|
Liliaspis
''Liliaspis philippovae'' is an extinct cyathaspidiform heterostracan agnathan from early Devonian marine strata of the Ural Mountains. ''Liliaspis'' was, at various times, placed in the families Cyathaspididae, Poraspididae, and Anglaspididae. Currently, it is placed in Ariaspidae with ''Ariaspis'', and '' Listraspis'', and is considered to be closely related to the similar-looking ''Paraliliaspis''. ''Anglaspis ''Anglaspis'' is an extinct genus of cyathaspidiform heterostracan agnathan. Fossils are found in marine strata of Europe, from the late Silurian period until the genus' extinction during the Early Devonian. As with other cyathaspidiforms, i ...'' is considered the ancestor or sister-taxon of both ''L. philippovae'' and ''Paraliliaspis''. References Cyathaspidiformes genera Early Devonian fish of Europe Cyathaspidida {{Pteraspidomorphi-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraliliaspis
''Paraliliaspis egregia'' is an extinct cyathaspidiform heterostracan agnathan from early Devonian marine strata of the Ural Mountains. ''Paraliliaspis'' was, at various times, placed in the families Cyathaspididae, and Anglaspididae. Currently, it is placed in Ariaspidae with ''Ariaspis ''Ariaspis'' is an extinct genus of cyathaspidiform heterostracan agnathan. Fossils are found in marine strata of Canada and Europe from the late Silurian period until its extinction during the Early Devonian The Devonian ( ) is a geolog ...'', and '' Listraspis'', and is considered to be closely related to the similar-looking '' Liliaspis'', which is also from Early Devonian Ural marine strata. ''Anglaspis'' is considered the ancestor or sister-taxon of both ''Liliaspis'' and ''P. egregia''. References Cyathaspidiformes genera Early Devonian fish of Europe Cyathaspidida {{Pteraspidomorphi-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyathaspidiformes Genera
Cyathaspidiformes is an extinct order of heterostracan vertebrates known from extensive fossil remains primarily from Silurian to Early Devonian strata of Europe, and North America, and from Early Devonian marine strata of Siberia. Anatomy Like their descendants, the pteraspidids, all cyathaspidiform heterostracans had the cephalothorax enclosed in armor, formed from several plates, including dorsal, ventral, a dorsal spine derived from a scale, and a large, scale-covered tail. Thus, the living animals would have resembled tadpoles encased in massive armor. The majority of taxa have the rostral and pineal plates fused or merged with the dorsal plate, and in the amphiaspidids, all the plates of the cephalothorax were fused together into a single "muff-like" unit. Unlike the pteraspidids, all cyathaspidiforms are thought to be almost uniformly benthic in lifestyle, though only the amphiaspids and the ctenaspids are thought to be burrowers. Taxonomy The taxonomy of Cyathaspidifo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglaspis
''Anglaspis'' is an extinct genus of cyathaspidiform heterostracan agnathan. Fossils are found in marine strata of Europe, from the late Silurian period until the genus' extinction during the Early Devonian. As with other cyathaspidiforms, individuals of ''Anglaspis'' had dorsal and ventral plates covering the forebody, gill pouches, and nasal openings that lay on the roof of the oral cavity. Late Silurian species of ''Anglaspis'' are found in marine strata of Wales and England, while most of the Early Devonian species are found in the Devonian-aged strata of Spitsbergen island, in Svalbard, Norway. Taxonomy ''Anglaspis'' was, at various times, placed in the families Cyathaspididae, Poraspididae, and in its own family, Anglaspididae. Currently, it is placed in Ariaspidae with ''Ariaspis ''Ariaspis'' is an extinct genus of cyathaspidiform heterostracan agnathan. Fossils are found in marine strata of Canada and Europe from the late Silurian period until its extinct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyathaspidiformes
Cyathaspidiformes is an extinct order of heterostracan vertebrates known from extensive fossil remains primarily from Silurian to Early Devonian strata of Europe, and North America, and from Early Devonian marine strata of Siberia. Anatomy Like their descendants, the pteraspidids, all cyathaspidiform heterostracans had the cephalothorax enclosed in armor, formed from several plates, including dorsal, ventral, a dorsal spine derived from a scale, and a large, scale-covered tail. Thus, the living animals would have resembled tadpoles encased in massive armor. The majority of taxa have the rostral and pineal plates fused or merged with the dorsal plate, and in the amphiaspidids, all the plates of the cephalothorax were fused together into a single "muff-like" unit. Unlike the pteraspidids, all cyathaspidiforms are thought to be almost uniformly benthic in lifestyle, though only the amphiaspids and the ctenaspids are thought to be burrowers. Taxonomy The taxonomy of Cyathaspidifo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyathaspidida
Cyathaspidida is a taxon of extinct cyathaspidiform heterostracan agnathans whose fossils are found in Silurian to Lower Devonian marine strata of Europe and North America.Lundgren, Mette, and Henning Blom. "Phylogenetic relationships of the cyathaspidids (Heterostraci)." GFF 135.1 (2013): 74-84. In life, they are thought to be benthic animals that lived most of their lives either mostly buried in or resting directly on top of the substrate. Taxonomy The cyathaspidids of Cyathaspidida were tadpole-like animals with drum-shaped, cigar-shaped or wedge-shaped cephalothoraxes, and were anatomically similar to several other heterostracan groups. However, with some groups, such as the traquairaspids, cardiopeltids, and corvaspidids, this similarity appears to be superficial. With other groups, namely the tolypelepidids, the similarity suggests a close relationship. The type genus of the tolypelepidids, '' Tolypelepis'', in particular, was determined to be the sister-taxon of Cya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ariaspidae
Ariaspidae is a family of extinct cyathaspidiform heterostracan agnathans in the suborder Cyathaspidida. Family Ariaspidae contains ''Ariaspis'', and its sister-taxa originally contained within Anglaspididae/Anglaspidinae, including ''Anglaspis ''Anglaspis'' is an extinct genus of cyathaspidiform heterostracan agnathan. Fossils are found in marine strata of Europe, from the late Silurian period until the genus' extinction during the Early Devonian. As with other cyathaspidiforms, i ...'', '' Listraspis'', '' Liliaspis'', and '' Paraliliaspis''.Lundgren, Mette, and Henning Blom. "Phylogenetic relationships of the cyathaspidids (Heterostraci)." GFF 135.1 (2013): 74-84. References * Phylogenetic patterns in the heterostracan families Cyathaspidae, Ariaspidae and Ctenaspidae. Lundgren Mette and Blom Henning, The 2nd Wiman meeting : Carl Wiman's Legacy: 100 years of Swedish Palaeontology : Uppsala 17–18 November 2011, 16-17 p. Cyathaspidida Prehistoric jawless fish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyathaspidiformes
Cyathaspidiformes is an extinct order of heterostracan vertebrates known from extensive fossil remains primarily from Silurian to Early Devonian strata of Europe, and North America, and from Early Devonian marine strata of Siberia. Anatomy Like their descendants, the pteraspidids, all cyathaspidiform heterostracans had the cephalothorax enclosed in armor, formed from several plates, including dorsal, ventral, a dorsal spine derived from a scale, and a large, scale-covered tail. Thus, the living animals would have resembled tadpoles encased in massive armor. The majority of taxa have the rostral and pineal plates fused or merged with the dorsal plate, and in the amphiaspidids, all the plates of the cephalothorax were fused together into a single "muff-like" unit. Unlike the pteraspidids, all cyathaspidiforms are thought to be almost uniformly benthic in lifestyle, though only the amphiaspids and the ctenaspids are thought to be burrowers. Taxonomy The taxonomy of Cyathaspidifo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lochkovian
The Lochkovian is one of three faunal stages in the Early Devonian Epoch. It lasted from 419.2 ± 3.2 million years ago to 410.8 ± 2.8 million years ago. It marked the beginning of the Devonian Period, and was followed by the Pragian Stage. It is named after the village of Lochkov in the Czech Republic, now part of the city of Prague Prague ( ; cs, Praha ; german: Prag, ; la, Praga) is the capital and largest city in the Czech Republic, and the historical capital of Bohemia. On the Vltava river, Prague is home to about 1.3 million people. The city has a temperate .... The GSSP is located within the Lochkow Formation at the Klonk Section in Prague. In North America the Lochkovian Stage is represented by Gedinnian or Helderbergian time. References Early Devonian {{geochronology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ariaspis
''Ariaspis'' is an extinct genus of cyathaspidiform heterostracan agnathan. Fossils are found in marine strata of Canada and Europe from the late Silurian period until its extinction during the Early Devonian The Devonian ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the Silurian, million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Carboniferous, Mya. It is named after Devon, England, whe .... A new species, ''A. arctata'', was described by David K. Elliott and Sandra Swift in 2010. References Cyathaspidiformes genera Devonian jawless fish Silurian jawless fish Silurian first appearances Early Devonian genus extinctions Cyathaspidida Silurian fish of North America Silurian fish of Europe Paleozoic life of the Northwest Territories {{Pteraspidomorphi-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
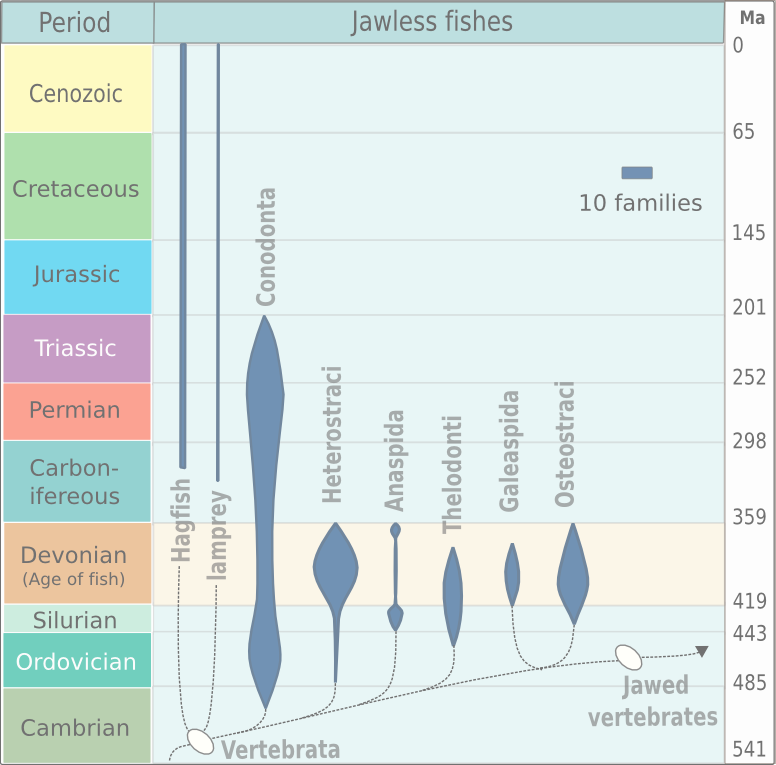
Agnatha
Agnatha (, Ancient Greek 'without jaws') is an infraphylum of jawless fish in the phylum Chordata, subphylum Vertebrata, consisting of both present (cyclostomes) and extinct ( conodonts and ostracoderms) species. Among recent animals, cyclostomes are sister to all vertebrates with jaws, known as gnathostomes. Recent molecular data, both from rRNA and from mtDNA as well as embryological data, strongly supports the hypothesis that living agnathans, the cyclostomes, are monophyletic. The oldest fossil agnathans appeared in the Cambrian, and two groups still survive today: the lampreys and the hagfish, comprising about 120 species in total. Hagfish are considered members of the subphylum Vertebrata, because they secondarily lost vertebrae; before this event was inferred from molecular and developmental data, the group Craniata was created by Linnaeus (and is still sometimes used as a strictly morphological descriptor) to reference hagfish plus vertebrates. While a few scie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ural Mountains
The Ural Mountains ( ; rus, Ура́льские го́ры, r=Uralskiye gory, p=ʊˈralʲskʲɪjə ˈɡorɨ; ba, Урал тауҙары) or simply the Urals, are a mountain range that runs approximately from north to south through western Russia, from the coast of the Arctic Ocean to the river Ural and northwestern Kazakhstan.Ural Mountains Encyclopædia Britannica on-line The mountain range forms part of the conventional boundary between the regions of and |