|
Li Lanjuan
Li Lanjuan (; born 13 September 1947), also romanized as Lan-Juan Li, is a Chinese epidemiologist and hepatologist. She is a professor at Zhejiang University School of Medicine, an academician of the Chinese Academy of Engineering, and serves as the director of the State Key Laboratory for Diagnosis and Treatment of Infectious Diseases. She developed Li-NBAL, an artificial liver support system that is used to sustain the lives of people suffering from acute liver failure, and won multiple national awards for her roles in combatting the SARS, H1N1, and H7N9 epidemics. Early life and education Li was born on 13 September 1947 into a poor peasant family in Shaoxing, Zhejiang. She excelled in her studies and tested into Hangzhou High School, a provincial key school. After graduation, she became a middle school substitute teacher in her township. She also studied acupuncture at Zhejiang Chinese Medicine Hospital and performed acupuncture for local elders. Her village later recomme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Li (surname 李)
Li or Lee (; ) is a common Chinese surname, Chinese-language surname, it is the 4th name listed in the famous ''Hundred Family Surnames.'' Li is one of the most common surnames in Asia, shared by 92.76 million people in China, and more than 100 million in Asia. It is the List of common Chinese surnames, second most common surname in China as of 2018, the second most common surname in Hong Kong, and the 5th most common surname in Taiwan, where it is usually romanized as "Lee". The surname is pronounced as () in Cantonese, ''Lí'' (Pe̍h-ōe-jī, poj) in Taiwanese Hokkien, but is often spelled as "Lee" in Hong Kong, Macau, Taiwan and many overseas Chinese communities. In Macau, it is also spelled as "Lei". In Indonesia it is commonly spelled as "Lie". The common Korean name#Family names, Korean surname, "Lee (Korean surname), Lee" (also romanized as "I", "Yi", "Ri", or "Rhee"), and the Vietnamese name#Family name, Vietnamese surname, "Lý (Vietnamese name), Lý", are both derived f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liver Support System
A liver support system or diachysis is a type of therapeutic device to assist in performing the functions of the liver. Such systems focus either on removing the accumulating toxins (liver dialysis), or providing additional replacement of the metabolic functions of the liver through the inclusion of hepatocytes to the device (bioartificial liver device). This system is in trial to help people with acute liver failure (ALF) or acute-on-chronic liver failure. The primary functions of the liver include removing toxic substances from the blood, manufacturing blood proteins, storing energy in the form of glycogen, and secreting bile. The hepatocytes that perform these tasks can be killed or impaired by disease, resulting in hepatic insufficiency. A sudden onset of life-threatening hepatic insufficiency is known as acute liver failure (ALF). Etymology * The word diachysis derives from the Greek word, διάχυσησ, which means "Diffusion" * The word dialysis derives from the Greek w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2003 SARS Outbreak
3 (three) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 2 and preceding 4, and is the smallest odd prime number and the only prime preceding a square number. It has religious or cultural significance in many societies. Evolution of the Arabic digit The use of three lines to denote the number 3 occurred in many writing systems, including some (like Roman and Chinese numerals) that are still in use. That was also the original representation of 3 in the Brahmic (Indian) numerical notation, its earliest forms aligned vertically. However, during the Gupta Empire the sign was modified by the addition of a curve on each line. The Nāgarī script rotated the lines clockwise, so they appeared horizontally, and ended each line with a short downward stroke on the right. In cursive script, the three strokes were eventually connected to form a glyph resembling a with an additional stroke at the bottom: ३. The Indian digits spread to the Caliphate in the 9th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ministry Of Health Of The People's Republic Of China
The Ministry of Health of the People's Republic of China (MOH) was a cabinet-level executive department which plays the role of providing information, raising health awareness and education, ensuring the accessibility of health services, and monitoring the quality of health services provided to citizens and visitors in the mainland of the People's Republic of China. In the reforms of 2013 the ministry has been dissolved and its functions integrated into the new agency called the National Health and Family Planning Commission. The MOH was also involved in the control of illness and disease, coordinating the utilisation of resources and expertise where necessary. It also cooperates and keeps in touch with other health ministries and departments, including those of the special administrative regions, and the World Health Organization (WHO). As part of the National Health and Family Planning Commission it is now headed by Ms. Li Bin. Until 2013 it was headed by the Minister for He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liver Transplantation
Liver transplantation or hepatic transplantation is the replacement of a diseased liver with the healthy liver from another person (allograft). Liver transplantation is a treatment option for end-stage liver disease and acute liver failure, although availability of donor organs is a major limitation. The most common technique is orthotopic transplantation, in which the native liver is removed and replaced by the donor organ in the same anatomic position as the original liver. The surgical procedure is complex, requiring careful harvest of the donor organ and meticulous implantation into the recipient. Liver transplantation is highly regulated, and only performed at designated transplant medical centers by highly trained transplant physicians and supporting medical team. The duration of the surgery ranges from 4 to 18 hours depending on outcome. Favorable outcomes require careful screening for eligible recipient, as well as a well-calibrated live or cadaveric donor match. Medic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the ''Hepatitis B virus'' (HBV) that affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. It can cause both acute and chronic infection. Many people have no symptoms during an initial infection. For others, symptoms may appear 30 to 180 days after becoming infected and can include a rapid onset of sickness with nausea, vomiting, yellowish skin, fatigue, dark urine, and abdominal pain. Symptoms during acute infection typically last for a few weeks, though some people may feel sick for up to six months. Deaths resulting from acute stage HBV infections are rare. An HBV infection lasting longer than six months is usually considered chronic. The likelihood of developing chronic hepatitis B is higher for those who are infected with HBV at a younger age. About 90% of those infected during or shortly after birth develop chronic hepatitis B, while less than 10% of those infected after the age of five develop chronic cases. Most of those wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acute Liver Failure
Acute liver failure is the appearance of severe complications rapidly after the first signs (such as jaundice) of liver disease, and indicates that the liver has sustained severe damage (loss of function of 80–90% of liver cells). The complications are hepatic encephalopathy and impaired protein synthesis (as measured by the levels of serum albumin and the prothrombin time in the blood). The 1993 classification defines ''hyperacute'' as within 1 week, ''acute'' as 8–28 days, and ''subacute'' as 4–12 weeks; both the speed with which the disease develops and the underlying cause strongly affect outcomes. Signs and symptoms The main features of acute liver failure are rapid-onset jaundice, weakness, and eventually, changes in mental status that can begin as mild confusion but progress to coma, known as hepatic encephalopathy. Encephalopathy and cerebral edema In ALF, hepatic encephalopathy leads to cerebral edema, coma, brain herniation, and eventually death. Detection of e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Worker-Peasant-Soldier Student
Worker-Peasant-Soldier students () were Chinese students who entered colleges between 1970 and 1976, during the later part of the Cultural Revolution (1966–1976). They were accepted not for their academic qualifications, but rather for their work experience as workers, peasants, or soldiers favored by the Chinese Communist Party as part of the "Five Red Categories" and enjoyed affirmative action during the Cultural Revolution. No one was admitted directly from high school without work experience. In 1977, after Chairman Mao Zedong's death, the Worker-Peasant-Soldier program ended when Deng Xiaoping reinstated the National Higher Education Entrance Examination, where high school graduates were once again allowed to enter colleges without having to work first. Notable students * Xi Jinping, General Secretary of the Chinese Communist Party (since 2012), studied at Tsinghua University as a Worker-Peasant-Soldier student. * Zhao Leji (赵乐际; 1957) is a senior leader of the Chin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barefoot Doctor
Barefoot doctors () were healthcare providers who underwent basic medical training and worked in rural villages in China. They included farmers, folk healers, rural healthcare providers, and recent middle or secondary school graduates who received minimal basic medical and paramedical education. Their purpose was to bring healthcare to rural areas where urban-trained doctors would not settle. They promoted basic hygiene, preventive healthcare, and family planning and treated common illnesses. The name comes from southern farmers, who would often work barefoot in the rice paddies, and simultaneously worked as medical practitioners. In the 1930s, the Rural Reconstruction Movement had pioneered village health workers trained in basic health as part of a coordinated system, and there had been provincial experiments after 1949, but after Mao Zedong's healthcare speech in 1965 the concept was developed and institutionalized. China's health policy began to emphasize the importance of b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acupuncture
Acupuncture is a form of alternative medicine and a component of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) in which thin needles are inserted into the body. Acupuncture is a pseudoscience; the theories and practices of TCM are not based on scientific knowledge, and it has been characterized as quackery. There is a range of acupuncture variants which originated in different philosophies, and techniques vary depending on the country in which it is performed, but can be divided into two main foundational philosophical applications and approaches, the first being the modern standardized form called eight principles TCM and the second an older system that is based on the ancient Daoist '' wuxing'', better known as the five elements or phases in the West. Acupuncture is most often used to attempt pain relief, though acupuncturists say that it can also be used for a wide range of other conditions. Acupuncture is generally used only in combination with other forms of treatment. The global ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hangzhou High School
Hangzhou High School (), or Hanggao, established in 1899, is one of the most famous high schools in Southern China. It was the earliest-founded public high school in Zhejiang Province. Its history dates back to Yangzheng College founded by Lin Qi. There are 52 academicians who graduated from the institution as of 2018. Hangzhou High School has two campuses, the Gongyuan Campus at No.238, Fengqi Road, and the Qianjiang Campus at No.1958 East Zhijiang Road. The Qianjiang Campus started operating in September, 2015. This new campus including the International Division, which provide AP Courses to students. Hangzhou High School also participates in several international exchange programs with high schools oversea. There is Dover-Sherborn Exchange with Dover-Sherborn High School in Boston, MA.http://www.hanggao.net/index.php/dwjl/gw_detail/209 Club activities Hanggao Observatory Hanggao Observatory, also known as "Hangzhou High School Astronomy Club", is the student astronomy club. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
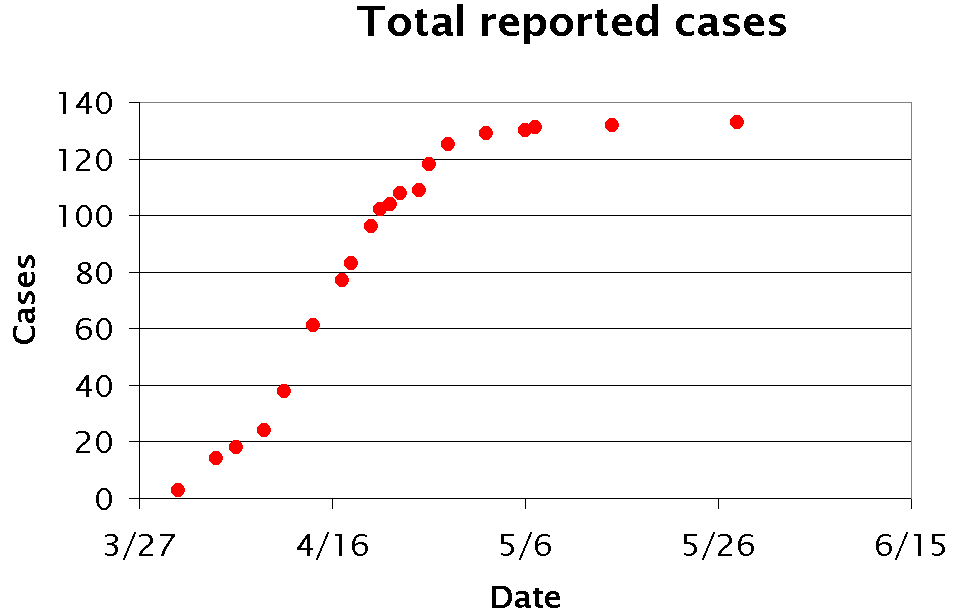
H7N9
Influenza A virus subtype H7N9 (A/H7N9) is a bird flu strain of the species Influenza virus A (avian influenza virus or bird flu virus). Avian influenza A H7 viruses normally circulate amongst avian populations with some variants known to occasionally infect humans. An H7N9 virus was first reported to have infected humans in March 2013, in China. Cases continued to be reported throughout April and then dropped to only a few cases during the summer months. At the closing of the year, 144 cases had been reported of which 46 had died.WHO: Global Alert and Response: Human infection with avian influenza A(H7N9) virus – update (accessed November 7, 2013) It is known that influenza tends to strike during the winter months, and the second wave, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |