|
Limtoc
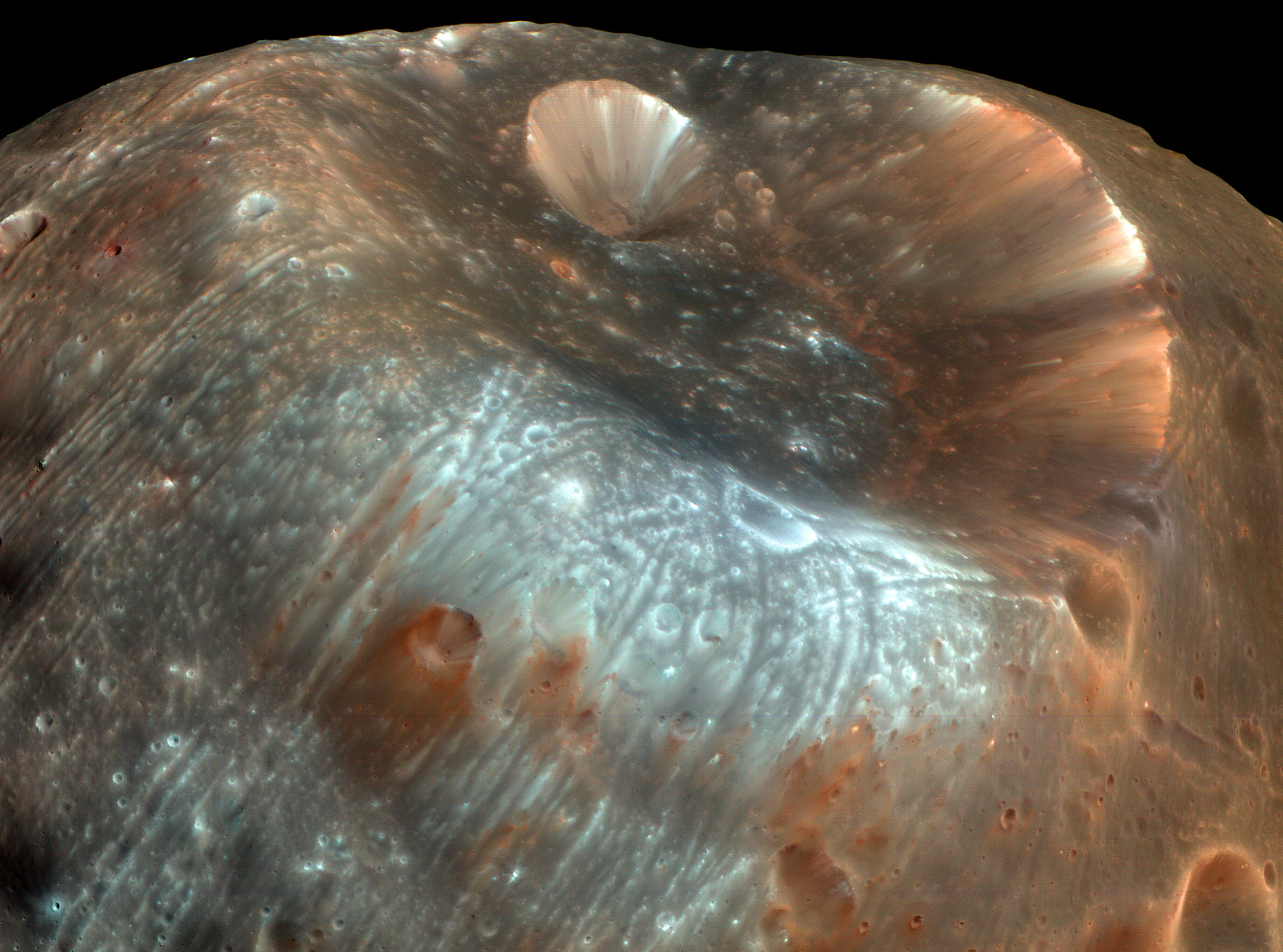
Limtoc is a crater on the surface of Mars's inner moon Phobos. The crater, the diameter of which is 2 kilometers, is located within the larger, and more well-known surface feature, Stickney crater. Limtoc was officially named by the International Astronomical Union on 29 November 2006, after a character from ''Gulliver's Travels''. Limtoc formed roughly 109 million years ago, making it one of the youngest features on Phobos. When the Limtoc impactor collided with Phobos, it created a significant amount of ejecta Ejecta (from the Latin: "things thrown out", singular ejectum) are particles ejected from an area. In volcanology, in particular, the term refers to particles including pyroclastic materials (tephra) that came out of a volcanic explosion and magma ...; ejecta which was sent towards the northern edge of Stickney collided with that crater's rim, while ejecta sent towards the southern edge was largely catapulted out of Stickney altogether. This ejecta has partially contr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phobos (moon)
Phobos (; astronomical naming conventions, systematic designation: ) is the innermost and larger of the two moons of Mars, natural satellites of Mars, the other being Deimos (moon), Deimos. The two moons were discovered in 1877 by American astronomer Asaph Hall. It is named after Phobos (mythology), Phobos, the Greek mythology, Greek god of fear and panic, who is the son of Ares (Mars) and twin brother of Deimos (deity), Deimos. Phobos is a small, irregularly shaped object with a mean radius of . Phobos orbits from the Martian surface, closer to its Primary (astronomy), primary body than any other known Natural satellite, planetary moon. It is so close that it orbits Mars much faster than Mars rotates, and completes an orbit in just 7 hours and 39 minutes. As a result, from the surface of Mars it appears to rise in the west, move across the sky in 4 hours and 15 minutes or less, and set in the east, twice each Mars sol, Martian day. Phobos is one of the least reflective bodie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stickney (crater)
Stickney is the largest crater on Phobos, which is a satellite of Mars. It is in diameter, taking up a substantial proportion of the moon's surface. Naming The crater is named after mathematician Chloe Angeline Stickney Hall, the wife of Phobos' discoverer Asaph Hall whose support was credited by her husband as critical for his discovery of the moon. The crater was named in 1973, based on ''Mariner 9'' images, by an IAU nomenclature committee chaired by Carl Sagan.. Formation There are two models for the age of Stickney, based on the differing possible dates at which Phobos began to orbit around Mars. If Phobos has been orbiting for 4.3 Ga (billion years) then Stickney formed 4.2 Ga ago, but if it has only been orbiting for 3.5 Ga then the crater is 2.6 Ga old. The impact created a large amount of ejecta which escaped Phobos' gravity and ended up in orbit around Mars for a period not exceeding 1000 years, some of this material then crashed back onto Phobos and created second ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stickney Mro
Stickney may refer to: Places * Stickney, Lincolnshire, England * Stickney, Illinois, United States * Stickney, Kansas, United States * Stickney, South Dakota, United States * Stickney, New Brunswick, Canada Surname * Alpheus Beede Stickney, American railroad executive * Angeline Stickney, American suffragist, abolitionist, and mathematician * Charles D. Stickney (c.1859–1924), New York assemblyman * Dorothy Stickney, American actress * Frederick Stickney, American architect. * Pamelia Stickney, American musician * Highland Stickney, American football coach * Morgan Stickney (born 1997), American Paralympic swimmer * Stuart Stickney, American golfer * Thomas Stickney, early American military officer * Timothy Stickney, American actor * Trumbull Stickney, American classical scholar * Wallace Stickney, American civil servant * William Stickney (golfer), American golfer * William W. Stickney (politician) (William Wallace Stickney), American lawyer and politician in Verm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury (planet), Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Mars (mythology), Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin atmosphere (less than 1% that of Earth's), and has a crust primarily composed of elements similar to Earth's crust, as well as a core made of iron and nickel. Mars has surface features such as impact craters, valleys, dunes and polar ice caps. It has two small and irregularly shaped moons, Phobos (moon), Phobos and Deimos (moon), Deimos. Some of the most notable surface features on Mars include Olympus Mons, the largest volcano and List of tallest mountains in the Solar System, highest known mountain in the Solar System and Valles Marineris, one of the largest canyons in the Solar System. The North Polar Basin (Mars), Borealis basin in the Northern Hemisphere covers approximately 40% of the planet and may be a la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Astronomical Union
The International Astronomical Union (IAU; french: link=yes, Union astronomique internationale, UAI) is a nongovernmental organisation with the objective of advancing astronomy in all aspects, including promoting astronomical research, outreach, education, and development through global cooperation. It was founded in 1919 and is based in Paris, France. The IAU is composed of individual members, who include both professional astronomers and junior scientists, and national members, such as professional associations, national societies, or academic institutions. Individual members are organised into divisions, committees, and working groups centered on particular subdisciplines, subjects, or initiatives. As of 2018, the Union had over 13,700 individual members, spanning 90 countries, and 82 national members. Among the key activities of the IAU is serving as a forum for scientific conferences. It sponsors nine annual symposia and holds a triannual General Assembly that sets policy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulliver's Travels
''Gulliver's Travels'', or ''Travels into Several Remote Nations of the World. In Four Parts. By Lemuel Gulliver, First a Surgeon, and then a Captain of Several Ships'' is a 1726 prose satire by the Anglo-Irish writer and clergyman Jonathan Swift, satirising both human nature and the "travellers' tales" literary subgenre. It is Swift's best known full-length work, and a classic of English literature. Swift claimed that he wrote ''Gulliver's Travels'' "to vex the world rather than divert it". The book was an immediate success. The English dramatist John Gay remarked: "It is universally read, from the cabinet council to the nursery." In 2015, Robert McCrum released his selection list of 100 best novels of all time in which ''Gulliver's Travels'' is listed in third place as "a satirical masterpiece". Plot Part I: A Voyage to Lilliput The travel begins with a short preamble in which Lemuel Gulliver gives a brief outline of his life and history before his voyages. ;4 May ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Icarus (journal)
''ICARUS'' is a scientific journal dedicated to the field of planetary science. It is officially endorsed by the American Astronomical Society's Division for Planetary Sciences (DPS). The journal contains articles discussing the results of new research on astronomy, geology, meteorology, physics, chemistry, biology, and other scientific aspects of the Solar System or extrasolar systems. The journal was founded in 1962, and became affiliated with the DPS in 1974. Its original owner and publisher was Academic Press, which was purchased by Elsevier in 2000. The journal is named for the mythical Icarus, and the frontispiece of every issue contains an extended quotation from Sir Arthur Eddington equating Icarus' adventurousness with the scientific investigator who "strains his theories to the breaking-point till the weak joints gape." Abstracting and indexing This journal is indexed by the following services: * Science Citation Index * Current Contents /Physical, Chemical & E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elsevier
Elsevier () is a Dutch academic publishing company specializing in scientific, technical, and medical content. Its products include journals such as ''The Lancet'', ''Cell'', the ScienceDirect collection of electronic journals, '' Trends'', the '' Current Opinion'' series, the online citation database Scopus, the SciVal tool for measuring research performance, the ClinicalKey search engine for clinicians, and the ClinicalPath evidence-based cancer care service. Elsevier's products and services also include digital tools for data management, instruction, research analytics and assessment. Elsevier is part of the RELX Group (known until 2015 as Reed Elsevier), a publicly traded company. According to RELX reports, in 2021 Elsevier published more than 600,000 articles annually in over 2,700 journals; as of 2018 its archives contained over 17 million documents and 40,000 e-books, with over one billion annual downloads. Researchers have criticized Elsevier for its high profit marg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ejecta Blanket
An ejecta blanket is a generally symmetrical apron of ejecta that surrounds an impact crater; it is layered thickly at the crater's rim and thin to discontinuous at the blanket's outer edge. The impact cratering is one of the basic surface formation mechanisms of the solar system bodies (including the Earth) and the formation and emplacement of ejecta blankets are the fundamental characteristics associated with impact cratering event. The ejecta materials are considered as the transported materials beyond the transient cavity formed during impact cratering regardless of the state of the target materials. Formation A blanket of ejecta is formed during the formation of meteor impact cratering and is composed usually of the materials of that are ejected from the cratering process. Ejecta materials are deposited on the preexisting layer of target materials and therefore it form an inverted stratigraphy than the underlying bedrock. In some cases, the excavated fragment of ejects ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar And Planetary Science Conference
The Lunar and Planetary Science Conference (LPSC), jointly sponsored by the Lunar and Planetary Institute (LPI) and NASA Johnson Space Center (JSC), brings together international specialists in petrology, geochemistry, geophysics, geology, and astronomy to present the latest results of research in planetary science. Since its beginning in 1970, the LPSC has been a significant focal point for planetary science research, with more than 2000 planetary scientists and students attending from all over the world. History In a speech delivered at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC) in Houston, Texas in March 1968, President Lyndon B. Johnson announced the formation of the Lunar Science Institute (LSI). The creation of the LSI was the culmination of meetings and events involving the National Aeronautics and Space Administration, the National Academy of Sciences, Universities Research Association, and several major universities. Initially operated by the National Academy of Sciences, the Uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar And Planetary Institute
The Lunar and Planetary Institute (LPI) is a scientific research institute dedicated to study of the Solar System, its formation, evolution, and current state. The Institute is part of the Universities Space Research Association (USRA) and is supported by the Science Mission Directorate of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). Located at 3600 Bay Area Boulevard in Houston, Texas, the LPI maintains an extensive collection of lunar and planetary data, carries out education and public outreach programs, and offers meeting coordination and publishing services. The LPI sponsors and organizes several workshops and conferences throughout the year, including the Lunar and Planetary Science Conference (LPSC) held in March in the Houston area. History In his March 1968 speech at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC) in Houston, Texas, President Lyndon B. Johnson announced the formation of the Lunar Science Institute (LSI). "We will welcome here all who are interested i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johnson Space Center
The Lyndon B. Johnson Space Center (JSC) is NASA's center for human spaceflight (originally named the Manned Spacecraft Center), where human spaceflight training, research, and flight control are conducted. It was renamed in honor of the late US president and Texas native, Lyndon B. Johnson, by an act of the United States Senate on February 19, 1973. It consists of a complex of 100 buildings constructed on in the Clear Lake Area of Houston, which acquired the official nickname "Space City" in 1967. The center is home to NASA's astronaut corps, and is responsible for training astronauts from both the US and its international partners. It houses the Christopher C. Kraft Jr. Mission Control Center, which has provided the flight control function for every NASA human spaceflight since Gemini 4 (including Apollo, Skylab, Apollo–Soyuz, and Space Shuttle). It is popularly known by its radio call signs "Mission Control" and "Houston". The original Manned Spacecraft Center grew out ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |