|
Lift-to-drag
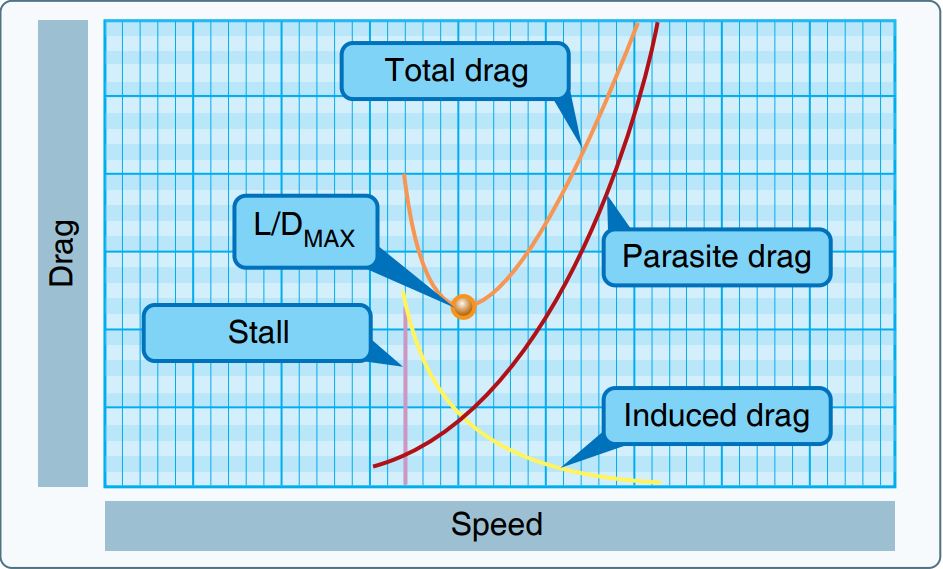
In aerodynamics, the lift-to-drag ratio (or L/D ratio) is the lift generated by an aerodynamic body such as an aerofoil or aircraft, divided by the aerodynamic drag caused by moving through air. It describes the aerodynamic efficiency under given flight conditions. The L/D ratio for any given body will vary according to these flight conditions. For an aerofoil wing or powered aircraft, the L/D is specified when in straight and level flight. For a glider it determines the glide ratio, of distance travelled against loss of height. The term is calculated for any particular airspeed by measuring the lift generated, then dividing by the drag at that speed. These vary with speed, so the results are typically plotted on a 2-dimensional graph. In almost all cases the graph forms a U-shape, due to the two main components of drag. The L/D may be calculated using computational fluid dynamics or computer simulation. It is measured empirically by testing in a wind tunnel or in free flight te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lift-to-drag Ratio
In aerodynamics, the lift-to-drag ratio (or L/D ratio) is the lift generated by an aerodynamic body such as an aerofoil or aircraft, divided by the aerodynamic drag caused by moving through air. It describes the aerodynamic efficiency under given flight conditions. The L/D ratio for any given body will vary according to these flight conditions. For an aerofoil wing or powered aircraft, the L/D is specified when in straight and level flight. For a glider it determines the glide ratio, of distance travelled against loss of height. The term is calculated for any particular airspeed by measuring the lift generated, then dividing by the drag at that speed. These vary with speed, so the results are typically plotted on a 2-dimensional graph. In almost all cases the graph forms a U-shape, due to the two main components of drag. The L/D may be calculated using computational fluid dynamics or computer simulation. It is measured empirically by testing in a wind tunnel or in free flight te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspect Ratio (aeronautics)
In aeronautics, the aspect ratio of a wing is the ratio of its span to its mean chord. It is equal to the square of the wingspan divided by the wing area. Thus, a long, narrow wing has a high aspect ratio, whereas a short, wide wing has a low aspect ratio.Kermode, A.C. (1972), ''Mechanics of Flight'', Chapter 3, (p.103, eighth edition), Pitman Publishing Limited, London Aspect ratio and other features of the planform are often used to predict the aerodynamic efficiency of a wing because the lift-to-drag ratio increases with aspect ratio, improving the fuel economy in powered airplanes and the gliding angle of sailplanes. Definition The aspect ratio \text is the ratio of the square of the wingspan b to the projected wing area S, which is equal to the ratio of the wingspan b to the standard mean chord \text: \text \equiv \frac = \frac Mechanism As a useful simplification, an airplane in flight can be imagined to affect a circular cylinder of air with a diameter equal to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fuel Economy In Aircraft
The fuel economy in aircraft is the measure of the transport energy efficiency of aircraft. Efficiency is increased with better aerodynamics and by reducing weight, and with improved engine BSFC and propulsive efficiency or TSFC. Endurance and range can be maximized with the optimum airspeed, and economy is better at optimum altitudes, usually higher. An airline efficiency depends on its fleet fuel burn, seating density, air cargo and passenger load factor, while operational procedures like maintenance and routing can save fuel. Average fuel burn of new aircraft fell 45% from 1968 to 2014, a compounded annual reduction 1.3% with a variable reduction rate. In 2018, CO₂ emissions totalled 747 million tonnes for passenger transport, for 8.5 trillion revenue passenger kilometres (RPK), giving an average of 88 gram CO₂ per RPK. A 88 gCO₂/km represents g of fuel per km, or a fuel consumption. New technology can reduce engine fuel consumption, like higher pressure a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drag Curve
The drag curve or drag polar is the relationship between the drag on an aircraft and other variables, such as lift, the coefficient of lift, angle-of-attack or speed. It may be described by an equation or displayed as a graph (sometimes called a "polar plot"). Drag may be expressed as actual drag or the coefficient of drag. Drag curves are closely related to other curves which do not show drag, such as the power required/speed curve, or the sink rate/speed curve. The drag curve The significant aerodynamic properties of aircraft wings are summarised by two dimensionless quantities, the lift and drag coefficients and . Like other such aerodynamic quantities, they are functions only of the angle of attack , the Reynolds number and the Mach number . and can be plotted against , or can be plotted against each other. The lift and the drag forces, and , are scaled by the same factor to get and , so = . and are at right angles, with parallel to the free stream velocit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wind Tunnel
Wind tunnels are large tubes with air blowing through them which are used to replicate the interaction between air and an object flying through the air or moving along the ground. Researchers use wind tunnels to learn more about how an aircraft will fly. NASA uses wind tunnels to test scale models of aircraft and spacecraft. Some wind tunnels are large enough to contain full-size versions of vehicles. The wind tunnel moves air around an object, making it seem as if the object is flying. Most of the time, large powerful fans suck air through the tube. The object being tested is held securely inside the tunnel so that it remains stationary. The object can be an aerodynamic test object such as a cylinder or an airfoil, an individual component, a small model of the vehicle, or a full-sized vehicle. The air moving around the stationary object shows what would happen if the object was moving through the air. The motion of the air can be studied in different ways; smoke or dye can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cruising Speed
Cruise is the phase of aircraft flight that starts when the aircraft levels off after a climb, until it begins to descend for landing. Cruising usually consumes the majority of a flight, and it may include changes in heading (direction of flight), airspeed and altitude. Commercial or passenger aircraft are usually designed for optimum performance around their cruise speed ( VC) and cruise altitude. Factors affecting optimum cruise speed and altitude include payload, center of gravity, air temperature, and humidity. Cruise altitude is usually where the higher ground speed is balanced against the decrease in engine thrust and efficiency at higher altitudes. A typical cruising airspeed for a long-distance commercial passenger aircraft is approximately . The typical cruising altitude for commercial airliners is . The speed which covers the greatest distance for a given amount of fuel is known as the maximum range speed. This is the speed at which drag is minimised. For jet aircraft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camber (aerodynamics)
In aeronautics and aeronautical engineering, camber is the asymmetry between the two acting surfaces of an airfoil, with the top surface of a wing (or correspondingly the front surface of a propeller blade) commonly being more convex (positive camber). An airfoil that is not cambered is called a ''symmetric airfoil''. The benefits of cambering were discovered and first utilized by George Cayley in the early 19th century. Overview Camber is usually designed into an airfoil to maximize its lift coefficient. This minimizes the stalling speed of aircraft using the airfoil. An aircraft with cambered wings will have a lower stalling speed than an aircraft with a similar wing loading and symmetric airfoil wings. An aircraft designer may also reduce the angle of attack of the outboard section of the wings. This ensures that, as the aircraft approaches the stall, the wing root stalls before the tip, giving the aircraft resistance to spinning and maintaining aileron effectiveness c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Form Drag
Parasitic drag, also known as profile drag, is a type of aerodynamic drag that acts on any object when the object is moving through a fluid. Parasitic drag is a combination of form drag and skin friction drag. It affects all objects regardless of whether they are capable of generating lift. Total drag on an aircraft is made up of parasitic drag and lift-induced drag. Parasitic drag comprises all types of drag except lift-induced drag. Form drag Form drag arises because of the shape of the object. The general size and shape of the body are the most important factors in form drag; bodies with a larger presented cross-section will have a higher drag than thinner bodies; sleek ("streamlined") objects have lower form drag. Form drag follows the drag equation, meaning that it increases with the square of the velocity, and thus becomes more important for high-speed aircraft. Form drag depends on the longitudinal section of the body. A prudent choice of body profile is essential for a lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Resistance
In fluid dynamics, drag (sometimes called air resistance, a type of friction, or fluid resistance, another type of friction or fluid friction) is a force acting opposite to the relative motion of any object moving with respect to a surrounding fluid. This can exist between two fluid layers (or surfaces) or between a fluid and a solid surface. Unlike other resistive forces, such as dry friction, which are nearly independent of velocity, the drag force depends on velocity. Drag force is proportional to the velocity for low-speed flow and the squared velocity for high speed flow, where the distinction between low and high speed is measured by the Reynolds number. Even though the ultimate cause of drag is viscous friction, turbulent drag is independent of viscosity. Drag forces always tend to decrease fluid velocity relative to the solid object in the fluid's path. Examples Examples of drag include the component of the net aerodynamic or hydrodynamic force acting opposite to the dire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airfoil Lift And Drag
An airfoil (American English) or aerofoil (British English) is the cross-sectional shape of an object whose motion through a gas is capable of generating significant lift, such as a wing, a sail, or the blades of propeller, rotor, or turbine. A solid body moving through a fluid produces an aerodynamic force. The component of this force perpendicular to the relative freestream velocity is called lift. The component parallel to the relative freestream velocity is called drag. An airfoil is a streamlined shape that is capable of generating significantly more lift than drag. Airfoils can be designed for use at different speeds by modifying their geometry: those for subsonic flight generally have a rounded leading edge, while those designed for supersonic flight tend to be slimmer with a sharp leading edge. All have a sharp trailing edge. Foils of similar function designed with water as the working fluid are called hydrofoils. The lift on an airfoil is primarily the result of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Profile Drag
Parasitic drag, also known as profile drag, is a type of aerodynamic drag that acts on any object when the object is moving through a fluid. Parasitic drag is a combination of form drag and skin friction drag. It affects all objects regardless of whether they are capable of generating lift. Total drag on an aircraft is made up of parasitic drag and lift-induced drag. Parasitic drag comprises all types of drag except lift-induced drag. Form drag Form drag arises because of the shape of the object. The general size and shape of the body are the most important factors in form drag; bodies with a larger presented cross-section will have a higher drag than thinner bodies; sleek ("streamlined") objects have lower form drag. Form drag follows the drag equation, meaning that it increases with the square of the velocity, and thus becomes more important for high-speed aircraft. Form drag depends on the longitudinal section of the body. A prudent choice of body profile is essential for a lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |