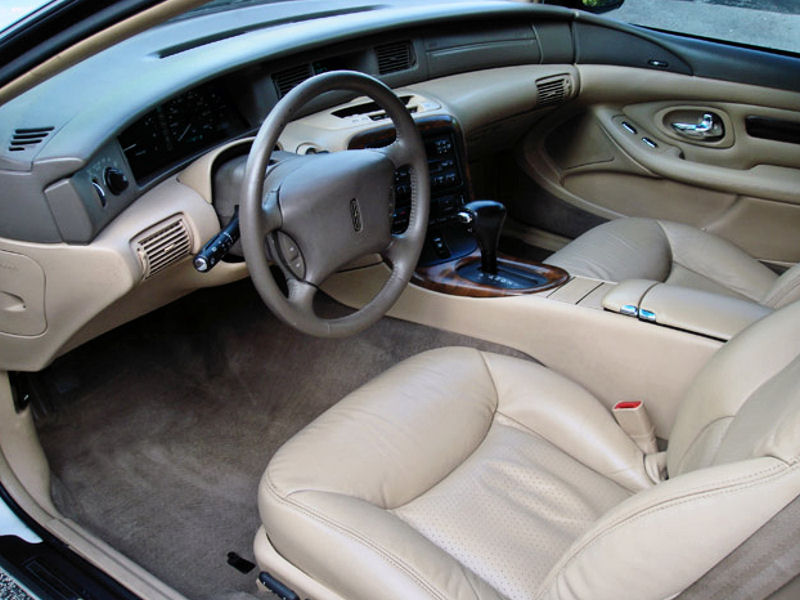
The Lincoln Mark VIII is a grand touring luxury coupe marketed by Lincoln from the 1993 to 1998 model years over a single generation, manufactured at Ford's Wixom Assembly Plant. Succeeding the Lincoln Mark VII, the Mark VIII shared underpinnings with the Ford Thunderbird and Mercury Cougar. Following the 1998 model year, the Mark VIII was discontinued without replacement, remaining the last model of the Lincoln Mark series. Development Development of the Mark VIII (FN-10) began in 1984 with a projected release for the 1990 model year. Design work began in 1986 and was oriented toward evolutionary changes. By 1987, Lincoln designers emphasized interior design, as ordered by then Ford design director Dave Rees. In the autumn of 1988, FN-10 development was pushed and went through several revisions. This was done to further develop a more precise product to accommodate the use of a DOHC modular engine, using the upcoming MN12 platform due to be launched in December 1988. Havin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lincoln Motor Company
Lincoln Motor Company, or simply Lincoln, is the luxury vehicle division of American automobile manufacturer Ford Motor Company, Ford. Marketed among the top luxury vehicle brands in the United States, Lincoln was positioned closely against its General Motors counterpart Cadillac. The division helped to establish the personal luxury car segment with the 1940 Lincoln Continental. Lincoln Motor Company was founded in 1917 by Henry M. Leland, naming it after Abraham Lincoln. In February 1922, the company was acquired by Ford, its parent company to this day. Following World War II, Ford formed the Lincoln-Mercury Division, pairing Lincoln with its mid-range Mercury (automobile), Mercury brand; the pairing lasted through the 2010 closure of Mercury. At the end of 2012, Lincoln reverted to its original name, Lincoln Motor Company. Following the divestiture of Premier Automotive Group (Jaguar Cars, Jaguar, Land Rover, Aston Martin, and Volvo Cars, Volvo) and the closure of Mercury (a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DOHC
An overhead camshaft (OHC) engine is a piston engine where the camshaft is located in the cylinder head above the combustion chamber. This contrasts with earlier overhead valve engines (OHV), where the camshaft is located below the combustion chamber in the engine block. ''Single overhead camshaft'' (SOHC) engines have one camshaft per bank of cylinders. ''Dual overhead camshaft'' (DOHC, also known as "twin-cam".) engines have two camshafts per bank. The first production car to use a DOHC engine was built in 1910. Use of DOHC engines slowly increased from the 1940s, leading to many automobiles by the early 2000s using DOHC engines. Design In an OHC engine, the camshaft is located at the top of the engine, above the combustion chamber. This contrasts the earlier overhead valve engine (OHV) and flathead engine configurations, where the camshaft is located down in the engine block. The valves in both OHC and OHV engines are located above the combustion chamber; however an OHV ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ride Height
Ride height or ground clearance is the amount of space between the base of an automobile tire and the lowest point of the automobile (typically the axle); or, more properly, to the shortest distance between a flat, level surface, and the lowest part of a vehicle other than those parts designed to contact the ground (such as tires, tracks, skis, etc.). Ground clearance is measured with standard vehicle equipment, and for cars, is usually given with no cargo or passengers. Function Ground clearance is a critical factor in several important characteristics of a vehicle. For all vehicles, especially cars, variations in clearance represent a trade-off between handling, ride quality, and practicality. A higher ride height and ground clearance means that the wheels have more vertical room to travel and absorb road shocks. Also, the car is more capable of being driven on roads that are not level, without the scraping against surface obstacles and possibly damaging the chassis and und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
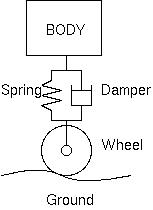
Air Suspension
Air suspension is a type of vehicle suspension powered by an electric or engine-driven air pump or compressor. This compressor pumps the air into a flexible bellows, usually made from textile-reinforced rubber. Unlike hydropneumatic suspension, which offers many similar features, air suspension does not use pressurized liquid, but pressurized air. The air pressure inflates the bellows, and raises the chassis from the axle. Overview Air suspension is used in place of conventional steel springs in heavy vehicle applications such as buses and trucks, and in some passenger cars. It is widely used on semi trailers and trains (primarily passenger trains). The purpose of air suspension is to provide a smooth, constant ride quality, but in some cases is used for sports suspension. Modern electronically controlled systems in automobiles and light trucks almost always feature self-leveling along with raising and lowering functions. Although traditionally called air bags or air bellows ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer-controlled Suspension
An active suspension is a type of automotive suspension on a vehicle. It uses an onboard system to control the vertical movement of the vehicle's wheels relative to the chassis or vehicle body rather than the passive suspension provided by large springs where the movement is determined entirely by the road surface. Active suspensions are divided into two classes: real active suspensions, and adaptive or semi-active suspensions. While semi-adaptive suspensions only vary shock absorber firmness to match changing road or dynamic conditions, active suspensions use some type of actuator to raise and lower the chassis independently at each wheel. These technologies allow car manufacturers to achieve a greater degree of ride quality and car handling by keeping the tires perpendicular to the road in corners, allowing better traction and control. An onboard computer detects body movement from sensors throughout the vehicle and, using that data, controls the action of the active and semi-act ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crumple Zones
Crumple zones, crush zones, or crash zones are a structural safety feature used in vehicles, mainly in automobiles, to increase the time over which a change in velocity (and consequently momentum) occurs from the impact during a collision by a controlled deformation; in recent years, it is also incorporated into trains and railcars. Crumple zones are designed to increase the time over which the total force from the change in momentum is applied to an occupant, as the average force applied to the occupants is inversely related to the time over which it is applied. The physics involved can be expressed by the equation: :F_\text\Delta t = m\Delta v where F is the force, t is the time, m is the mass, and v is the velocity of the body. In SI units, force is measured in Newtons, time in seconds, mass in kilograms, velocity in metres per second, and the resulting impulse is measured in newton seconds (N⋅s). Typically, crumple zones are located in the front part of the vehic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unibody
A vehicle frame, also historically known as its '' chassis'', is the main supporting structure of a motor vehicle to which all other components are attached, comparable to the skeleton of an organism. Until the 1930s, virtually every car had a structural frame separate from its body. This construction design is known as '' body-on-frame''. By the 1960s, unibody construction in passenger cars had become common, and the trend to unibody for passenger cars continued over the ensuing decades. Nearly all trucks, buses, and most pickups continue to use a separate frame as their chassis. Functions The main functions of a frame in a motor vehicle are: # To support the vehicle's mechanical components and body # To deal with static and dynamic loads, without undue deflection or distortion. :These include: ::*Weight of the body, passengers, and cargo loads. ::*Vertical and torsional twisting transmitted by going over uneven surfaces. ::*Transverse lateral forces caused by road cond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid digital subscribers. It also is a producer of popular podcasts such as '' The Daily''. Founded in 1851 by Henry Jarvis Raymond and George Jones, it was initially published by Raymond, Jones & Company. The ''Times'' has won 132 Pulitzer Prizes, the most of any newspaper, and has long been regarded as a national " newspaper of record". For print it is ranked 18th in the world by circulation and 3rd in the U.S. The paper is owned by the New York Times Company, which is publicly traded. It has been governed by the Sulzberger family since 1896, through a dual-class share structure after its shares became publicly traded. A. G. Sulzberger, the paper's publisher and the company's chairman, is the fifth generation of the family to head the pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Popular Mechanics
''Popular Mechanics'' (sometimes PM or PopMech) is a magazine of popular science and technology, featuring automotive, home, outdoor, electronics, science, do-it-yourself, and technology topics. Military topics, aviation and transportation of all types, space, tools and gadgets are commonly featured. It was founded in 1902 by Henry Haven Windsor, who was the editor and—as owner of the Popular Mechanics Company—the publisher. For decades, the tagline of the monthly magazine was "Written so you can understand it." In 1958, PM was purchased by the Hearst Corporation, now Hearst Communications. In 2013, the US edition changed from twelve to ten issues per year, and in 2014 the tagline was changed to "How your world works." The magazine added a podcast in recent years, including regular features ''Most Useful Podcast Ever'' and ''How Your World Works''. History ''Popular Mechanics'' was founded in Chicago by Henry Haven Windsor, with the first issue dated January 11, 1902. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)


.png)
