|
Life Regiment Dragoons
The Life Regiment Dragoons ( sv, Livregementets dragoner), designated K 2, was a Swedish Army cavalry regiment that was active in various forms 1791–1927. The unit was based in the Stockholm Garrison in Stockholm and belonged to the King's Life and Household Troops (''Kungl. Maj:ts Liv- och Hustrupper'') until 1974. History The regiment has its origins in the ''ryttarfanor'' ("horsemen; cavalry units") which were raised in Uppland, Södermanland, Västmanland, Närke and Värmland. These were combined into two regiments, which, according to the Instrument of Government of 1634, were amalgamated into one. The regiment was from 1636 usually referred to as ''Upplands ryttare'' ("Uppland Horsemen"). Its first commanding officer was Isak Axelsson Silversparre. On 26 November 1667, the regiment was upgraded into a royal life squad as a thank you for their efforts during the campaign of Charles X Gustav and received the name ''Livregementet till häst'' ("Life Regiment of Horse"). At t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lilla Riksvapnet, Med Serafimerorden
Lilla is a female given name, derived from Elizabeth. Given name * Lilla Barzó, a Hungarian tennis player * Lilla Bodor, a Hungarian painter * Lilla Brignone, an Italian film and theater actress * Lilla Cabot Perry, an American artist * Lilla Crawford, an American actress * Lilla Hansen, a Norwegian architect * Lilla Maldura, an Italian artist * Lilla Nagy, a Hungarian footballer * Lilla Sipos, a Hungarian footballer * Lilla Vincze, a Hungarian singer * Lilla Watson, an indigenous Australian artist * Lilla Zuckerman, an American television writer Surname * Mark Lilla, an American political scientist. Nickname * Iris Mary 'Lilla' Birtwistle, an English lyric poet and gallery owner See also * Lila (given name) Lila ( ar, ليلى) can be a variant of the Arabic and Hebrew words for "night". Other versions are Lyla (most common in Arabic) and Lilah. As a name it means night, beauty, or dark beauty. Lila is a common Indian female given name meaning "beauty ... References { ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
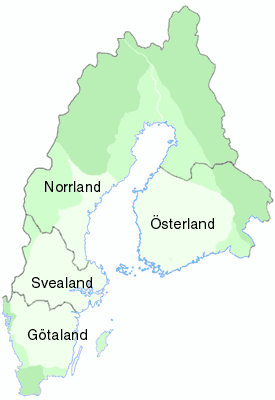
Värmland
Värmland () also known as Wermeland, is a '' landskap'' (historical province) in west-central Sweden. It borders Västergötland, Dalsland, Dalarna, Västmanland, and Närke, and is bounded by Norway in the west. Latin name versions are ''Varmelandia'', ''Vermelandia'', ''Wermelandia'', ''Værmalandia'', ''Værmolandia'', ''Virmolandia'' and ''Vermillandia''. Some of the Latinised forms show the origin of the name to come from the large local lake by the name of (from older ''*Virmil''); others from the river name ''*Værma'', the main outlet of that lake. The province was originally part of Götaland, and became part of Svealand in 1815. Geography The largest lake is Vänern. Most streams of importance lead to Vänern. However, the province is rich in small lakes, ponds and streams. The scenery, with mountains and lakes, is usually regarded as picturesque and has inspired painters and writers. Western Värmland There are several mountain plateaus in the western part of V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Life Guards Of Horse
Life Guards of Horse ( sv, Livgardet till häst, K 1) was a Swedish Army cavalry regiment, first raised in 1770. It saw service for two centuries, before being amalgamated with the Life Regiment Dragoons (K 2) to form the Life Regiment of Horse (K 1) in 1928. History The regiment was raised on 20 February 1770 by Jacob Magnus Sprengtporten as the Finnish Light Dragoon Corps (''Finska lätta dragonkåren''). The unit was set up as a regular dragoon corps in Nyland County, Finland as a reinforcement of the border guard along the Kymmene River. The corps then consisted of 150 men and was based in Borgå. In 1773 the corps was increased to 250 men (5 squadrons), and was given the name Life Guards of Horse (''Livgardet till häst'') and was based partly in Stockholm, partly in Borgå, Finland. In 1777, it was based in Stockholm, Södertälje, Enköping and Sigtuna. From 1811, the unit was only based in Stockholm. After changing its name several times, in 1806 it got its present n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Defence Act Of 1925 (Sweden)
The Defence Act of 1925 was a defence act passed by the Swedish Riksdag on 26 May 1925 and came into force on 1 January 1928. The Act specified how the Swedish Armed Forces would operate during the coming years. The Act resulted in a policy of disarmament. The Act would remain effective until the Defence Act of 1936. The new order of battle meant that the number of Army Divisions was decreased to 4. 17 military units were disbanded and conscription time was lowered to 140 days for most conscripts. Many conscripts were transferred to the Army Reserve. The Army and Naval air powers were combined into the Swedish Air Force. Background The Edén Cabinet had in 1919 started an investigation into the Swedish Armed Forces in order to lower the high defence expenditure the Defence Act of 1914 had resulted in. The investigation concluded in 1923 and the right-wing majority had decided on an expenditure cap of 120 million Swedish crowns per year, 62 million less than the Defence Act of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fellingsbro
Fellingsbro (, locally ) is a locality and a parish situated in Lindesberg Municipality, Örebro County, Sweden with 1,384 inhabitants in 2010. It is home to the Fellingsbro folk high school. History The parish of Fellingsbro is mentioned already in 1331 as ''Parochia Fælansbro'', but the first parish church was probably built already in the 12th century. In the late 16th and early 17th centuries many small ironworks were built at the rivers that are running from north to south in the parish. The main product at these ironworks were bar iron. Most of the people were employed in this small scale iron industry and in the rather extensive farming up until the late 19th century when most of the ironworks were closed. Some of the ironworks were then transformed into paper mills. In 1857 a railroad between Örebro and Arboga was built and a station in Fellingsbro was opened some kilometres east of the parish church. A new urban area with shops and small mechanical industries soon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
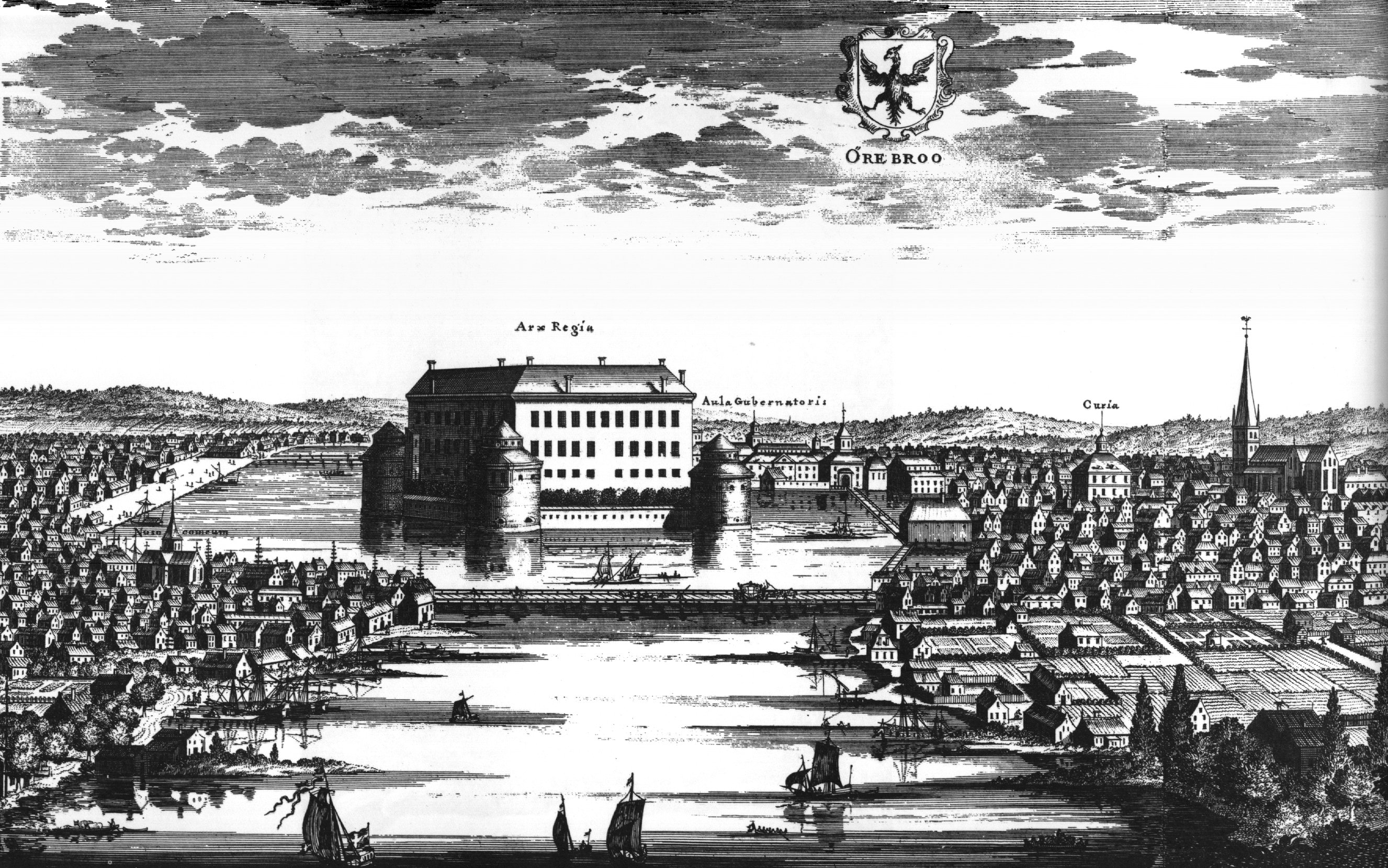
Örebro
Örebro ( , ) is the List of urban areas in Sweden by population, sixth-largest city in Sweden, the seat of Örebro Municipality, and capital of the Örebro County. It is situated by the Närke Plain, near the lake Hjälmaren, a few kilometers inland along the small river Svartån, Närke, Svartån, and has a population of approximately 126,000 in the city proper. It is one of the largest inland hubs of the country, and a major Logistics, logistic and commercial operating site. Örebro is home to Örebro University, a Örebro University Hospital, major university hospital, a Örebro Castle, medieval castle, the water park Gustavsvik as well as several large shopping malls and the Oset-Rynningeviken nature reserve at the lakefront. Örebro is served by Örebro Airport 10 km (6 mi) southwest of the city, and by Örebro Central Station, serviced by the Mälaren Line and Western Main Line. Etymology The name ''Örebro'' refers to a bridge (') crossing the river Svartån, Närke, S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russo-Swedish War (1788–1790)
The Russo-Swedish War of 1788–1790 was fought between Sweden and Russia from June 1788 to August 1790. The war was ended by the Treaty of Värälä on 14 August 1790 and took place concomitantly with both the Austro-Turkish War (1788–1791), Russo-Turkish War (1787–1792) and Theatre War. The war was, overall, mostly insignificant for the parties involved. Background The conflict was initiated by King Gustav III of Sweden for domestic political reasons, as he believed that a short war would leave the opposition with no recourse but to support him. Despite establishing himself as an autocrat in a bloodless ''coup d'état'' that ended parliamentary rule in 1772, his political powers did not give him the right to start a war. Also he was becoming increasingly unpopular, an issue which became obvious during the parliament session of 1786. This unpopularity was also encouraged by Russia, which believed an autocratic king to be a threat to its interests. However, Russian suppor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dragoon
Dragoons were originally a class of mounted infantry, who used horses for mobility, but dismounted to fight on foot. From the early 17th century onward, dragoons were increasingly also employed as conventional cavalry and trained for combat with swords and firearms from horseback. While their use goes back to the late 16th century, dragoon regiments were established in most European armies during the 17th and early 18th centuries; they provided greater mobility than regular infantry but were far less expensive than cavalry. The name reputedly derives from a type of firearm, called a ''dragon'', which was a handgun version of a blunderbuss, carried by dragoons of the French Army. The title has been retained in modern times by a number of armoured or ceremonial mounted regiments. Origins and name The establishment of dragoons evolved from the practice of sometimes transporting infantry by horse when speed of movement was needed. In 1552, Alexander Farnese, Duke of Parma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Svealand
Svealand (), or Swealand, is the historical core region of Sweden. It is located in south central Sweden and is one of three historical lands of Sweden, bounded to the north by Norrland and to the south by Götaland. Deep forests, Tiveden, Tylöskog, and Kolmården, separated Svealand from Götaland. Historically, its inhabitants were called , from which is derived the English 'Swedes'. Svealand consists of the capital region Mälardalen in the east, Roslagen in the north-east, the former mining district Bergslagen in the center, and Dalarna and Värmland in the west. The older name of Sweden in Swedish, (modern spelling: ) Realm of the Swedes, "Swea Region", originally only referred to Svealand. Other forms are (Old Norse/ Icelandic ), and . As the domains of the Swedish kings grew, the name Svealand began to be used to separate the original territory from the new. Provinces Svealand is made up of the following six provinces: *Dalarna *Närke *Södermanland *Uppland *V� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allotment System
The allotment system ( sv, indelningsverket; fi, ruotujakolaitos) was a system used in Sweden for keeping a trained army at all times. This system came into use in around 1640, and was replaced by the modern Swedish Armed Forces conscription system in 1901. Two different allotment systems have been in use in Sweden; they are the old allotment system (''äldre indelningsverket'') and the new allotment system (''yngre indelningsverket''), the latter often referred to as just "the allotment system". The soldiers who were part of these systems were known as "croft soldiers" (''indelta soldater'', the Swedish term, does not have the same meaning) due to the small crofts allotted to them. Originally, the allotment system was the name for a system used to pay servants of the state, like officers and clergy. It was introduced because of an often felt shortage of money, and the allotment system tried to solve this by localising taxes; meaning that payment consisted of an individual's r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles XI Of Sweden
Charles XI or Carl ( sv, Karl XI; ) was King of Sweden from 1660 until his death, in a period of Swedish history known as the Swedish Empire (1611–1721). He was the only son of King Charles X Gustav of Sweden and Hedwig Eleonora of Holstein-Gottorp. His father died when he was four years old, so Charles was educated by his governors until his coronation at the age of seventeen. Soon afterward, he was forced out on military expeditions to secure the recently acquired dominions from Danish troops in the Scanian War. Having successfully fought off the Danes, he returned to Stockholm and engaged in correcting the country's neglected political, financial, and economic situation. He managed to sustain peace during the remaining 20 years of his reign. Changes in finance, commerce, national maritime and land armaments, judicial procedure, church government, and education emerged during this period. Charles XI was succeeded by his only son Charles XII, who made use of the well-tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nils Bielke
Count Nils Bielke (7 February 1644 in Stockholm – 26 November 1716) was a member of the High Council of Sweden, military and politician. Born the eldest son of Baron Ture Nilsson Bielke, who died in 1648, Queen Christina granted the young boy the barony of Korpo in the archipelago of Finland Proper in 1649.Bielke, Nils Turesson , '''', 1906 He married countess Eva Horn, one of the heiresses of the sonless field marshal Count Gustav Horn af Björneborg. Nils Bielke entered the service of the Swedish Arm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_en2.png)