|
Libbie H. Hyman
Libbie Henrietta Hyman (December 6, 1888 – August 3, 1969), was a U.S. zoologist. She wrote numerous works on invertebrate zoology and the widely used ''A Laboratory Manual for Comparative Vertebrate Anatomy'' (1922, revised in 1942). Life Born in Des Moines, Iowa, she was the daughter of Joseph Hyman and Sabina ('Bena') Neumann. Hyman's father, a Polish/Russian Jew, adopted the surname when he immigrated to the United States as a youth. He successively owned clothing stores in Des Moines, in Sioux Falls, South Dakota, and in Fort Dodge, Iowa, but the family's resources were limited. Hyman attended public schools in Fort Dodge. At home she was required to do much of the housework. She enjoyed reading, especially books by Charles Dickens in her father's small den, and she took a strong interest in flowers, which she learned to classify with a copy of Asa Gray's ''Elements of Botany''. She also collected butterflies and moths and later wrote, "I believe my interest in nature is pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Des Moines, Iowa
Des Moines () is the capital and the most populous city in the U.S. state of Iowa. It is also the county seat of Polk County. A small part of the city extends into Warren County. It was incorporated on September 22, 1851, as Fort Des Moines, which was shortened to "Des Moines" in 1857. It is located on, and named after, the Des Moines River, which likely was adapted from the early French name, ''Rivière des Moines,'' meaning "River of the Monks". The city's population was 214,133 as of the 2020 census. The six-county metropolitan area is ranked 83rd in terms of population in the United States with 699,292 residents according to the 2019 estimate by the United States Census Bureau, and is the largest metropolitan area fully located within the state. Des Moines is a major center of the US insurance industry and has a sizable financial services and publishing business base. The city was credited as the "number one spot for U.S. insurance companies" in a ''Business Wire'' articl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Manning Child
Charles Manning Child (February 2, 1869 – December 19, 1954) was an American zoologist noted for his work on regeneration at the University of Chicago. Early life Child was born on February 2, 1869, in Ypsilanti, Michigan, to Charles Chauncy Child and Mary Elizabeth (née Manning) Child. He was the only surviving child to the couple. Growing up on a family farm in Higganum, Connecticut, Child enjoyed reading. After graduating from elementary school in 1882, Child attended Middletown High School in Middletown, Connecticut, until his graduation in 1886. Career Child was accepted to Wesleyan University in Middletown. In 1890 he graduated Wesleyan with a Bachelor of Philosophy and in 1892 he received a Master of Science degree from the same university, having served as a graduate assistant in biology at Wesleyan from 1890 to 1892. Working under Rudolf Leuckart at the University of Leipzig, Child graduated with a Doctor of Philosophy in 1894. Upon returning to the United ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ctenophora
Ctenophora (; ctenophore ; ) comprise a phylum of marine invertebrates, commonly known as comb jellies, that inhabit sea waters worldwide. They are notable for the groups of cilia they use for swimming (commonly referred to as "combs"), and they are the largest animals to swim with the help of cilia. Depending on the species, adult ctenophores range from a few millimeters to in size. Only 100 to 150 species have been validated, and possibly another 25 have not been fully described and named. The textbook examples are cydippids with egg-shaped bodies and a pair of retractable tentacles fringed with tentilla ("little tentacles") that are covered with colloblasts, sticky cells that capture prey. Their bodies consist of a mass of jelly, with a layer two cells thick on the outside, and another lining the internal cavity. The phylum has a wide range of body forms, including the egg-shaped cydippids with retractable tentacles that capture prey, the flat generally combless plat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protozoa
Protozoa (singular: protozoan or protozoon; alternative plural: protozoans) are a group of single-celled eukaryotes, either free-living or parasitic, that feed on organic matter such as other microorganisms or organic tissues and debris. Historically, protozoans were regarded as "one-celled animals", because they often possess animal-like behaviours, such as motility and predation, and lack a cell wall, as found in plants and many algae. When first introduced by Georg Goldfuss (originally spelled Goldfuß) in 1818, the taxon Protozoa was erected as a class within the Animalia, with the word 'protozoa' meaning "first animals". In later classification schemes it was elevated to a variety of higher ranks, including phylum, subkingdom and kingdom, and sometimes included within Protoctista or Protista. The approach of classifying Protozoa within the context of Animalia was widespread in the 19th and early 20th century, but not universal. By the 1970s, it became usual to require th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friday Harbor Laboratories
Friday Harbor Laboratories (FHL), is a marine biology field station of the University of Washington, located in Friday Harbor, San Juan Island, Washington, United States. Friday Harbor Labs is known for its intensive summer classes offered to competitive graduate students from around the world in fields of marine biology and other marine sciences. Autumn and spring academic terms include courses designed for advanced undergraduates as well as graduate students; most spring and fall classes run 10 weeks and feature an original research component. In addition to serving students, Friday Harbor Laboratories has a small resident scientific staff and offers year-round laboratory, library, and housing accommodations for visiting researchers and their families. Research areas include marine algae, marine conservation biology, marine invertebrate zoology, comparative invertebrate embryology, experimental and field approaches in biology and paleontology, functional morphology and ecology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Biological Laboratory
The Marine Biological Laboratory (MBL) is an international center for research and education in biological and environmental science. Founded in Woods Hole, Massachusetts, in 1888, the MBL is a private, nonprofit institution that was independent for most of its history, but became officially affiliated with the University of Chicago on July 1, 2013. It also collaborates with numerous other institutions. As of 2022, 60 Nobel Prize winners have been affiliated with MBL as students, faculty members or researchers. In addition since 1960, there have been, 137 Howard Hughes Medical Institute investigators, early career scientists, international researchers, and professors; 306 members of the National Academy of Sciences; and 236 Members of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences who have been affiliated with the lab. History 19th century The Marine Biological Laboratory grew from the vision of several Bostonians and Spencer Fullerton Baird, the United States' first Fish Commiss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bermuda Biological Station For Research
The Bermuda Institute of Ocean Sciences (known as BIOS) is an independent, non-profit marine science and education institute located in Ferry Reach, St. George's, Bermuda. The institute, founded in 1903 as the Bermuda Biological Station, hosts a full-time faculty of oceanographers, biologists, and environmental scientists, graduate and undergraduate students, K-12 groups, and Road Scholar (formerly Elderhostel) groups. BIOS's strategic mid-Atlantic Ocean location has at its doorstep a diverse marine environment, with close proximity to deep ocean as well as coral reef and near shore habitats. Prior to 5 September 2006, BIOS was known as the Bermuda Biological Station for Research (BBSR). History Founded in 1903 and incorporated in New York as a US not-for-profit institution in 1926, in its initial years BIOS was a seasonal field station for visiting zoologists and biologists to take advantage of Bermuda's diverse marine environment. After the Second World War, BIOS beca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Language
Russian (russian: русский язык, russkij jazyk, link=no, ) is an East Slavic languages, East Slavic language mainly spoken in Russia. It is the First language, native language of the Russians, and belongs to the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. It is one of four living East Slavic languages, and is also a part of the larger Balto-Slavic languages. Besides Russia itself, Russian is an official language in Belarus, Kazakhstan, and Kyrgyzstan, and is used widely as a lingua franca throughout Ukraine, the Caucasus, Central Asia, and to some extent in the Baltic states. It was the De facto#National languages, ''de facto'' language of the former Soviet Union,1977 Soviet Constitution, Constitution and Fundamental Law of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics, 1977: Section II, Chapter 6, Article 36 and continues to be used in public life with varying proficiency in all of the post-Soviet states. Russian has over 258 million total speakers worldwide. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
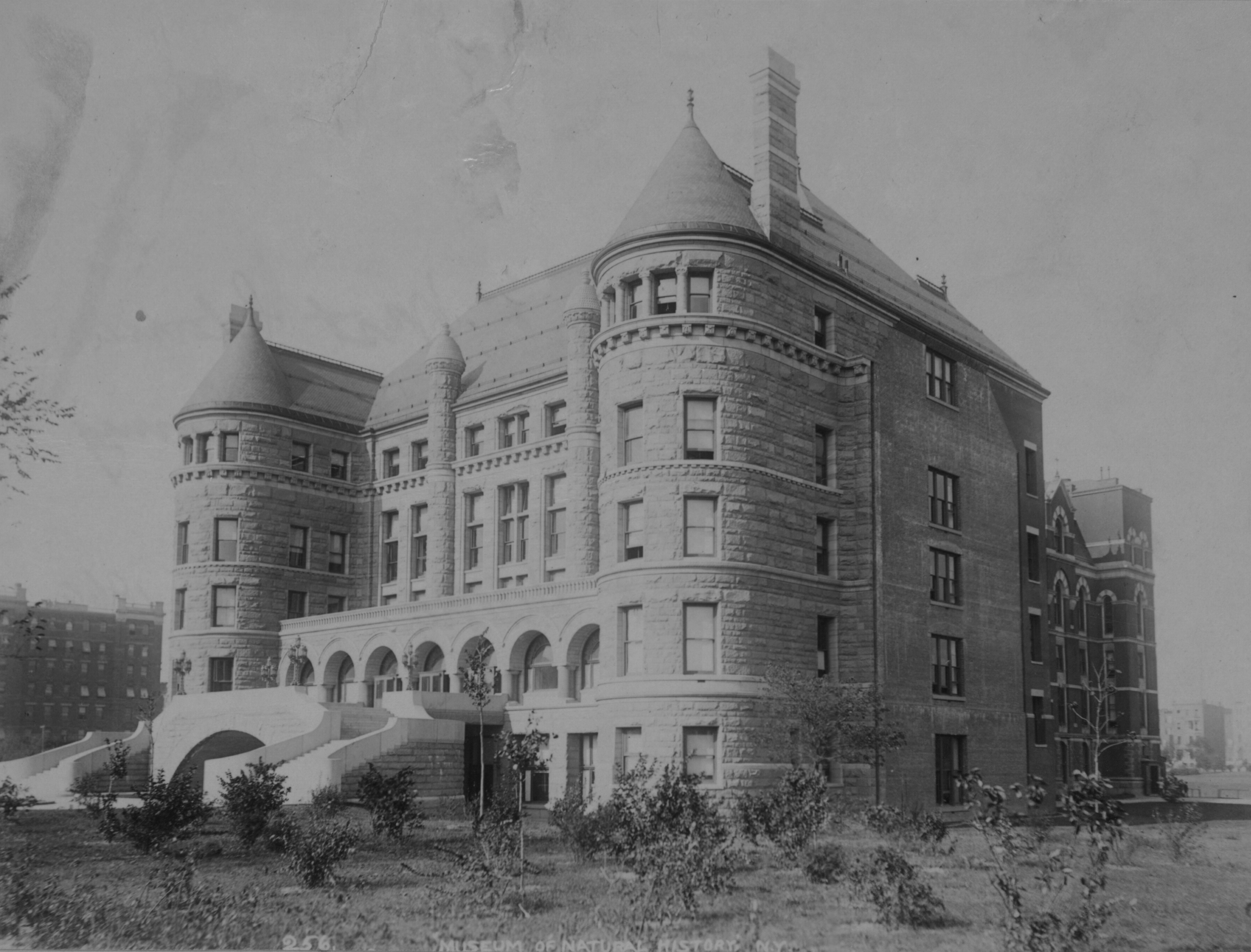
American Museum Of Natural History
The American Museum of Natural History (abbreviated as AMNH) is a natural history museum on the Upper West Side of Manhattan in New York City. In Theodore Roosevelt Park, across the street from Central Park, the museum complex comprises 26 interconnected buildings housing 45 permanent exhibition halls, in addition to a planetarium and a library. The museum collections contain over 34 million specimens of plants, animals, fossils, minerals, rocks, meteorites, human remains, and human cultural artifacts, as well as specialized collections for frozen tissue and genomic and astrophysical data, of which only a small fraction can be displayed at any given time. The museum occupies more than . AMNH has a full-time scientific staff of 225, sponsors over 120 special field expeditions each year, and averages about five million visits annually. The AMNH is a private 501(c)(3) organization. Its mission statement is: "To discover, interpret, and disseminate—through scientific research and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the List of United States cities by population density, most densely populated major city in the United States, and is more than twice as populous as second-place Los Angeles. New York City lies at the southern tip of New York (state), New York State, and constitutes the geographical and demographic center of both the Northeast megalopolis and the New York metropolitan area, the largest metropolitan area in the world by urban area, urban landmass. With over 20.1 million people in its metropolitan statistical area and 23.5 million in its combined statistical area as of 2020, New York is one of the world's most populous Megacity, megacities, and over 58 million people live within of the city. New York City is a global city, global Culture of New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydra (genus)
''Hydra'' ( ) is a genus of small, freshwater organisms of the phylum Cnidaria and class Hydrozoa. They are native to the temperate and tropical regions. The genus was named by Linnaeus in 1758 after the Hydra, which was the many-headed beast defeated by Hercules as when the animal had a part severed, it would regenerate much like the hydra’s heads. Biologists are especially interested in ''Hydra'' because of their regenerative ability; they do not appear to die of old age, or to age at all. Morphology ''Hydra'' has a tubular, radially symmetric body up to long when extended, secured by a simple adhesive foot known as the basal disc. Gland cells in the basal disc secrete a sticky fluid that accounts for its adhesive properties. At the free end of the body is a mouth opening surrounded by one to twelve thin, mobile tentacles. Each tentacle, or cnida (plural: cnidae), is clothed with highly specialised stinging cells called cnidocytes. Cnidocytes contain specialized s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turbellaria
The Turbellaria are one of the traditional sub-divisions of the phylum Platyhelminthes (flatworms), and include all the sub-groups that are not exclusively parasitic. There are about 4,500 species, which range from to large freshwater forms more than long or terrestrial species like ''Bipalium kewense'' which can reach in length. All the larger forms are flat with ribbon-like or leaf-like shapes, since their lack of respiratory system, respiratory and circulatory system, circulatory systems means that they have to rely on diffusion for internal transport of metabolites. However, many of the smaller forms are round in cross section. Most are predators, and all live in water or in moist terrestrial environments. Most forms reproduce sexual reproduction, sexually and with few exceptions all are hermaphrodites, simultaneous hermaphrodites. The Acoelomorpha and the genus ''Xenoturbella'' were formerly included in the Turbellaria, but are no longer regarded as Platyhelminthes. All th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpeg)





