|
Ligue Des Savanes
The Catholic League of France (french: Ligue catholique), sometimes referred to by contemporary (and modern) Catholics as the Holy League (), was a major participant in the French Wars of Religion. The League, founded and led by Henry I, Duke of Guise, intended the eradication of Protestantism from Catholic France, as well as the replacement of King Henry III. Pope Sixtus V, Philip II of Spain, and the Jesuits were all supporters of this Catholic party. Origins Local confraternities were initially established by French Catholics to counter the Edict of Beaulieu in 1576. King Henry III placed himself at the head of these associations as a political counter to the ultra-Catholic League of Peronne. Following the repudiation of that edict by the Estates General, most of the local leagues were disbanded. Following the illness and death of Francis, duke of Anjou, heir to the French throne, on 10 June 1584, Catholic nobles gathered at Nancy. In December 1584, the League drew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Wars Of Religion
The French Wars of Religion is the term which is used in reference to a period of civil war between French Catholic Church, Catholics and Protestantism, Protestants, commonly called Huguenots, which lasted from 1562 to 1598. According to estimates, between two and four million people died from violence, famine or diseases which were directly caused by the conflict; additionally, the conflict severely damaged the power of the French monarchy. The fighting ended in 1598 when Henry of Navarre, who had converted to Catholicism in 1593, was proclaimed Henry IV of France and issued the Edict of Nantes, which granted substantial rights and freedoms to the Huguenots. However, the Catholics continued to have a hostile opinion of Protestants in general and they also continued to have a hostile opinion of him as a person, and his assassination in 1610 triggered a fresh round of Huguenot rebellions in the 1620s. Tensions between the two religions had been building since the 1530s, exacerba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malcontents (France)
{{Other uses, Malcontents (other){{!Malcontents The Malcontents were a faction of gentlemen in the Fifth French War of Religion (1574–1576). It opposed the policy of Henry of Valois, duc d'Anjou, who had become king under the name Henry III on 30 May 1574, and allied itself to the Huguenots. The leader was the King's brother Francis, Duke of Alençon (made Duke of Anjou in 1576). The main goal of the Malcontents was to oppose the absolutist ambitions of the King. They were unhappy (''malcontent'') with the way the King treated the old French nobility. The Malcontent movement has been compared to the Fronde, 70 years later. Members The Malcontents had both Catholic and Huguenot members. The leaders were: * The Duke of Alençon, Catholic and the King's younger brother * Henri I de Montmorency, Catholic * Guillaume de Montmorency-Thoré, Catholic * Henri, Prince of Condé, Protestant * Henri de Navarre, Protestant and future King Henry IV of France * John Casimi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
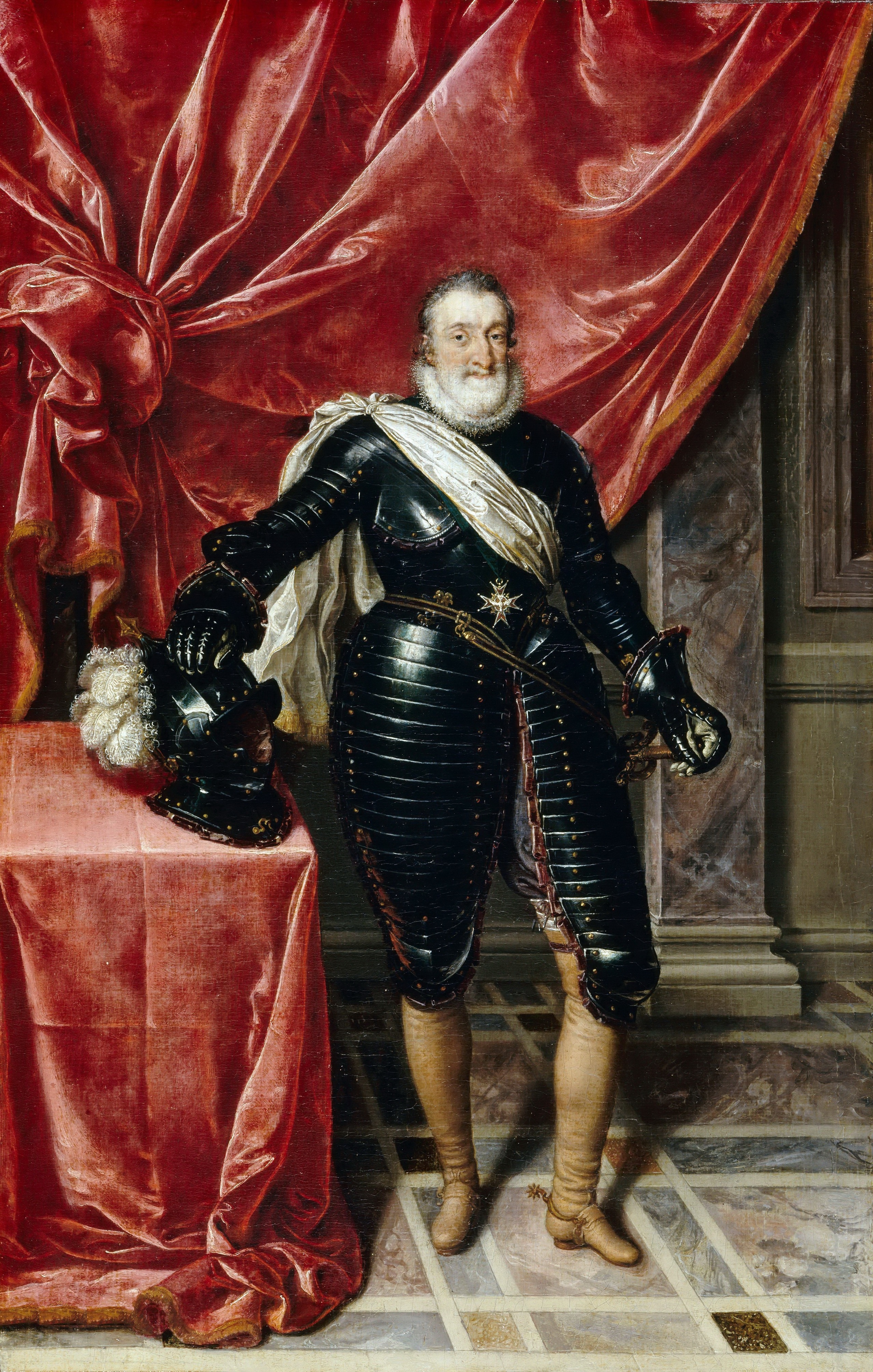
Henry III Of France
Henry III (french: Henri III, né Alexandre Édouard; pl, Henryk Walezy; lt, Henrikas Valua; 19 September 1551 – 2 August 1589) was King of France from 1574 until his assassination in 1589, as well as King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1573 to 1575. As the fourth son of King Henry II of France, he was not expected to inherit the French throne and thus was a good candidate for the vacant throne of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, where he was elected List of Polish rulers#Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, 1569–1795, monarch in 1573. During his brief rule, he signed the Henrician Articles into law, recognizing the szlachta's right to Royal elections in Poland, freely elect their monarch. Aged 22, Henry abandoned Poland–Lithuania upon inheriting the French throne when his brother, Charles IX of France, Charles IX, died without issue. France was at the time plagued by the French Wars of Religion, Wars of Religion, and Henry's authority was undermi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry I, Duke Of Guise
Henry I, Prince of Joinville, Duke of Guise, Count of Eu (31 December 1550 – 23 December 1588), sometimes called ('Scarface'), was the eldest son of Francis, Duke of Guise, and Anna d'Este. His maternal grandparents were Ercole II d'Este, Duke of Ferrara, and Renée of France. Through his maternal grandfather, he was a descendant of Lucrezia Borgia and Pope Alexander VI. A key figure in the French Wars of Religion, he was one of the namesakes of the War of the Three Henrys. A powerful opponent of the queen mother, Catherine de' Medici, Henry was assassinated by the bodyguards of her son, King Henry III. Early life Henry was born on 31 December 1550, the eldest son of Francis Duke of Guise, one of the leading magnates of France, and Anna d'Este, daughter of the Duke of Ferrara. In his youth he was friends with Henry III, the future king, and at the behest of Jacques, Duke of Nemours tried to persuade the young prince to run away with him in 1561 to join the arch-Catholic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a prominent role in the history and development of Western civilization.O'Collins, p. v (preface). The church consists of 24 ''sui iuris'' churches, including the Latin Church and 23 Eastern Catholic Churches, which comprise almost 3,500 dioceses and eparchies located around the world. The pope, who is the bishop of Rome, is the chief pastor of the church. The bishopric of Rome, known as the Holy See, is the central governing authority of the church. The administrative body of the Holy See, the Roman Curia, has its principal offices in Vatican City, a small enclave of the Italian city of Rome, of which the pope is head of state. The core beliefs of Catholicism are found in the Nicene Creed. The Catholic Church teaches that it is the on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Fontaine-Française
The Battle of Fontaine-Française occurred on 5 June 1595 between the French royal forces of King Henry IV of France and troops of Spain and the Catholic League commanded by Juan Fernández de Velasco and Charles of Lorraine, Duke of Mayenne, during the eighth and final war (1585-1598) of the French Wars of Religion. Background In early June 1595, Don Juan Fernández de Velasco ( governor of Milan and Constable of Castile) crossed the Alps with an army of 12,000 men from Italy and Sicily. In the Bishopric of Besançon he was joined by Charles of Mayenne (chief of the Catholic League). Together they moved on Dijon in order to take the city. Warned of their movements, Henry IV raced to Troyes with 3,000 men that he was able to gather. The battle The battle took place on 5 June at Fontaine-Française (Burgundy). That morning, Henry IV accompanied his scouts. They encountered the Spanish troops by accident, and – as at the Battle of Eu the year before – Henry attac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Morlaix (1594)
The siege of Morlaix took place from 6 September to 17 September 1594 during the French Wars of Religion and the Anglo-Spanish War (1585–1604).MacCaffrey pp 193 The siege was fought between the French Royal army under Jean VI d'Aumont reinforced by an English contingent under Sir John Norreys who besieged the town of Morlaix, which was held by the combined forces of Spain and the Catholic League of France.Hadfield & Hammond p 42-43 A relief force of Spanish troops under the Juan del Águila and another of Leaguers under the Duke of Mercœur were turned back by an English force under John Norreys.Nolan pp 210-13 With the arrival of a fleet of English ships under Martin Frobisher the garrison swiftly surrendered.Bicheno pp 279-80 Background Since 1562 France had been in the grip of the French Wars of Religion, in which Spain had regularly intervened in favour of the Catholic League of France.Horne pp.82–83 King Henry IV of France ( French: ''Henri de Bourbon'') had been fighti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Craon
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and Battle of Stalingrad, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, wherea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Caudebec
The siege of Caudebec (french: Retraite du Duc de Parme ) was a military event that took place between 24 April to 21 May 1592 as part of the French Wars of Religion and the Anglo-Spanish War (1585–1604). (French) The Spanish and the French Catholic League forces of Duke of Parma had captured the town of Caudebec on the Seine, where they soon found themselves trapped by the reinforced Royalist Protestant army led by Henry of Navarre consisting of French, English, and Dutch troops.Sutherland p 428 Seeing that Henry's force had now surrounded him, Parma seeing that defeat was inevitable, pulled his 15,000 men across the river in a single night to escape and retreat to the south.Jacques p 213 Background The Catholic forces of the Duke of Parma had relieved Rouen in April 1592 and had skilfully avoided an engagement with Henry's Protestant army.Alan James p.40 After having entered Rouen Parma then marched west and towards Caudebec on the Seine in the Pays de Caux, a town blocki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Rouen (1591)
Siege of Rouen may refer to: *Siege of Rouen (1143-44), the siege and capture of the town by Geoffrey Plantagenet, Count of Anjou *Siege of Rouen (1204), the siege and capture of the town and castle by the French during the French annexation of Normandy *Siege of Rouen (1418-1419), the siege and capture of the town and castle by the English during the Hundred Years' War *Siege of Rouen (1449), the siege and capture of the town and castle by the French during the Hundred Years’ War *Siege of Rouen (1562), the siege that set the stage for the main battle of the war at Dreux several months later *Siege of Rouen (1591-1592), the unsuccessful siege of the town and castle during the French Wars of Religion, by the Protestant King Henry IV of France Henry IV (french: Henri IV; 13 December 1553 – 14 May 1610), also known by the epithets Good King Henry or Henry the Great, was King of Navarre (as Henry III) from 1572 and King of France from 1589 to 1610. He was the firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Paris (1590)
The siege of Paris took place in 1590 during the French Wars of Religion when the French Royal Army under Henry of Navarre, and supported by the Huguenots, failed to capture the city of Paris from the Catholic League. Paris was finally relieved from the siege by an international Catholic and Spanish army under the command of Alexander Farnese, Duke of Parma. Background After his victory over the Catholic forces commanded by Charles, Duke of Mayenne and Charles of Guise, Duke of Aumale at the Battle of Ivry on 14 March, Henry of Navarre advanced with his troops on his main objective of Paris, possession of which would allow him to confirm his contested claim to the French throne. Paris at the time was a large walled city of around 200,000–220,000 people. Siege of Paris On 7 May, Henry's army surrounded the city, imposing a blockade and burnt windmills to prevent food from reaching Paris. Henry had at this point only around 12,000–13,000 troops, facing defenders estimated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Ivry
The Battle of Ivry was fought on 14 March 1590, during the French Wars of Religion. The battle was a decisive victory for Henry IV of France, leading French royal and English forces against the Catholic League by the Duc de Mayenne and Spanish forces under the Count of Egmont. Henry's forces were victorious and he went on to lay siege to Paris. The battle occurred on the plain of Épieds, Eure near Ivry (later renamed Ivry-la-Bataille), Normandy. Ivry-la-Bataille is located on the river Eure and about thirty miles west of Paris, at the boundary between the Île-de-France and the Beauce regions. Prelude Henry IV had moved rapidly to besiege Dreux, a town controlled by the League. As Mayenne followed intending to raise the siege, Henry withdrew but stayed within sight. He deployed his army on the plain of Saint André between the towns of Nonancourt and Ivry. Henry had been reinforced by English troops sent in support by Queen Elizabeth I.Morris p 342 * Henry had 12,000 foot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)