|
Liesegang
Liesegang rings () are a phenomenon seen in many, if not most, chemical systems undergoing a precipitation reaction under certain conditions of concentration and in the absence of convection. Rings are formed when weakly soluble salts are produced from reaction of two soluble substances, one of which is dissolved in a gel medium. The phenomenon is most commonly seen as rings in a Petri dish or bands in a test tube; however, more complex patterns have been observed, such as dislocations of the ring structure in a Petri dish, helices, and "Saturn rings" in a test tube. Despite continuous investigation since rediscovery of the rings in 1896, the mechanism for the formation of Liesegang rings is still unclear. History The phenomenon was first noticed in 1855 by the German chemist Friedlieb Ferdinand Runge. He observed them in the course of experiments on the precipitation of reagents in blotting paper. In 1896 the German chemist Raphael Eduard Liesegang, Raphael E. Liesegang noted th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liesegang Rings
Liesegang rings () are a phenomenon seen in many, if not most, chemical systems undergoing a precipitation reaction under certain conditions of concentration and in the absence of convection. Rings are formed when weakly soluble salts are produced from reaction of two soluble substances, one of which is dissolved in a gel medium. The phenomenon is most commonly seen as rings in a Petri dish or bands in a test tube; however, more complex patterns have been observed, such as dislocations of the ring structure in a Petri dish, helices, and " Saturn rings" in a test tube. Despite continuous investigation since rediscovery of the rings in 1896, the mechanism for the formation of Liesegang rings is still unclear. History The phenomenon was first noticed in 1855 by the German chemist Friedlieb Ferdinand Runge. He observed them in the course of experiments on the precipitation of reagents in blotting paper. In 1896 the German chemist Raphael E. Liesegang noted the phenomenon when he dro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
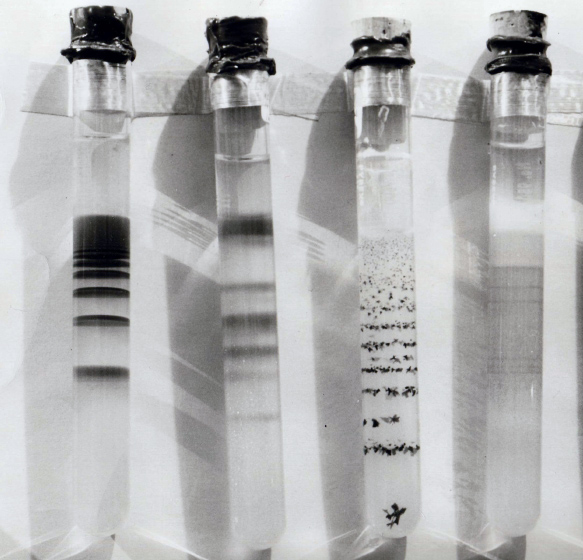
Liesegang Rings Of Magnesium Hydroxide In Agar Gel - (4)
Liesegang rings () are a phenomenon seen in many, if not most, chemical systems undergoing a precipitation reaction under certain conditions of concentration and in the absence of convection. Rings are formed when weakly soluble salts are produced from reaction of two soluble substances, one of which is dissolved in a gel medium. The phenomenon is most commonly seen as rings in a Petri dish or bands in a test tube; however, more complex patterns have been observed, such as dislocations of the ring structure in a Petri dish, helices, and " Saturn rings" in a test tube. Despite continuous investigation since rediscovery of the rings in 1896, the mechanism for the formation of Liesegang rings is still unclear. History The phenomenon was first noticed in 1855 by the German chemist Friedlieb Ferdinand Runge. He observed them in the course of experiments on the precipitation of reagents in blotting paper. In 1896 the German chemist Raphael E. Liesegang noted the phenomenon when he dro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liesegang Band Experiment
Liesegang rings () are a phenomenon seen in many, if not most, chemical systems undergoing a precipitation reaction under certain conditions of concentration and in the absence of convection. Rings are formed when weakly soluble salts are produced from reaction of two soluble substances, one of which is dissolved in a gel medium. The phenomenon is most commonly seen as rings in a Petri dish or bands in a test tube; however, more complex patterns have been observed, such as dislocations of the ring structure in a Petri dish, helices, and "Saturn rings" in a test tube. Despite continuous investigation since rediscovery of the rings in 1896, the mechanism for the formation of Liesegang rings is still unclear. History The phenomenon was first noticed in 1855 by the German chemist Friedlieb Ferdinand Runge. He observed them in the course of experiments on the precipitation of reagents in blotting paper. In 1896 the German chemist Raphael E. Liesegang noted the phenomenon when he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raphael Eduard Liesegang
Raphael Eduard Liesegang () (1 November 1869 – 13 November 1947) was a German chemist, photographer and entrepreneur born in Elberfeld. He is known for his work on Liesegang rings. He also helped develop the methods of capillary analysis, a precursor to paper chromatography, published a paper on the possibility of television (years before the discovery of the electron), contributed to chromosome theory, worked on properties of aerosols and gelatins, the origins of silicosis, the role of carbon dioxide in plant life and the mechanism of both black and white and colour photographic processes. The son of a painter (and eventual photographer), Liesegang longed for an artistic career but lacked the ability to draw or paint. His father would later invent a camera and photography would go on to be one of Liesegangs passions. Research into photographic emulsions led to his personal discovery of Liesegang rings. He was not the first person to observe the effect, but they bear his n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilhelm Ostwald
Friedrich Wilhelm Ostwald (; 4 April 1932) was a Baltic German chemist and German philosophy, philosopher. Ostwald is credited with being one of the founders of the field of physical chemistry, with Jacobus Henricus van 't Hoff, Walther Nernst, and Svante Arrhenius. He received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1909 for his scientific contributions to the fields of catalysis, chemical equilibria and Reaction velocity, reaction velocities. Following his 1906 retirement from academic life, Ostwald became much involved in philosophy, art, and politics. He made significant contributions to each of these fields. He has been described as a polymath. Early life and education Ostwald was born ethnically Baltic German in Riga, Russian Empire (now Latvia) to cooper (profession), master-cooper Gottfried Wilhelm Ostwald (1824–1903) and Elisabeth Leuckel (1824–1903). He was the middle child of three, born after Eugen (1851–1932) and before Gottfried (1855–1918). Ostwald developed an i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedlieb Ferdinand Runge
Friedlieb Ferdinand Runge (8 February 1794 – 25 March 1867) was a German analytical chemist. Runge identified the mydriatic (pupil dilating) effects of belladonna (deadly nightshade) extract, identified caffeine, and discovered the first coal tar dye ( aniline blue). Early life Friedlieb Ferdinand Runge was born near Hamburg on 8 February 1794. From a young age, Runge conducted chemical experiments, serendipitously identifying the mydriatic (pupil dilating) effects of belladonna (deadly nightshade) extract. Career In 1819, Runge was invited to show Goethe how belladonna caused dilation of the pupil, which Runge did, using a cat as an experimental subject. Goethe was so impressed with the demonstration that :"Nachdem Goethe mir seine größte Zufriedenheit sowol über die Erzählung des durch scheinbaren schwarzen Staar Geretteten, wie auch über das andere ausgesprochen, übergab er mir noch eine Schachtel mit Kaffeebohnen, die ein Grieche ihm als etwas Vorzügliches gesand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concentration
In chemistry, concentration is the abundance of a constituent divided by the total volume of a mixture. Several types of mathematical description can be distinguished: '' mass concentration'', ''molar concentration'', ''number concentration'', and ''volume concentration''. The concentration can refer to any kind of chemical mixture, but most frequently refers to solutes and solvents in solutions. The molar (amount) concentration has variants, such as normal concentration and osmotic concentration. Etymology The term concentration comes from the word concentrate, from the French , from con– + center, meaning “to put at the center”. Qualitative description Often in informal, non-technical language, concentration is described in a qualitative way, through the use of adjectives such as "dilute" for solutions of relatively low concentration and "concentrated" for solutions of relatively high concentration. To concentrate a solution, one must add more solute (for example, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbonates
A carbonate is a salt of carbonic acid (H2CO3), characterized by the presence of the carbonate ion, a polyatomic ion with the formula . The word ''carbonate'' may also refer to a carbonate ester, an organic compound containing the carbonate group C(=O)(O–)2. The term is also used as a verb, to describe carbonation: the process of raising the concentrations of carbonate and bicarbonate ions in water to produce carbonated water and other carbonated beverageseither by the addition of carbon dioxide gas under pressure or by dissolving carbonate or bicarbonate salts into the water. In geology and mineralogy, the term "carbonate" can refer both to carbonate minerals and carbonate rock (which is made of chiefly carbonate minerals), and both are dominated by the carbonate ion, . Carbonate minerals are extremely varied and ubiquitous in chemically precipitated sedimentary rock. The most common are calcite or calcium carbonate, CaCO3, the chief constituent of limestone (as well as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precipitation Reaction
In an aqueous solution, precipitation is the process of transforming a dissolved substance into an insoluble solid from a super-saturated solution. The solid formed is called the precipitate. In case of an inorganic chemical reaction leading to precipitation, the chemical reagent causing the solid to form is called the ''precipitant''. The clear liquid remaining above the precipitated or the centrifuged solid phase is also called the 'supernate' or 'supernatant'. The notion of precipitation can also be extended to other domains of chemistry (organic chemistry and biochemistry) and even be applied to the solid phases (''e.g.'', metallurgy and alloys) when solid impurities segregate from a solid phase. Supersaturation The precipitation of a compound may occur when its concentration exceeds its solubility. This can be due to temperature changes, solvent evaporation, or by mixing solvents. Precipitation occurs more rapidly from a strongly supersaturated solution. The formati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroxylamine Hydrochloride
Hydroxylammonium chloride is the hydrochloric acid salt of hydroxylamine. Hydroxylamine is a biological intermediate in nitrification (biological oxidation of ammonia with oxygen into nitrite) and in anammox (biological oxidation of nitrite and ammonium into dinitrogen gas) which are important in the nitrogen cycle in soil and in wastewater treatment plants. Applications Hydroxylammonium chloride is used in organic synthesis for preparation of oximes and hydroxamic acids from carboxylic acids, N- and O- substituted hydroxylamines, and addition reactions of carbon-carbon double bond. During the acetyl bromide method of extracting lignin from lignocellulosic biomass, hydroxylammonium chloride can be used to remove bromine and polybromide from the solution. In surface treatments, it is used in the preparation of anti-skinning agents, corrosion inhibitors, and cleaner additives. It is also a starting material for pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals manufacturing. In the rubber and pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper Sulfate
Copper sulfate may refer to: * Copper(II) sulfate, CuSO4, a common compound used as a fungicide and herbicide * Copper(I) sulfate Copper(I) sulfate, also known as cuprous sulfate, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Cu2 SO4. It is a white solid that has attracted little attention, in contrast to copper(II) sulfate. It is an unusual example of a copper(I) ..., Cu2SO4, which is uncommonly used * Copper(II) sulfate, CuSO4 is greenish blue Copper compounds {{Chem-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)

