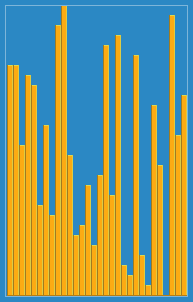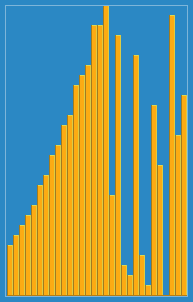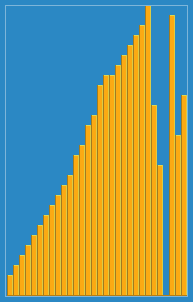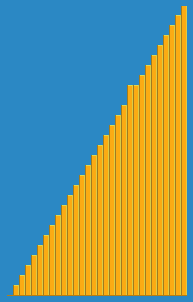|
Library Sort
Library sort, or gapped insertion sort is a sorting algorithm that uses an insertion sort, but with gaps in the array to accelerate subsequent insertions. The name comes from an analogy: Suppose a librarian were to store their books alphabetically on a long shelf, starting with the As at the left end, and continuing to the right along the shelf with no spaces between the books until the end of the Zs. If the librarian acquired a new book that belongs to the B section, once they find the correct space in the B section, they will have to move every book over, from the middle of the Bs all the way down to the Zs in order to make room for the new book. This is an insertion sort. However, if they were to leave a space after every letter, as long as there was still space after B, they would only have to move a few books to make room for the new one. This is the basic principle of the Library Sort. The algorithm was proposed by Michael A. Bender, Martín Farach-Colton, and Miguel Mostei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sorting Algorithm
In computer science, a sorting algorithm is an algorithm that puts elements of a list into an order. The most frequently used orders are numerical order and lexicographical order, and either ascending or descending. Efficient sorting is important for optimizing the efficiency of other algorithms (such as search and merge algorithms) that require input data to be in sorted lists. Sorting is also often useful for canonicalizing data and for producing human-readable output. Formally, the output of any sorting algorithm must satisfy two conditions: # The output is in monotonic order (each element is no smaller/larger than the previous element, according to the required order). # The output is a permutation (a reordering, yet retaining all of the original elements) of the input. For optimum efficiency, the input data should be stored in a data structure which allows random access rather than one that allows only sequential access. History and concepts From the beginning of c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Array Data Structure
In computer science, an array is a data structure consisting of a collection of ''elements'' ( values or variables), each identified by at least one ''array index'' or ''key''. An array is stored such that the position of each element can be computed from its index tuple by a mathematical formula. The simplest type of data structure is a linear array, also called one-dimensional array. For example, an array of ten 32-bit (4-byte) integer variables, with indices 0 through 9, may be stored as ten words at memory addresses 2000, 2004, 2008, ..., 2036, (in hexadecimal: 0x7D0, 0x7D4, 0x7D8, ..., 0x7F4) so that the element with index ''i'' has the address 2000 + (''i'' × 4). The memory address of the first element of an array is called first address, foundation address, or base address. Because the mathematical concept of a matrix can be represented as a two-dimensional grid, two-dimensional arrays are also sometimes called "matrices". In some cases the term "vector" is used in com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sorting Algorithm
In computer science, a sorting algorithm is an algorithm that puts elements of a list into an order. The most frequently used orders are numerical order and lexicographical order, and either ascending or descending. Efficient sorting is important for optimizing the efficiency of other algorithms (such as search and merge algorithms) that require input data to be in sorted lists. Sorting is also often useful for canonicalizing data and for producing human-readable output. Formally, the output of any sorting algorithm must satisfy two conditions: # The output is in monotonic order (each element is no smaller/larger than the previous element, according to the required order). # The output is a permutation (a reordering, yet retaining all of the original elements) of the input. For optimum efficiency, the input data should be stored in a data structure which allows random access rather than one that allows only sequential access. History and concepts From the beginning of c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insertion Sort
Insertion sort is a simple sorting algorithm that builds the final sorted array (or list) one item at a time by comparisons. It is much less efficient on large lists than more advanced algorithms such as quicksort, heapsort, or merge sort. However, insertion sort provides several advantages: * Simple implementation: Jon Bentley shows a three-line C/ C++ version that is five lines when optimized. * Efficient for (quite) small data sets, much like other quadratic (i.e., O(''n''2)) sorting algorithms * More efficient in practice than most other simple quadratic algorithms such as selection sort or bubble sort * Adaptive, i.e., efficient for data sets that are already substantially sorted: the time complexity is O(''kn'') when each element in the input is no more than places away from its sorted position * Stable; i.e., does not change the relative order of elements with equal keys * In-place; i.e., only requires a constant amount O(1) of additional memory space * Online; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael A
Michael may refer to: People * Michael (given name), a given name * Michael (surname), including a list of people with the surname Michael Given name "Michael" * Michael (archangel), ''first'' of God's archangels in the Jewish, Christian and Islamic religions * Michael (bishop elect), English 13th-century Bishop of Hereford elect * Michael (Khoroshy) (1885–1977), cleric of the Ukrainian Orthodox Church of Canada * Michael Donnellan (1915–1985), Irish-born London fashion designer, often referred to simply as "Michael" * Michael (footballer, born 1982), Brazilian footballer * Michael (footballer, born 1983), Brazilian footballer * Michael (footballer, born 1993), Brazilian footballer * Michael (footballer, born February 1996), Brazilian footballer * Michael (footballer, born March 1996), Brazilian footballer * Michael (footballer, born 1999), Brazilian footballer Rulers =Byzantine emperors= * Michael I Rangabe (d. 844), married the daughter of Emperor Nikephoro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martín Farach-Colton
Martin Farach-Colton is an American computer scientist, known for his work in streaming algorithms, suffix tree construction, pattern matching in compressed data, cache-oblivious algorithms, and lowest common ancestor data structures. He is a Distinguished Professor of computer science at Rutgers University, and a co-founder of storage technology startup company Tokutek.. Early life and education Farach-Colton is of Argentine descent, and grew up in South Carolina. While attending medical school, he met his future husband, with whom he now has twin children. He obtained his M.D. in 1988 from the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine and his Ph.D. in computer science in 1991 from the University of Maryland, College Park under the supervision of Amihood Amir. Research contributions After completing his Ph.D., he went on to work at Google and co-founded Tokutek. He was program chair of the 14th ACM-SIAM Symposium on Discrete Algorithms (SODA 2003). The cache-oblivious B-tree data st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miguel Mosteiro
--> Miguel is a given name and surname, the Portuguese and Spanish form of the Hebrew name Michael. It may refer to: Places *Pedro Miguel, a parish in the municipality of Horta and the island of Faial in the Azores Islands *São Miguel (other), various locations in Azores, Portugal, Brazil and Cape Verde People * Miguel (surname) Arts, entertainment, and media *Miguel (singer) (born 1985), Miguel Jontel Pimentel, American recording artist *Miguel Bosé (born 1956), Spanish pop new wave musician and actor *Miguel Calderón (born 1971), artist and writer *Miguel Cancel (born 1968), former American singer *Miguel Córcega (1929–2008), Mexican actor and director *Miguel de Cervantes (1547–1616), Spanish author *Miguel Delibes (1920–2010), Spanish novelist *Miguel Ferrer (1955–2017), American actor *Miguel Galván (1957–2008), Mexican actor *Miguel Gómez (photographer) (born 1974), Colombian / American photographer. *Miguel Ángel Landa (born 1936), Venezuelan ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comparison Sort
A comparison sort is a type of sorting algorithm that only reads the list elements through a single abstract comparison operation (often a "less than or equal to" operator or a three-way comparison) that determines which of two elements should occur first in the final sorted list. The only requirement is that the operator forms a total preorder over the data, with: # if ''a'' ≤ ''b'' and ''b'' ≤ ''c'' then ''a'' ≤ ''c'' (transitivity) # for all ''a'' and ''b'', ''a'' ≤ ''b'' or ''b'' ≤ ''a'' (connexity). It is possible that both ''a'' ≤ ''b'' and ''b'' ≤ ''a''; in this case either may come first in the sorted list. In a stable sort, the input order determines the sorted order in this case. A metaphor for thinking about comparison sorts is that someone has a set of unlabelled weights and a balance scale. Their goal is to line up the weights in order by their weight without any information except that obtained by placing two weights on the scale and seeing which on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quicksort
Quicksort is an efficient, general-purpose sorting algorithm. Quicksort was developed by British computer scientist Tony Hoare in 1959 and published in 1961, it is still a commonly used algorithm for sorting. Overall, it is slightly faster than merge sort and heapsort for randomized data, particularly on larger distributions. Quicksort is a divide-and-conquer algorithm. It works by selecting a 'pivot' element from the array and partitioning the other elements into two sub-arrays, according to whether they are less than or greater than the pivot. For this reason, it is sometimes called partition-exchange sort. The sub-arrays are then sorted recursively. This can be done in-place, requiring small additional amounts of memory to perform the sorting. Quicksort is a comparison sort, meaning that it can sort items of any type for which a "less-than" relation (formally, a total order) is defined. Most implementations of quicksort are not stable, meaning that the relative order o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Online Algorithm
In computer science, an online algorithm is one that can process its input piece-by-piece in a serial fashion, i.e., in the order that the input is fed to the algorithm, without having the entire input available from the start. In contrast, an offline algorithm is given the whole problem data from the beginning and is required to output an answer which solves the problem at hand. In operations research, the area in which online algorithms are developed is called online optimization. As an example, consider the sorting algorithms selection sort and insertion sort: selection sort repeatedly selects the minimum element from the unsorted remainder and places it at the front, which requires access to the entire input; it is thus an offline algorithm. On the other hand, insertion sort considers one input element per iteration and produces a partial solution without considering future elements. Thus insertion sort is an online algorithm. Note that the final result of an insertion sort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mergesort
In computer science, merge sort (also commonly spelled as mergesort) is an efficient, general-purpose, and comparison-based sorting algorithm. Most implementations produce a stable sort, which means that the order of equal elements is the same in the input and output. Merge sort is a divide-and-conquer algorithm that was invented by John von Neumann in 1945. A detailed description and analysis of bottom-up merge sort appeared in a report by Goldstine and von Neumann as early as 1948. Algorithm Conceptually, a merge sort works as follows: #Divide the unsorted list into ''n'' sublists, each containing one element (a list of one element is considered sorted). #Repeatedly merge sublists to produce new sorted sublists until there is only one sublist remaining. This will be the sorted list. Top-down implementation Example C-like code using indices for top-down merge sort algorithm that recursively splits the list (called ''runs'' in this example) into sublists until sublist size ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary Search
In computer science, binary search, also known as half-interval search, logarithmic search, or binary chop, is a search algorithm that finds the position of a target value within a sorted array. Binary search compares the target value to the middle element of the array. If they are not equal, the half in which the target cannot lie is eliminated and the search continues on the remaining half, again taking the middle element to compare to the target value, and repeating this until the target value is found. If the search ends with the remaining half being empty, the target is not in the array. Binary search runs in logarithmic time in the worst case, making O(\log n) comparisons, where n is the number of elements in the array. Binary search is faster than linear search except for small arrays. However, the array must be sorted first to be able to apply binary search. There are specialized data structures designed for fast searching, such as hash tables, that can be searched ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |