|
Libertatea (Pančevo)
''Libertatea'' (lit. ''Liberty'') is leading Romanian language weekly newspaper in Serbia published in Pančevo (), in the autonomous province of Vojvodina. The newspaper was established in 1945 after the end of World War II in Yugoslavia. While originally established by the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina the region transferred all rights and responsibilities to the National Council of the Romanian National Minority in 2004. History The newspaper was established in 1945 while the transfer of rights happened in 2004. In 2018 newspaper was awarded the Ordinul "Meritul Cultural" by the President of Romania Klaus Iohannis. 2020 management board dismissal controversy In February 2020 telephone session the ''National Council of the Romanian National Minority'' dismissed the Management Board and appointed new members of that body. The 20 staff members of the newspaper's publishing house (including the director Niku Čobanu) strongly condemned the action of the Romanian National Cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Current Affairs (news Format)
Current affairs is a genre of broadcast journalism in which major news stories are discussed at length in a timely manner. This differs from regular News broadcasting, news broadcasts that place emphasis on news reports presented for simple presentation as soon as possible, often with a minimum of analysis. It is also different from the news magazine show format in that events are discussed immediately. The UK's BBC programmes, such as ''This World (TV series), This World'', ''Panorama (TV series), Panorama'', ''Real Story'', ''BBC Scotland Investigates'', ''Spotlight (NI), Spotlight'', ''Week In Week Out'', and ''Inside Out (2002 TV programme), Inside Out'', fit the definition. In Canada, CBC Radio produces a number of current affairs shows both nationally, such as ''The Current (radio program), The Current'' and ''As It Happens'', as well as regionally with morning current affairs shows such as ''Information Morning'' — a focus the radio network developed in the 1970s as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
League Of Social Democrats Of Vojvodina
The League of Social Democrats of Vojvodina (, abbr. LSV) is an autonomist political party in Serbia. Its current leader is Bojan Kostreš, who succeeded Nenad Čanak. They're colloquially known as ''ligaši'' (Leaguemen). History The party was founded by Nenad Čanak on 14 July 1990 in Novi Sad. At the First Party Congress, the LSV adopted the party program, which defined following principles of the party: liberty, equality, justice, solidarity, and publicity. At the Second Congress, which was held in July 1997, the LSV adopted a new statute.''Enciklopedija Novog Sada'', knjiga 13, Novi Sad, 1999, pages 40–41. In the first years of its existence, the party's activities were mainly directed towards organisation of anti-war actions. Together with other parties, it organised anti-war demonstrations in Vojvodina and publicly opposed mobilisation of Vojvodina citizens for the front lines in Croatia and Bosnia and Herzegovina. Ideology LSV is positioned on the centre-left o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Publications With Year Of Establishment Missing
To publish is to make content available to the general public.Berne Convention, article 3(3) URL last accessed 2025-05-23.Universal Copyright Convention, Geneva text (1952), article VI . URL last accessed 2010-05-10. While specific use of the term may vary among countries, it is usually applied to , images, or other [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newspapers Published In Serbia
A newspaper is a periodical publication containing written information about current events and is often typed in black ink with a white or gray background. Newspapers can cover a wide variety of fields such as politics, business, sports, art, and science. They often include materials such as opinion columns, weather forecasts, reviews of local services, obituaries, birth notices, crosswords, editorial cartoons, comic strips, and advice columns. Most newspapers are businesses, and they pay their expenses with a mixture of subscription revenue, newsstand sales, and advertising revenue. The journalism organizations that publish newspapers are themselves often metonymically called newspapers. Newspapers have traditionally been published in print (usually on cheap, low-grade paper called newsprint). However, today most newspapers are also published on websites as online newspapers, and some have even abandoned their print versions entirely. Newspapers developed in the 17t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanian-language Newspapers
Romanian (obsolete spelling: Roumanian; , or , ) is the official and main language of Romania and Moldova. Romanian is part of the Eastern Romance languages, Eastern Romance sub-branch of Romance languages, a linguistic group that evolved from several dialects of Vulgar Latin which separated from the Italo-Western languages, Western Romance languages in the course of the period from the 5th to the 8th centuries. To distinguish it within the Eastern Romance languages, in comparative linguistics it is called ''#Dialects, Daco-Romanian'' as opposed to its closest relatives, Aromanian language, Aromanian, Megleno-Romanian language, Megleno-Romanian, and Istro-Romanian language, Istro-Romanian. It is also spoken as a minority language by stable communities in the countries surrounding Romania (Romanians in Bulgaria, Bulgaria, Romanians in Hungary, Hungary, Romanians in Serbia, Serbia and Romanians in Ukraine, Ukraine), and by the large Romanian diaspora. In total, it is spoken by 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanians In Serbia
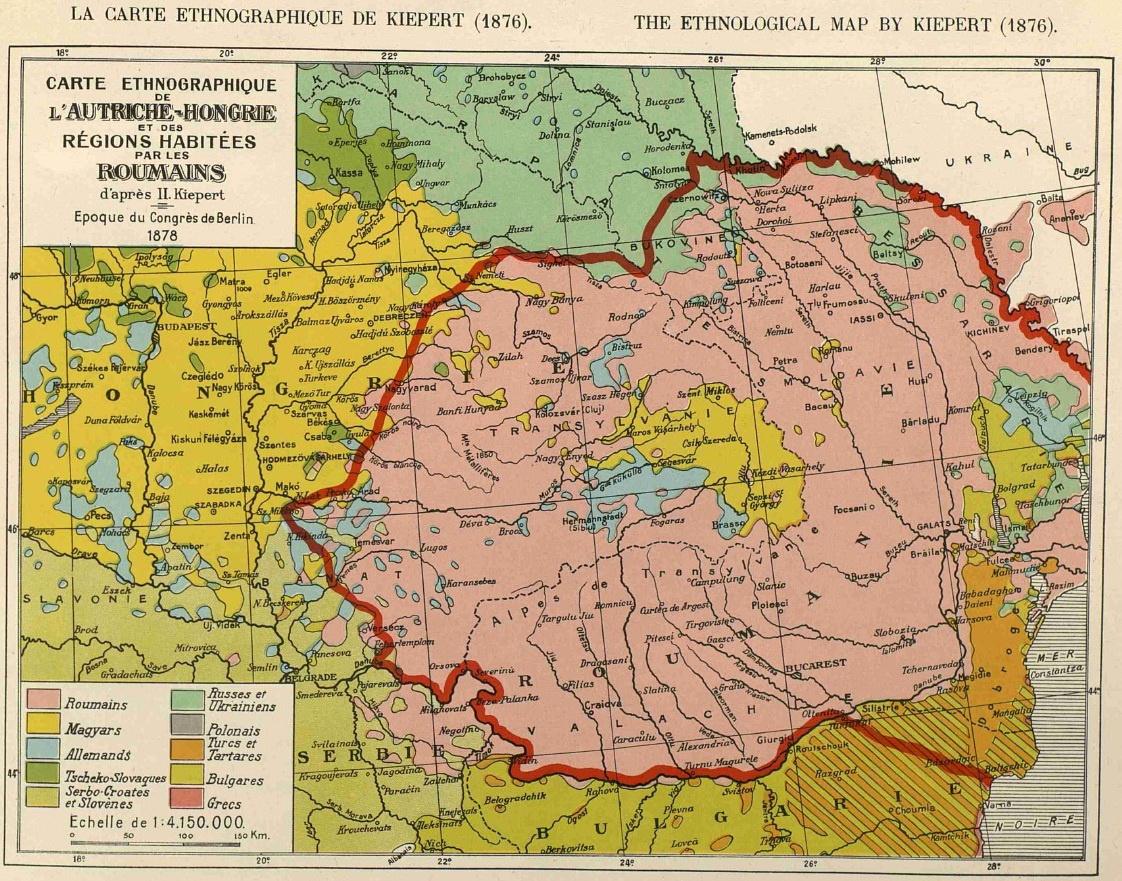
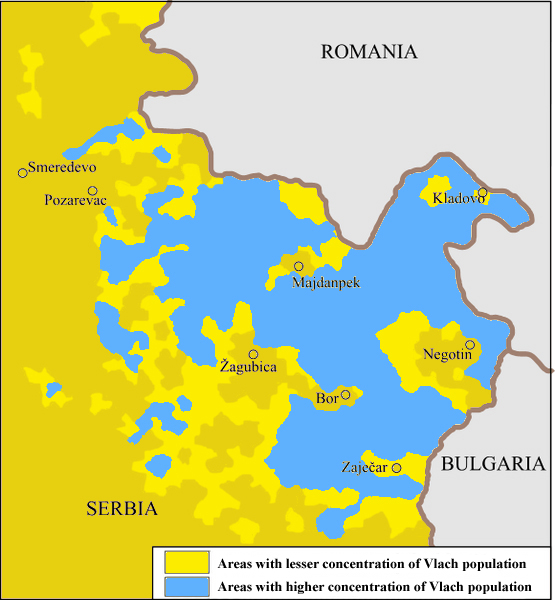
Romanians in Serbia (; ) are a recognized national minority in Serbia. The total number of self-declared Romanians according to the 2022 census was 23,044, while 21,013 people declared themselves Vlachs; there are differing views among some of the Vlachs over whether they should be regarded as Romanians or as members of a distinctive nationality. Declared Romanians are mostly concentrated in Banat, in Vojvodina, while declared Vlachs are mostly concentrated in the Timok Valley, in eastern Serbia. History As Daco-Romanian-speakers, the Vlachs have a connection to Roman heritage in Serbia. An area inhabited with Thracian Tribalians, came under Roman control in 75 BC, when Roman province Moesia was established. Following Roman withdrawal from the province of Dacia at the end of the 3rd century, the name of the Roman region was changed to Dacia Aureliana, and (later Dacia Ripensis) spread over most of what is now called Serbia and Bulgaria. Roman military presence in the region p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magyar Szó
''Magyar Szó'' (, lit. ''Hungarian Word'') is a Hungarian-language daily newspaper in Vojvodina, Serbia. History It was founded in 1944, with the purpose of serving as the information source for the Hungarian minority of Vojvodina. It is published in Novi Sad. Magyar Szó is considered the main ethnic Hungarian media in Serbia and in the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina. To begin with, the newspaper was called Szabad Vajdaság, but the name was changed to Magyar Szó in 1945. The newspaper is a member of MIDAS ( European Association of Daily Newspapers in Minority and Regional Languages). Newspapers with same name There was and is a number of newspapers that bare the same name. Here is a partial list of them: * ''Magyar Szó (1900–1907)'' – a daily newspaper published in Budapest at the beginning of the 20th century; * ''Magyar Szó (1919–1920)'' – belletristic weekly magazine, published in Oradea; * ''Magyar Szó (1929–1937)'' – a daily newspaper, published in O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanian Language In Serbia
The Romanian language is widely spoken in Serbia. This country hosts large native Romanian-speaking populations, which can be divided into the ethnic Romanians in the autonomous region of Vojvodina and the Romanian/Vlachs of the Timok Valley, a geographical region in Central Serbia. The former speak the Banat Romanian, identify as Romanians and have full rights within the autonomous region. Romanian is one of the six officially recognized languages of Vojvodina. Romanian/Vlachs speak archaic varieties of the Banat and Oltenian Romanian. Some of the members of community do not identify as Romanians and their language is not recognized as Romanian within Serbia. A "Vlach language" has gone under attempted standardization in the country, using a Cyrillic alphabet. This has been criticized in Romania, and attempts to bring Romanian-language resources and education to the Timok Vlachs have been blocked by the Serbian authorities. In January 2020, the Romanian Academy and the Academy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanians Of Serbia
Romanians in Serbia (; ) are a recognized national minority in Serbia. The total number of self-declared Romanians according to the 2022 census was 23,044, while 21,013 people declared themselves Vlachs; there are differing views among some of the Vlachs over whether they should be regarded as Romanians or as members of a distinctive nationality. Declared Romanians are mostly concentrated in Banat, in Vojvodina, while declared Vlachs are mostly concentrated in the Timok Valley, in eastern Serbia. History As Daco-Romanian-speakers, the Vlachs have a connection to Roman heritage in Serbia. An area inhabited with Thracian Tribalians, came under Roman control in 75 BC, when Roman province Moesia was established. Following Roman withdrawal from the province of Dacia at the end of the 3rd century, the name of the Roman region was changed to Dacia Aureliana, and (later Dacia Ripensis) spread over most of what is now called Serbia and Bulgaria. Roman military presence in the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alliance For Serbia
The Alliance for Serbia ( sr-cyrl, Савез за Србију, Savez za Srbiju, abbr. SZS) was an opposition alliance of List of political parties in Serbia, political parties in Serbia that was founded in September 2018. The alliance boycotted the 2020 Serbian parliamentary election, 2020 parliamentary election, due to claims that the elections would not be held under fair conditions. The alliance officially dissolved in August 2020, as the new alliance called United Opposition of Serbia was formed. History Coalition was founded by Dragan Đilas in September 2018. The political background of alliance members is diverse, with both left-wing, liberal, moderate, right-wing and far-right factions voicing opposition to the government. It is composed of the Democratic Party (Serbia), Democratic Party, Dveri, People's Party (Serbia, 2017), People's Party, Party of Freedom and Justice, as well some minor and local anti-government parties and organisations. They have called for the insti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serbian Progressive Party
The Serbian Progressive Party (, SNS) is a major populist, catch-all party, catch-all List of political parties in Serbia, political party in Serbia. It has been the Ruling party, ruling party since 2012. Miloš Vučević, the former prime minister of Serbia, has served as its president since 2023. Founded by Tomislav Nikolić and Aleksandar Vučić in 2008 as a split from the Serbian Radical Party, SNS served in opposition to the Democratic Party (Serbia), Democratic Party until 2012. SNS gained prominence and became the largest opposition party due to their anti-corruption platform and the protests in 2011 at which they demanded early elections. In 2012, Nikolić 2012 Serbian presidential election, was elected president of Serbia and succeeded by Vučić as president of SNS. A coalition government led by SNS and Socialist Party of Serbia (SPS) was also formed. Vučić became prime minister in 2014 Serbian parliamentary election, 2014 while SNS became the largest party in Bel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klaus Iohannis
Klaus Werner Iohannis (; ; born 13 June 1959) is a Romanian politician, physicist, and former teacher who served as the fifth president of Romania from 2014 until his resignation in 2025. Prior to entering Politics of Romania, national politics, Iohannis was a physics teacher at the Samuel von Brukenthal National College in his native Sibiu where he eventually served as mayor from 2000 to 2014 before ascending to the presidency. Iohannis was first elected the mayor of the Romanian town of Sibiu in 2000 Romanian local elections, 2000, on behalf of the Democratic Forum of Germans in Romania (FDGR/DFDR). Although the Transylvanian Saxons, Transylvanian Saxon population of Sibiu had declined to a tiny minority by the early 2000s, he won a surprise victory and was re-elected by landslides in 2004 Romanian local elections, 2004, 2008 Romanian local elections, 2008, and 2012 Romanian local elections, 2012. He is credited with turning his home town into one of Romania's most popular tour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |