|
Lily And Clover
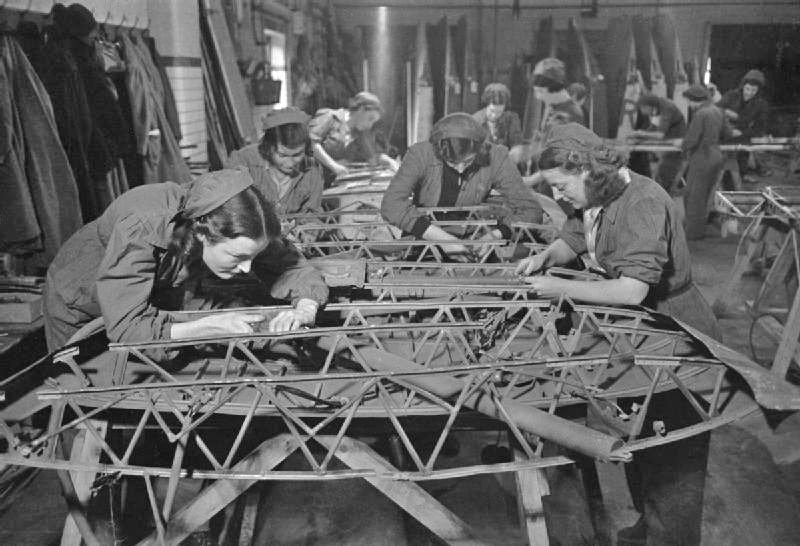
''Lily'' and ''Clover'' were two experimental floating airfields tested towards the end of the Second World War by the British Admiralty. Based on a similar concept to the Mulberry harbour used for the Normandy landings in 1944, ''Lily'' and ''Clover'' were two different types of floating airstrips that would allow the Royal Navy to operate aircraft before a shore base is secured and removed the need for an aircraft carrier. ''Lily'' was a collection of flotation units developed for the floating roadways used in the Mulberry harbour. Each was six feet across, plates being fitted on the top to form the runway. The complete structure could be towed and weighed 5,000 tons, taking 400 man-hours to construct. ''Clover'' was built mainly of wood with wooden deck planking which could take a load of eight tons. It weighed more than Lily at 5,200 tons but would take 21,000 man-hours to assemble. The resulting runway was long and wide with of parking area and for storage and maint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Royal Navy During The Second World War A30297
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things already mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with pronouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of pronoun ''thee'') when followed by a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fairey Swordfish
The Fairey Swordfish is a biplane torpedo bomber, designed by the Fairey Aviation Company. Originating in the early 1930s, the Swordfish, nicknamed "Stringbag", was principally operated by the Fleet Air Arm of the Royal Navy. It was also used by the Royal Air Force (RAF), as well as several overseas operators, including the Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF) and the Royal Netherlands Navy. It was initially operated primarily as a fleet attack aircraft. During its later years, the Swordfish was increasingly used as an anti-submarine and training platform. The type was in frontline service throughout the Second World War. Despite being outmoded by 1939, the Swordfish achieved some spectacular successes during the war. Notable events included sinking one battleship and damaging two others of the ''Regia Marina'' (the Italian navy) during the Battle of Taranto, and the famous attack on the German battleship ''Bismarck'', which contributed to her eventual demise. Swordfish sank a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airfields
An aerodrome (Commonwealth English) or airdrome (American English) is a location from which aircraft flight operations take place, regardless of whether they involve air cargo, passengers, or neither, and regardless of whether it is for public or private use. Aerodromes include small general aviation airfields, large commercial airports, and military air bases. The term ''airport'' may imply a certain stature (having satisfied certain certification criteria or regulatory requirements) that not all aerodromes may have achieved. That means that all airports are aerodromes, but not all aerodromes are airports. Usage of the term "aerodrome" remains more common in Ireland and Commonwealth nations, and is conversely almost unknown in American English, where the term "airport" is applied almost exclusively. A water aerodrome is an area of open water used regularly by seaplanes, floatplanes or amphibious aircraft for landing and taking off. In formal terminology, as defined by the I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air-Britain
Air-Britain, traditionally sub-titled "The International Association of Aviation Enthusiasts", is a non-profit aviation society founded in July 1948. As from 2015, it is constituted as a British charitable trust and book publisher. History Air-Britain was formed in 1948 as an amateur association of aviation enthusiasts. In April 1968, it was incorporated into a company limited by guarantee, Air-Britain (Historians) Ltd. On 16 April 2015, the status of Air-Britain changed from a Private company limited by guarantee, in the form of Air-Britain (Historians) Ltd, to a British charity, in the form of Air-Britain Trust Ltd. Air-Britain organised an annual international aircraft recognition contest that started with an event in September 1961, for all comers, and attracted applications from individuals and teams from various sources such as Royal Observer Corps (ROC), Air Training Corps (ATC), and Air-Britain regional branches. The annual aircraft recognition contest was discontinued af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Project Habakkuk
Project Habakkuk or Habbakuk (spelling varies) was a plan by the British during the Second World War to construct an aircraft carrier out of pykrete (a mixture of wood pulp and ice) for use against German U-boats in the mid-Atlantic, which were beyond the flight range of land-based planes at that time. The plan was to create what would have been the largest ship ever at 600 m long and would indeed have been much bigger than even USS ''Enterprise'', the largest naval vessel ever, at 342 m long.The idea came from Geoffrey Pyke, who worked for Combined Operations Headquarters. After promising scale tests and the creation of a prototype on Patricia Lake, Jasper National Park, in Alberta, Canada, the project was shelved due to rising costs, added requirements, and the availability of longer-range aircraft and escort carriers which closed the Mid-Atlantic gap that the project was intended to address. History Initial concept Geoffrey Pyke was an old friend of J. D. Bernal an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aircraft Carrier
An aircraft carrier is a warship that serves as a seagoing airbase, equipped with a full-length flight deck and facilities for carrying, arming, deploying, and recovering aircraft. Typically, it is the capital ship of a fleet, as it allows a naval force to project air power worldwide without depending on local bases for staging aircraft operations. Carriers have evolved since their inception in the early twentieth century from wooden vessels used to deploy balloons to nuclear-powered warships that carry numerous fighters, strike aircraft, helicopters, and other types of aircraft. While heavier aircraft such as fixed-wing gunships and bombers have been launched from aircraft carriers, these aircraft have not successfully landed on a carrier. By its diplomatic and tactical power, its mobility, its autonomy and the variety of its means, the aircraft carrier is often the centerpiece of modern combat fleets. Tactically or even strategically, it replaced the battleship in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
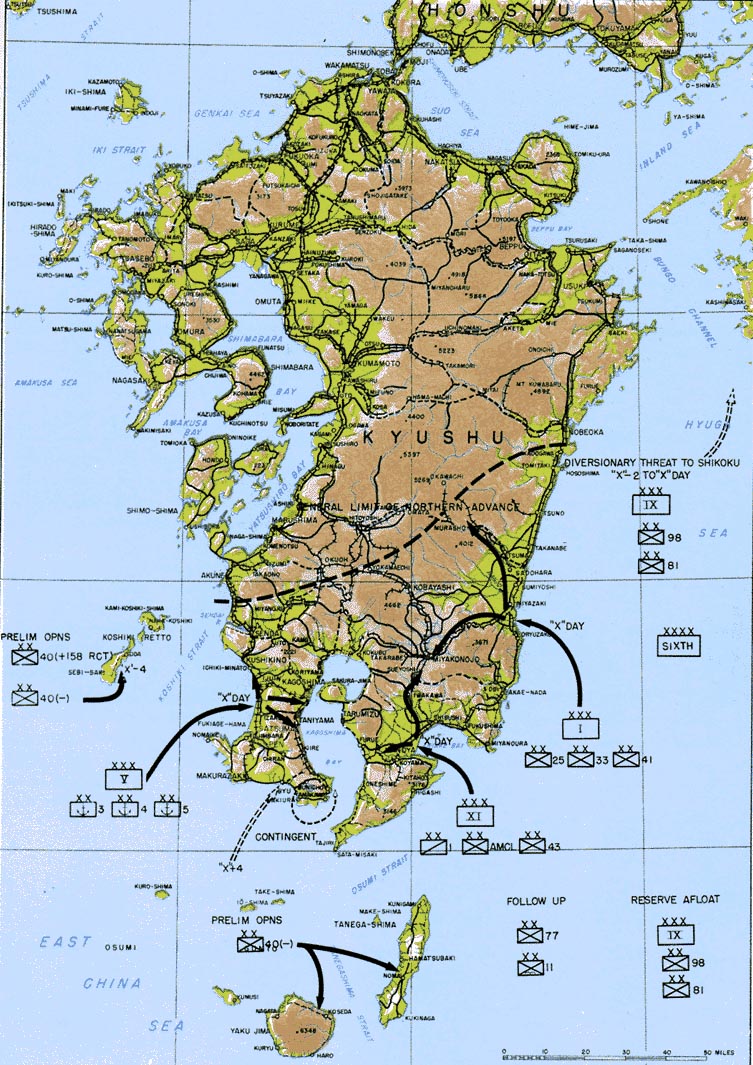
Operation Downfall
Operation Downfall was the proposed Allied plan for the invasion of the Japanese home islands near the end of World War II. The planned operation was canceled when Japan surrendered following the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, the Soviet declaration of war, and the invasion of Manchuria. The operation had two parts: Operation Olympic and Operation Coronet. Set to begin in November 1945, Operation Olympic was intended to capture the southern third of the southernmost main Japanese island, Kyūshū, with the recently captured island of Okinawa to be used as a staging area. In early 1946 would come Operation Coronet, the planned invasion of the Kantō Plain, near Tokyo, on the main Japanese island of Honshu. Airbases on Kyūshū captured in Operation Olympic would allow land-based air support for Operation Coronet. If Downfall had taken place, it would have been the largest amphibious operation in history, surpassing D-Day. Japan's geography made this invasion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supermarine Spitfires
The Supermarine Spitfire is a British single-seat fighter aircraft used by the Royal Air Force and other Allied countries before, during, and after World War II. Many variants of the Spitfire were built, from the Mk 1 to the Rolls-Royce Griffon engined Mk 24 using several wing configurations and guns. It was the only British fighter produced continuously throughout the war. The Spitfire remains popular among enthusiasts; around 70 remain airworthy, and many more are static exhibits in aviation museums throughout the world. The Spitfire was designed as a short-range, high-performance interceptor aircraft by R. J. Mitchell, chief designer at Supermarine Aviation Works, which operated as a subsidiary of Vickers-Armstrong from 1928. Mitchell developed the Spitfire's distinctive elliptical wing with innovative sunken rivets (designed by Beverley Shenstone) to have the thinnest possible cross-section, achieving a potential top speed greater than that of several contemporary fight ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escort Carrier
The escort carrier or escort aircraft carrier (U.S. hull classification symbol CVE), also called a "jeep carrier" or "baby flattop" in the United States Navy (USN) or "Woolworth Carrier" by the Royal Navy, was a small and slow type of aircraft carrier used by the Royal Navy, the United States Navy, the Imperial Japanese Navy and Imperial Japanese Army Air Force in World War II. They were typically half the length and a third the displacement of larger fleet carriers, slower, more-lightly armed and armored, and carried fewer planes. Escort carriers were most often built upon a commercial ship hull, so they were cheaper and could be built quickly. This was their principal advantage as they could be completed in greater numbers as a stop-gap when fleet carriers were scarce. However, the lack of protection made escort carriers particularly vulnerable, and several were sunk with great loss of life. The light carrier (U.S. hull classification symbol CVL) was a similar concept to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arrestor Gear
An arresting gear, or arrestor gear, is a mechanical system used to rapidly decelerate an aircraft as it lands. Arresting gear on aircraft carriers is an essential component of naval aviation, and it is most commonly used on CATOBAR and STOBAR aircraft carriers. Similar systems are also found at land-based airfields for expeditionary or emergency use. Typical systems consist of several steel wire ropes laid across the aircraft landing area, designed to be caught by an aircraft's tailhook. During a normal arrestment, the tailhook engages the wire and the aircraft's kinetic energy is transferred to hydraulic damping systems attached below the carrier deck. There are other related systems which use nets to catch aircraft wings or landing gear. These ''barricade'' and ''barrier'' systems are only used for emergency arrestments for aircraft without operable tailhooks. History Arresting cable systems were invented by Hugh Robinson and were utilized by Eugene Ely on his first lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
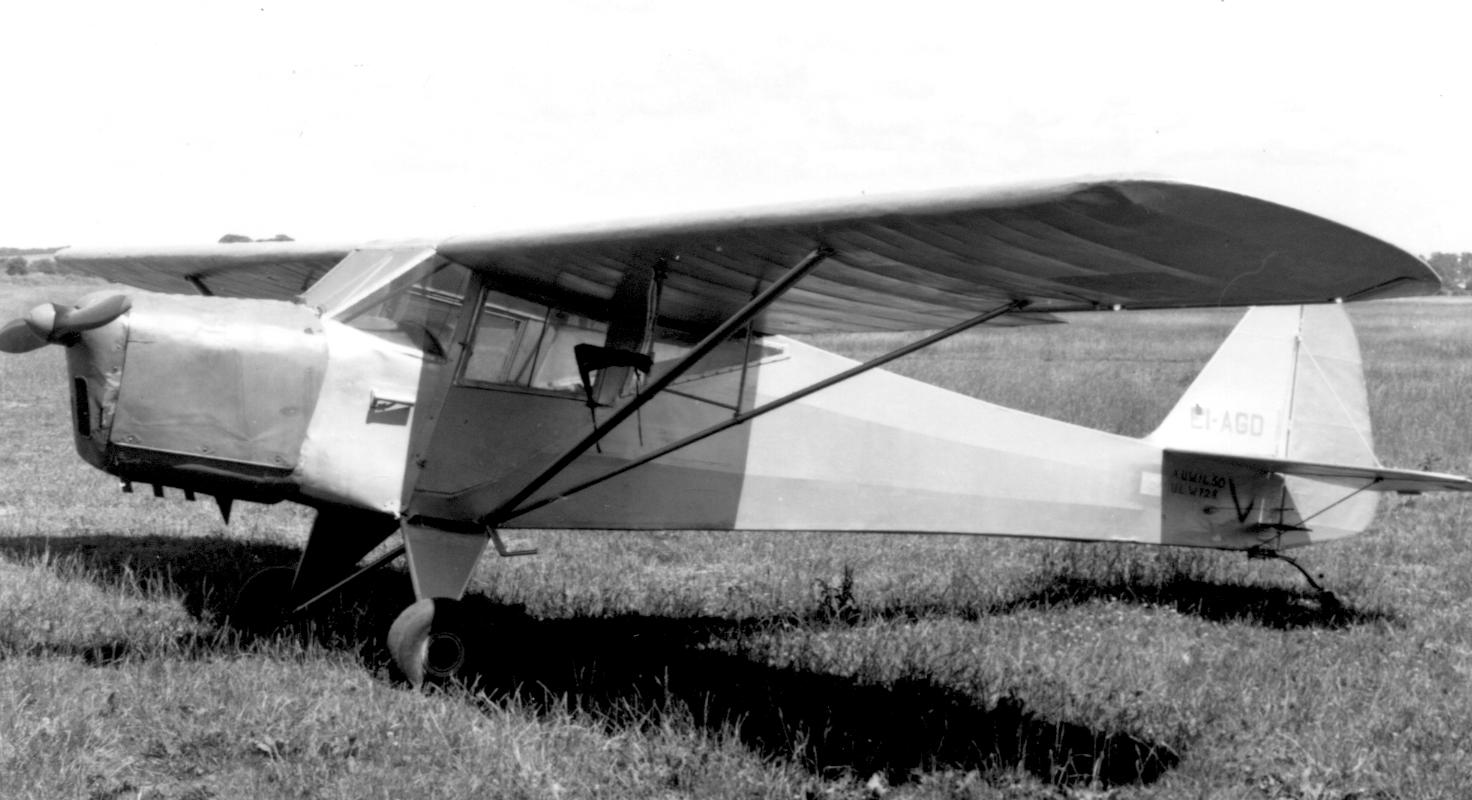
Taylorcraft Auster
The Taylorcraft Auster was a British military liaison and observation aircraft produced by the Taylorcraft Aeroplanes (England) Limited company during the Second World War. Design and development The Auster was a twice-removed development of an American Taylorcraft design of civilian aircraft, the Model A. The Model A had to be redesigned in Britain to meet more stringent Civil Aviation standards and was named the Taylorcraft Plus C.Mondey 1994, p. 71.March 2000, p. 225. After the start of the Second World War, the company developed the model further as an Air Observation Post (AOP)—flown by officers of the Royal Artillery and used for directing artillery fire of British Army Royal Artillery units. The Plus C was re-engined with the Blackburn Cirrus Minor I engine and redesignated the Taylorcraft Plus D. Most of the civil Plus Cs and Ds were impressed into Royal Air Force service, the Plus Cs were re-engined with the Cirrus Minor I and redesignated as Plus C2. Prewar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Floating Airport
A floating airport is an airport built and situated on a very large floating structure (VLFS) located many miles out at sea utilizing a flotation type of device or devices such as pneumatic stabilized platform (PSP) technology. As the population increases and land becomes more expensive and scarce, very large floating structures (VLFS) such as floating airports could help solve land use, pollution and aircraft noise issues. Early history The first discussion of a floating airport was for trans-Atlantic flights. At that time a passenger aircraft capable of making the trip could be built, but because of the massive need for fuel for the flight, it had a limited payload. An article appeared in the January 1930 issue of ''Popular Mechanics'' in which a model of a floating airport located in the Atlantic was proposed. To make safe flight possible with the aviation technology of that time, it called for eight such airports in the Atlantic. But unlike future floating airport ideas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)