|
Lignans
The lignans are a large group of low molecular weight polyphenols found in plants, particularly seeds, whole grains, and vegetables. The name derives from the Latin word for "wood". Lignans are precursors to phytoestrogens. They may play a role as antifeedants in the defense of seeds and plants against herbivores. Biosynthesis and metabolism Lignans and lignin differ in their molecular weight, the former being small and soluble in water, the latter being high polymers that are undigestable. Both are polyphenolic substances derived by oxidative coupling of monolignols. Thus, most lignans feature a C18 cores, resulting from the dimerization of C9 precursors. The coupling of the lignols occurs at C8. Eight classes of lignans are: "furofuran, furan, dibenzylbutane, dibenzylbutyrolactone, aryltetralin, arylnaphthalene, dibenzocyclooctadiene, and dibenzylbutyrolactol." Many lignans are metabolized by mammalian gut microflora, producing so-called enterolignans. Food sources F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matairesinol
Matairesinol is an organic compound. It is classified as a lignan, i.e., a type of phenylpropanoid. It is present in some cereals, e.g. rye, and together with Secoisolariciresinol, has attracted much attention for its beneficial nutritional effects. Metabolism The plant lignans are precursors of the enterolignans (mammalian lignans). A number of plant lignans are metabolized to the enterolignans ( enterodiol and enterolactone) that can potentially reduce the risk of certain cancers and cardiovascular diseases. Biomedical considerations Although some studies attribute disease preventative (cardio-protective and hormone associated cancers like breast cancer) benefits of lignans, the results are inconclusive. Matairesinol has been found to act as an agonist An agonist is a chemical that activates a receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an antagonist blocks t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enterolignan
Enterolignans are organic compounds formed by the action of gut microflora on lignans. They are thus the products of the combined action of both plants and of the animal gut. Prominent enterolignans are enterodiol and enterolactone Enterolactone is a organic compound classified as an enterolignan. It is formed by the action of intestinal bacteria on plant lignan precursors present in the diet. Sources Many dietary plant lignan precursors, such as secoisolariciresinol, .... Enterolignans are also called "mammalian lignans", although that term is self-contradictory since mammals do not produce lignans. . Enterolignans have attracted intense attention because of their potential beneficial roles in nutrition. Elevated levels of enterodiol in urine are attributed consumption of tea and other lignan-rich foods. References Polyols Lignans Phenols {{aromatic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soybean
The soybean, soy bean, or soya bean (''Glycine max'') is a species of legume native to East Asia, widely grown for its edible bean, which has numerous uses. Traditional unfermented food uses of soybeans include soy milk, from which tofu and tofu skin are made. Fermented soy foods include soy sauce, fermented bean paste, nattō, and tempeh. Fat-free (defatted) soybean meal is a significant and cheap source of protein for animal feeds and many packaged meals. For example, soybean products, such as textured vegetable protein (TVP), are ingredients in many meat and dairy substitutes. Soybeans contain significant amounts of phytic acid, dietary minerals and B vitamins. Soy vegetable oil, used in food and industrial applications, is another product of processing the soybean crop. Soybean is the most important protein source for feed farm animals (that in turn yields animal protein for human consumption). Etymology The word "soy" originated as a corruption of the Cant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monolignol
Monolignols, also called lignols, are the source materials for biosynthesis of both lignans and lignin and consist mainly of paracoumaryl alcohol (H), coniferyl alcohol (G) and sinapyl alcohol (S). These monolignols differ in their degree of methoxilation of the aromatic ring. The monolignols are derived from the amino acid phenylalanine via the phenylpropanoid pathway involving various enzymes. Phenylalanine is first converted to paracoumaryl alcohol (H), which is subsequently elaborated to coniferyl alcohol (G) and sinapyl alcohol (S). This reaction happens in the cytosol, while the polymerization of the monolignols occurs in the apoplast to which the monolignols have to be transported to though the cell membrane. The monolignols have been found as monolignol-4-O-β-d- glucosides, which might be their major way of storage. Another theory for this conversion is that is improving the transportation of the monolignols. The polymerization consists of oxidative coupling reaction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
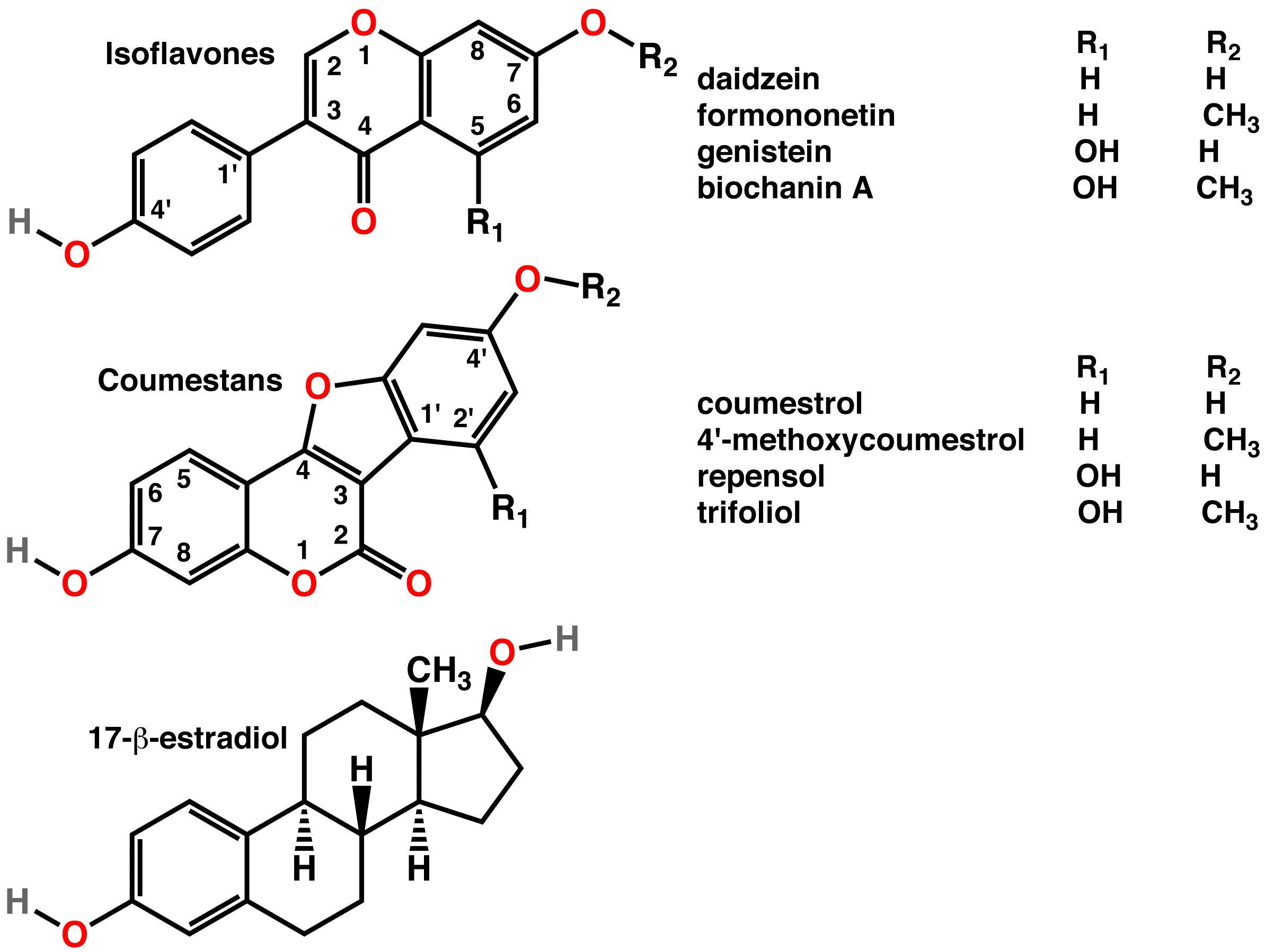
Phytoestrogen
A phytoestrogen is a plant-derived xenoestrogen (see estrogen) not generated within the endocrine system, but consumed by eating plants or manufactured foods. Also called a "dietary estrogen", it is a diverse group of naturally occurring nonsteroidal plant compounds that, because of its structural similarity with estradiol (17-β-estradiol), have the ability to cause estrogenic or antiestrogenic effects. Phytoestrogens are not essential nutrients because their absence from the diet does not cause a disease, nor are they known to participate in any normal biological function. Common foods containing phytoestrogens are soy protein, beans, oats, barley, rice, coffee, apples, carrots (see Food Sources section below for bigger list). Its name comes from the Greek ''phyto'' ("plant") and ''estrogen'', the hormone which gives fertility to female mammals. The word "estrus" - Greek οίστρος - means "sexual desire", and "gene" - Greek γόνο - is "to generate". It has been hypot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
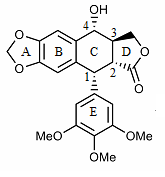
Podophyllotoxin
Podophyllotoxin (PPT) is the active ingredient in Podofilox, which is a medical cream that is used to treat genital warts and molluscum contagiosum. It is not recommended in HPV infections without external warts. It can be applied either by a healthcare provider or the person themselves. It is a non-alkaloid toxin lignin extracted from the roots and rhizomes of '' Podophyllum'' species. A less refined form known as podophyllum resin is also available, but has greater side effects. Podophyllotoxin was first isolated in pure form in 1880 by Valerian Podwyssotzki (1818 – 28 January 1892), a Polish-Russian privatdozent at the University of Dorpat (now: Tartu, Estonia) and assistant at the Pharmacological Institute there. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Medical uses Podophyllotoxin possesses a large number of medical applications, as it is able to stop replication of both cellular and viral DNA by binding necessary enzymes. It can add ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinoresinol
Pinoresinol is a tetrahydrofuran lignan found in ''Styrax sp.'', '' Forsythia suspensa, and in Forsythia koreana''. It is also found in the caterpillar of the cabbage butterfly, ''Pieris rapae'' where it serves as a defence against ants. In food, it is found in sesame seed, in ''Brassica'' vegetables and in olive oil. Pinoresinol has also been found to be toxic to larvae of the milkweed bug Oncopeltus fasciatus and of the haematophagous insect Rhodnius prolixus, which is a vector of chagas disease. Currently, pinoresinol is isolated from plants with low efficiency and low yield. Biosynthesis A first dirigent protein was discovered in '' Forsythia intermedia''. This protein has been found to direct the stereoselective biosynthesis of (+)-pinoresinol from coniferyl alcohol monomers. Recently, a second, enantiocomplementary dirigent protein was identified in ''Arabidopsis thaliana'', which directs enantioselective synthesis of (-)-pinoresinol. Pharmacology Pinoresinol inhi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sesame Seed
Sesame ( or ; ''Sesamum indicum'') is a flowering plant in the genus '' Sesamum'', also called benne. Numerous wild relatives occur in Africa and a smaller number in India. It is widely naturalized in tropical regions around the world and is cultivated for its edible seeds, which grow in pods. World production in 2018 was , with Sudan, Myanmar, and India as the largest producers. Sesame seed is one of the oldest oilseed crops known, domesticated well over 3,000 years ago. ''Sesamum'' has many other species, most being wild and native to sub-Saharan Africa. ''S. indicum,'' the cultivated type, originated in India. It tolerates drought conditions well, growing where other crops fail. Sesame has one of the highest oil contents of any seed. With a rich, nutty flavor, it is a common ingredient in cuisines around the world. Like other foods, it can trigger allergic reactions in some people. Etymology The word "sesame" is from Latin ''sesamum'' and Greek σήσαμον : ''sē ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyphenol
Polyphenols () are a large family of naturally occurring organic compounds characterized by multiples of phenol units. They are abundant in plants and structurally diverse. Polyphenols include flavonoids, tannic acid, and ellagitannin, some of which have been used historically as dyes and for tanning garments. Etymology The name derives from the Ancient Greek word (''polus'', meaning "many, much") and the word phenol which refers to a chemical structure formed by attaching to an aromatic benzenoid (phenyl) ring to a hydroxyl (-OH) group as is found in alcohols (hence the ''-ol'' suffix). The term polyphenol has been in use at least since 1894. Definition The term polyphenol is not well-defined, but is generally agreed that they are natural products "having a polyphenol structure (i.e., several hydroxyl groups on aromatic rings)" including four principal classes: "phenolic acids, flavonoids, stilbenes, and lignans". *Flavonoids include flavones, flavonols, flavanol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secoisolariciresinol
Secoisolariciresinol is an organic compound. It is classified as a lignan, i.e., a type of phenylpropanoid. It is present in some cereals, e.g. rye, and together with matairesinol, has attracted much attention for its beneficial nutritional effects. Occurrence The water extract of silver fir wood contains more than 5% of secoisolariciresinol. It is also present in nettle brew. Its content in flaxseed (Linum usitatıssimum) was found to be 0.3%, which is the highest known content in food. Biomedical aspects In the intestine the gut microflora can form secoisolariciresinol from the secoisolariciresinol diglucoside and it can then be further transformed into the enterolignan enterodiol. Epidemiological studies showed associations between secoisolariciresinol intake and decreased risk of cardiovascular disease Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels. CVD includes coronary artery diseases (CAD) such as angina and myocardial i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barley
Barley (''Hordeum vulgare''), a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains, particularly in Eurasia as early as 10,000 years ago. Globally 70% of barley production is used as animal fodder, while 30% as a source of fermentable material for beer and certain distilled beverages, and as a component of various foods. It is used in soups and stews, and in barley bread of various cultures. Barley grains are commonly made into malt in a traditional and ancient method of preparation. In 2017, barley was ranked fourth among grains in quantity produced () behind maize, rice and wheat. Etymology The Old English word for barley was ', which traces back to Proto-Indo-European and is cognate to the Latin word ' "flour" (''see corresponding entries''). The direct ancestor of modern English ''barley'' in Old English was the derived adjective ''bærlic'', meaning "of barley". The first citation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mill (grinding)
A mill is a device, often a structure, machine or home appliance, kitchen appliance, that breaks solid materials into smaller pieces by grinding, crushing, or cutting. Such comminution is an important unit operation in many process (engineering), processes. There are many different types of mills and many types of materials processed in them. Historically mills were powered by hand or by animals (e.g., via a crank (mechanism), hand crank), working animal (e.g., horse mill), wind (windmill) or water (watermill). In modern era, they are usually powered by electricity. The grinding of solid materials occurs through mechanical forces that break up the structure by overcoming the interior bonding forces. After the grinding the state of the solid is changed: the grain size, the grain size disposition and the grain shape. Milling also refers to the process of breaking down, separating, sizing, or classifying aggregate material (e.g. mining ore). For instance rock crushing or grinding to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |