|
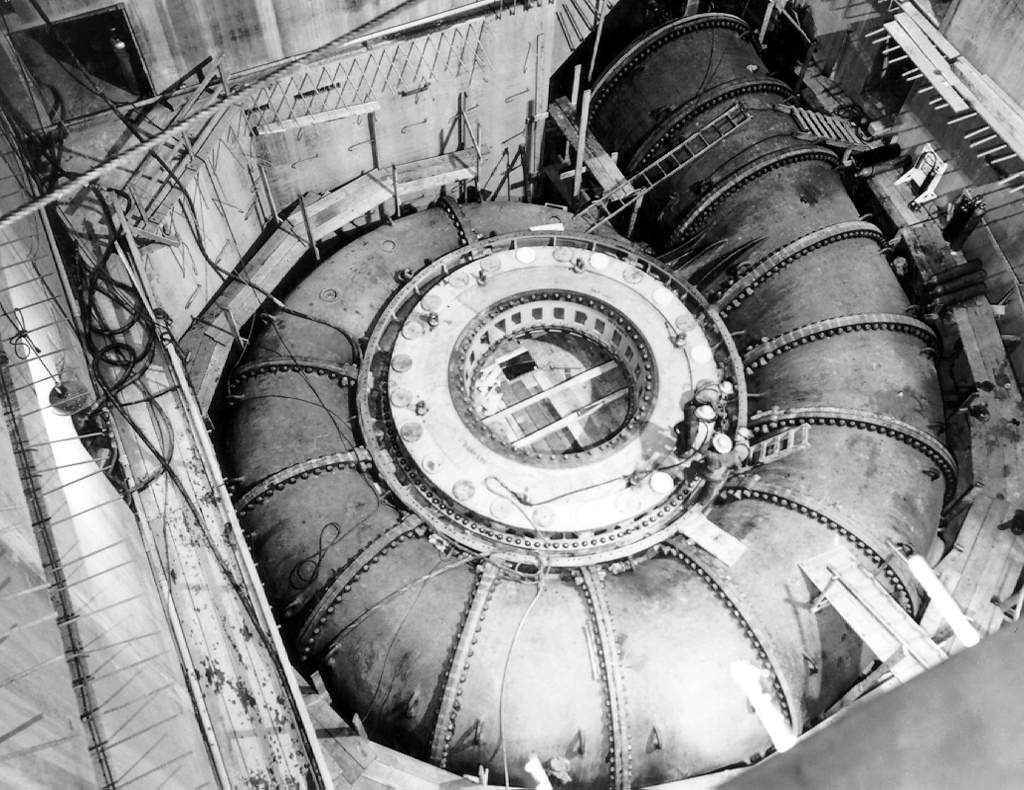
Lianhua Dam
The Lianhua Dam is a concrete-face rock-fill dam on the Mudan River in Linkou County of Heilongjiang Province, China. It is located about north of Mudanjiang. The tall dam serves several purposes to include hydroelectric power generation, flood control and water supply for irrigation. The dam withholds a large capacity reservoir and supports a 550 MW power station. Construction on the dam began in November 1992 and its first 137.5 MW Francis turbine-generator was operational in December 1996. Two more generators were commissioned on 12 December 1997 and the remaining generator was commissioned on 28 September 1998. It is the first large modern water conservancy project in Heilongjiang. The dam's reservoir displaced 40,000 people and will serve as the lower reservoir for the Huanggou Pumped Storage Power Station when it is complete. See also *List of dams and reservoirs in China Dams and reservoirs in China are numerous and have had a profound effect on the country's devel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linkou County
Linkou County () is a county in the southeast of Heilongjiang Province, China. It is under the jurisdiction of the prefecture-level city of Mudanjiang. Administrative divisions Linkou County is divided into 11 towns. ;11 towns * Linkou (), Gucheng (), Diaoling (), Zhujia (), Liushu (), Sandaotong (), Longzhua (), Lianhua (), Qingshan (), Jiantang Jiantang or Gyaitang is a town in northern Yunnan, seat of Shangri-La County and Dêqên Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture. Climate Jiantang has a subtropical highland climate An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate, is the humid t ... () and Kuishan () Demographics The population of the district was in 2020. National Population Statistics Materials by County and City - 2010 Period, ''in'/ref> Climate References External links www.hljmzt.gov.cn/ Administrative subdivisions of Heilongjiang Mudanjiang {{Heilongjiang-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow Crop, crops, Landscape plant, landscape plants, and Lawn, lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,000 years and has been developed by many cultures around the world. Irrigation helps to grow crops, maintain landscapes, and revegetation, revegetate disturbed soils in dry areas and during times of below-average rainfall. In addition to these uses, irrigation is also employed to protect crops from frost, suppress weed growth in grain fields, and prevent soil consolidation. It is also used to cool livestock, reduce dust, dispose of sewage, and support mining operations. Drainage, which involves the removal of surface and sub-surface water from a given location, is often studied in conjunction with irrigation. There are several methods of irrigation that differ in how water is supplied to plants. Surface irrigation, also known as gravity irri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Infrastructure Completed In 1998
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek: ἐνέργεια, ''enérgeia'', “activity”) is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat and light. Energy is a conserved quantity—the law of conservation of energy states that energy can be converted in form, but not created or destroyed. The unit of measurement for energy in the International System of Units (SI) is the joule (J). Common forms of energy include the kinetic energy of a moving object, the potential energy stored by an object (for instance due to its position in a field), the elastic energy stored in a solid object, chemical energy associated with chemical reactions, the radiant energy carried by electromagnetic radiation, and the internal energy contained within a thermodynamic system. All living organisms constantly take in and release energy. Due to mass–energy equivalence, any object that has mass whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dams Completed In 1996
A dam is a barrier that stops or restricts the flow of surface water or underground streams. Reservoirs created by dams not only suppress floods but also provide water for activities such as irrigation, human consumption, industrial use, aquaculture, and navigability. Hydropower is often used in conjunction with dams to generate electricity. A dam can also be used to collect or store water which can be evenly distributed between locations. Dams generally serve the primary purpose of retaining water, while other structures such as floodgates or levees (also known as dikes) are used to manage or prevent water flow into specific land regions. The earliest known dam is the Jawa Dam in Jordan, dating to 3,000 BC. The word ''dam'' can be traced back to Middle English, and before that, from Middle Dutch, as seen in the names of many old cities, such as Amsterdam and Rotterdam. History Ancient dams Early dam building took place in Mesopotamia and the Middle East. Dams were used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dams In China
Dams and reservoirs in China are numerous and have had a profound effect on the country's development and people. According to the World Commission on Dams in 2000, there were 22,104 dams over the height of operating in China. Of the world's total large dams, China accounts for the most – of them; of which are used for irrigation. Accordingly, the oldest in China still in use belongs to the Dujiangyan Irrigation System which dates back to 256 BC. In 2005, there were over 80,000 reservoirs in the country and over 4,800 dams completed or under construction that stands at or exceed in height. As of 2007, China is also the world's leader in the construction of large dams; followed by Turkey, and Japan in third. The tallest dam in China is the Jinping-I Dam at , an arch dam, which is also the tallest dam in the world. The largest reservoir is created by the Three Gorges Dam, which stores 39.3 billion m3 (31,900,000 acre feet) of water and has a surface area of . Three Gorges is al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Dams And Reservoirs In China
Dams and reservoirs in China are numerous and have had a profound effect on the country's development and people. According to the World Commission on Dams in 2000, there were 22,104 dams over the height of operating in China. Of the world's total large dams, China accounts for the most – of them; of which are used for irrigation. Accordingly, the oldest in China still in use belongs to the Dujiangyan Irrigation System which dates back to 256 BC. In 2005, there were over 80,000 reservoirs in the country and over 4,800 dams completed or under construction that stands at or exceed in height. As of 2007, China is also the world's leader in the construction of large dams; followed by Turkey, and Japan in third. The tallest dam in China is the Jinping-I Dam at , an arch dam, which is also the tallest dam in the world. The largest reservoir is created by the Three Gorges Dam, which stores 39.3 billion m3 (31,900,000 acre feet) of water and has a surface area of . Three Gorges is al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huanggou Pumped Storage Power Station
The Huanggou Pumped Storage Power Station is a 1,200 MW pumped-storage hydroelectric power station currently under construction about north of Mudanjiang in Hailin County of Heilongjiang Province, China. Construction on the project began on 8 May 2014. The first generator is scheduled to be commissioned in January 2019 and the project complete in January 2020. The power station operates by shifting water between an upper and lower reservoir to generate electricity. The lower reservoir, Lianhua Reservoir, is located on the Mudan River and the upper reservoir is located in a valley above the north side of the lower reservoir. During periods of low energy demand, such as at night, water is pumped from Huanggou Lower Reservoir up to the upper reservoir. When energy demand is high, the water is released back down to the lower reservoir but the pump turbines that pumped the water up now reverse mode and serve as generators to produce electricity. The process is repeated as necessary and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Turbine
The Francis turbine is a type of water turbine. It is an inward-flow reaction turbine that combines radial and axial flow concepts. Francis turbines are the most common water turbine in use today, and can achieve over 95% efficiency. The process of arriving at the modern Francis runner design took from 1848 to approximately 1920. It became known as the Francis turbine around 1920, being named after British-American engineer James B. Francis who in 1848 created a new turbine design. Francis turbines are primarily used for producing electricity. The power output of the electric generators generally ranges from just a few kilowatts up to 1000 MW, though mini-hydro installations may be lower. The best performance is seen when the head height is between . Penstock diameters are between . The speeds of different turbine units range from 70 to 1000 rpm. A wicket gate around the outside of the turbine's rotating runner controls the rate of water flow through the turbine for d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flood Control
Flood control methods are used to reduce or prevent the detrimental effects of flood waters."Flood Control", MSN Encarta, 2008 (see below: Further reading). Flood relief methods are used to reduce the effects of flood waters or high water levels. Flooding can be caused by a mix of both natural processes, such as extreme weather upstream, and human changes to waterbodies and runoff. Though building hard infrastructure to prevent flooding, such as flood walls, can be effective at managing flooding, increased best practice within landscape engineering is to rely more on soft infrastructure and natural systems, such as marshes and flood plains, for handling the increase in water. For flooding on coasts, coastal management practices have to not only handle changes water flow, but also natural processes like tides. Flood control and relief is a particularly important part of climate change adaptation and climate resilience, both sea level rise and changes in the weather (climate cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heilongjiang Province
Heilongjiang () formerly romanized as Heilungkiang, is a province in northeast China. The standard one-character abbreviation for the province is (). It was formerly romanized as "Heilungkiang". It is the northernmost and easternmost province of the country and contains China's northernmost point (in Mohe City along the Amur) and easternmost point (at the junction of the Amur and Ussuri rivers). The province is bordered by Jilin to the south and Inner Mongolia to the west. It also shares a border with Russia (Amur Oblast, Jewish Autonomous Oblast, Khabarovsk Krai, Primorsky Krai and Zabaykalsky Krai) to the north and east. The capital and the largest city of the province is Harbin. Among Chinese provincial-level administrative divisions, Heilongjiang is the sixth-largest by total area, the 15th-most populous, and the second-poorest by GDP per capita. The province takes its name from the Amur River (see the etymology section below for details) which marks the border betwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroelectric
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined and also more than nuclear power. Hydropower can provide large amounts of low-carbon electricity on demand, making it a key element for creating secure and clean electricity supply systems. A hydroelectric power station that has a dam and reservoir is a flexible source, since the amount of electricity produced can be increased or decreased in seconds or minutes in response to varying electricity demand. Once a hydroelectric complex is constructed, it produces no direct waste, and almost always emits considerably less greenhouse gas than fossil fuel-powered energy plants. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |