|
Lille Model
The Lille Model is a medical modeling tool for predicting mortality in patients with alcoholic hepatitis who are not responding to steroid therapy. The model risk stratifies patients who have been receiving steroid treatment for seven days to predict who will improve and who should be considered for alternative treatment options including early referral for transplant. The model is based on: * Age * Albumin * Bilirubin (initial) * Bilirubin (day 7) * Creatinine * PT Initial model was based on a study of 238 patients and published in the Journal of Hepatology in 2003. Recent cohort studies demonstrate that those with a Lille score above 0.45 are likely non-responders to steroid therapy. See also * Model for End-Stage Liver Disease The Model for End-Stage Liver Disease, or MELD, is a scoring system for assessing the severity of chronic liver disease. It was initially developed to predict mortality within three months of surgery in patients who had undergone a transjugular in ... ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
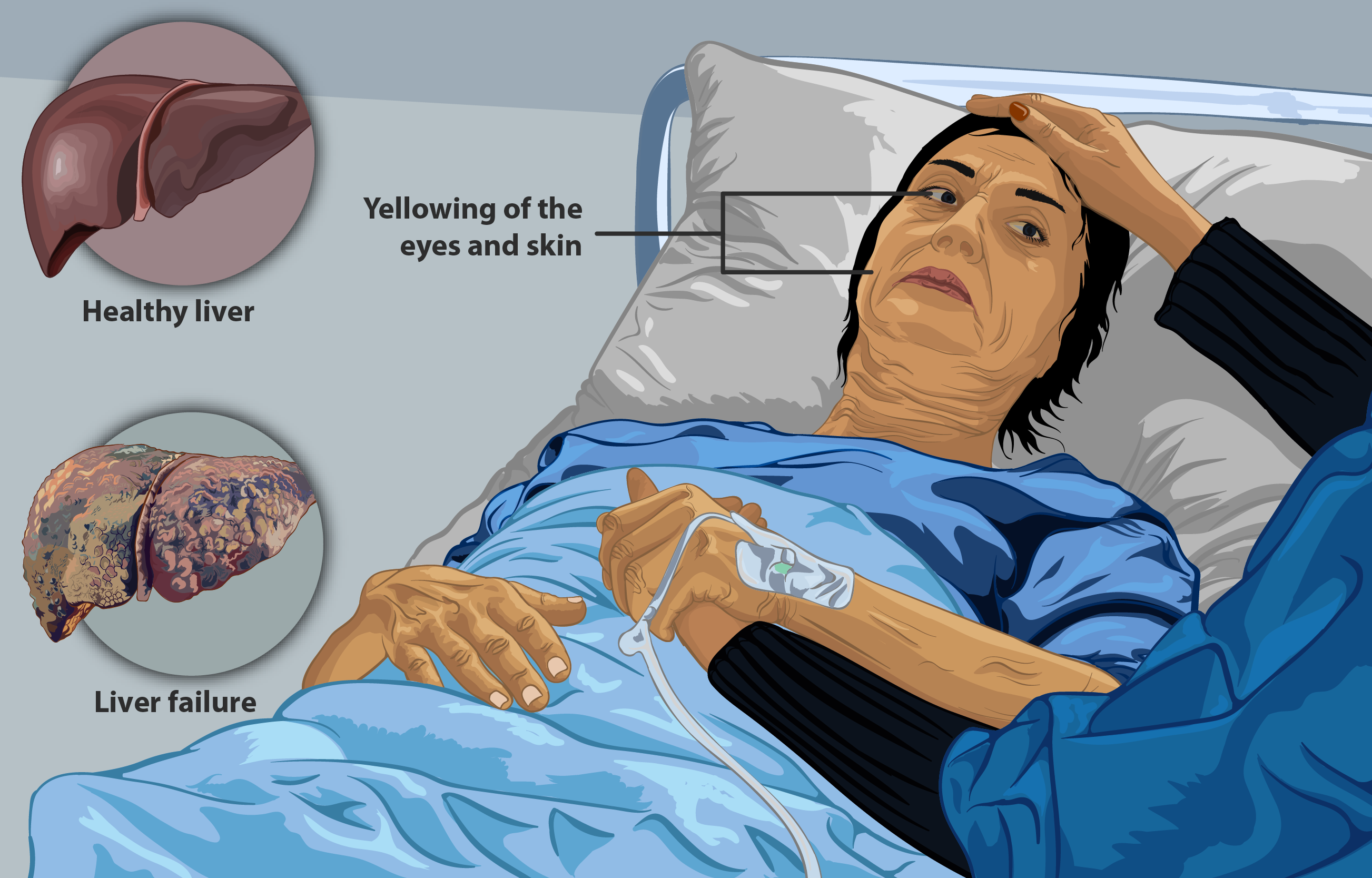
Alcoholic Hepatitis
Alcoholic hepatitis is hepatitis (inflammation of the liver) due to excessive intake of alcohol. Patients typically have a history of at least 10 years of heavy alcohol intake, typically 8–10 drinks per day. It is usually found in association with fatty liver, an early stage of alcoholic liver disease, and may contribute to the progression of fibrosis, leading to cirrhosis. Symptoms may present acutely after a large amount of alcoholic intake in a short time period, or after years of excess alcohol intake. Signs and symptoms of alcoholic hepatitis include jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), ascites (fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity), fatigue and hepatic encephalopathy (brain dysfunction due to liver failure). Mild cases are self-limiting, but severe cases have a high risk of death. Severity in alcoholic hepatitis is determined several clinical prediction models such as the Maddrey's Discriminant Function and the MELD score. Severe cases may be treated with glu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albumin
Albumin is a family of globular proteins, the most common of which are the serum albumins. All of the proteins of the albumin family are water- soluble, moderately soluble in concentrated salt solutions, and experience heat denaturation. Albumins are commonly found in blood plasma and differ from other blood proteins in that they are not glycosylated. Substances containing albumins are called ''albuminoids''. A number of blood transport proteins are evolutionarily related in the albumin family, including serum albumin, alpha-fetoprotein, vitamin D-binding protein and afamin. This family is only found in vertebrates. ''Albumins'' in a less strict sense can mean other proteins that coagulate under certain conditions. See ' for lactalbumin, ovalbumin and plant "2S albumin". Function Albumins in general are transport proteins that bind to various ligands and carry them around. Human types include: * Human serum albumin is the main protein of human blood plasma. It m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bilirubin
Bilirubin (BR) (adopted from German, originally bili—bile—plus ruber—red—from Latin) is a red-orange compound that occurs in the normcomponent of the straw-yellow color in urine. Another breakdown product, stercobilin, causes the brown color of feces. Although bilirubin is usually found in animals rather than plants, at least one plant species, '' Strelitzia nicolai'', is known to contain the pigment. Structure Bilirubin consists of an open-chain tetrapyrrole. It is formed by oxidative cleavage of a porphyrin in heme, which affords biliverdin. Biliverdin is reduced to bilirubin. After conjugation with glucuronic acid, bilirubin is water-soluble and can be excreted. Bilirubin is structurally similar to the pigment phycobilin used by certain algae to capture light energy, and to the pigment phytochrome used by plants to sense light. All of these contain an open chain of four pyrrolic rings. Like these other pigments, some of the double-bonds in bilirubin isomer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Creatinine
Creatinine (; ) is a breakdown product of creatine phosphate from muscle and protein metabolism. It is released at a constant rate by the body (depending on muscle mass). Biological relevance Serum creatinine (a blood measurement) is an important indicator of kidney function, because it is an easily measured byproduct of muscle metabolism that is excreted unchanged by the kidneys. Creatinine itself is produced via a biological system involving creatine, phosphocreatine (also known as creatine phosphate), and adenosine triphosphate (ATP, the body's immediate energy supply). Creatine is synthesized primarily in the liver by methylation of glycocyamine (guanidino acetate, synthesized in the kidney from the amino acids arginine and glycine) by S-adenosyl methionine. It is then transported in the blood to other organs, muscles, and the brain, where it is phosphorylated to phosphocreatine, a high-energy compound. Creatine conversion to phosphocreatine is catalysed by creatine ki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prothrombin Time
The prothrombin time (PT) – along with its derived measures of prothrombin ratio (PR) and international normalized ratio (INR) – is an assay for evaluating the Coagulation#Extrinsic pathway, extrinsic pathway and Coagulation#Common pathway, common pathway of coagulation. This blood test is also called ''protime INR'' and ''PT/INR''. They are used to determine the Thrombophilia, clotting tendency of blood, in conditions such as the measure of warfarin dosage, liver damage (cirrhosis), and vitamin K status. PT measures the following Coagulation#Coagulation factors, coagulation factors: fibrinogen, I (fibrinogen), thrombin, II (prothrombin), Factor V, V (proaccelerin), Factor VII, VII (proconvertin), and Factor X, X (Stuart–Prower factor). PT is often used in conjunction with the partial thromboplastin time, activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) which measures the Coagulation#intrinsic pathway, ''intrinsic'' pathway and common pathway of coagulation. Laboratory measur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albumin
Albumin is a family of globular proteins, the most common of which are the serum albumins. All of the proteins of the albumin family are water- soluble, moderately soluble in concentrated salt solutions, and experience heat denaturation. Albumins are commonly found in blood plasma and differ from other blood proteins in that they are not glycosylated. Substances containing albumins are called ''albuminoids''. A number of blood transport proteins are evolutionarily related in the albumin family, including serum albumin, alpha-fetoprotein, vitamin D-binding protein and afamin. This family is only found in vertebrates. ''Albumins'' in a less strict sense can mean other proteins that coagulate under certain conditions. See ' for lactalbumin, ovalbumin and plant "2S albumin". Function Albumins in general are transport proteins that bind to various ligands and carry them around. Human types include: * Human serum albumin is the main protein of human blood plasma. It m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Model For End-Stage Liver Disease
The Model for End-Stage Liver Disease, or MELD, is a scoring system for assessing the severity of chronic liver disease. It was initially developed to predict mortality within three months of surgery in patients who had undergone a transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) procedure, and was subsequently found to be useful in determining prognosis and prioritizing for receipt of a liver transplant. This score is now used by the United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS) and Eurotransplant for prioritizing allocation of Liver transplantation, liver transplants instead of the older Child-Pugh score. Determination MELD uses the patient's values for serum bilirubin, serum creatinine, and the Prothrombin time, international normalized ratio for prothrombin time (INR) to predict survival. It is calculated according to the following formula: \mathrm \overset 3.78\times \ln \left(\text\right) + 11.2 \times \ln(\text) + 9.57\times \ln\left( \text\right) + 6.43 MELD scores are repo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastroenterology
Gastroenterology (from the Greek gastḗr- "belly", -énteron "intestine", and -logía "study of") is the branch of medicine focused on the digestive system and its disorders. The digestive system consists of the gastrointestinal tract, sometimes referred to as the ''GI tract,'' which includes the esophagus, stomach, small intestine and large intestine as well as the accessory organs of digestion which include the pancreas, gallbladder, and liver. The digestive system functions to move material through the GI tract via peristalsis, break down that material via digestion, absorb nutrients for use throughout the body, and remove waste from the body via defecation. Physicians who specialize in the medical specialty of gastroenterology are called gastroenterologists or sometimes ''GI doctors''. Some of the most common conditions managed by gastroenterologists include gastroesophageal reflux disease, gastrointestinal bleeding, irritable bowel syndrome, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatology
Hepatology is the branch of medicine that incorporates the study of liver, gallbladder, biliary tree, and pancreas as well as management of their disorders. Although traditionally considered a sub-specialty of gastroenterology, rapid expansion has led in some countries to doctors specializing solely on this area, who are called hepatologists. Diseases and complications related to viral hepatitis and alcohol are the main reason for seeking specialist advice. More than two billion people have been infected with hepatitis B virus at some point in their life, and approximately 350 million have become persistent carriers. Up to 80% of liver cancers can be attributed to either hepatitis B or hepatitis C virus. In terms of Mortality rate, mortality, the former is second only to smoking among known agents causing cancer. With more widespread implementation of vaccination and strict Screening (medicine), screening before blood transfusion, lower infection rates are expected in the futur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |