|
Li Guang
Li Guang (184-119 BC) was a Chinese military general of the Western Han dynasty. Nicknamed "Flying General" by the Xiongnu, he fought primarily in the campaigns against the nomadic Xiongnu tribes to the north of China. He was known to the Xiongnu as a tough opponent when it came to fortress defense, and his presence was sometimes enough for the Xiongnu to abort a siege. Li Guang committed suicide shortly after the Battle of Mobei in 119 BC. He was blamed for failing to arrive at the battlefield in time (after getting lost in the desert), creating a gap in the encirclement and allowing Ichise Chanyu to escape after a confrontation between Wei Qing and the Chanyu's main force, which the Han army narrowly managed to defeat. Refusing to accept the humiliation of a court martial, Li Guang took his own life. Li Guang belonged to the Longxi branch of the Li clan ( 隴西李氏). Li Guang was a descendant of Laozi and the Qin general Li Xin, as well as an ancestor of the Western Lia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Li (surname 李)
Li or Lee (; ) is a common Chinese surname, Chinese-language surname, it is the 4th name listed in the famous ''Hundred Family Surnames.'' Li is one of the most common surnames in Asia, shared by 92.76 million people in China, and more than 100 million in Asia. It is the List of common Chinese surnames, second most common surname in China as of 2018, the second most common surname in Hong Kong, and the 5th most common surname in Taiwan, where it is usually romanized as "Lee". The surname is pronounced as () in Cantonese, ''Lí'' (Pe̍h-ōe-jī, poj) in Taiwanese Hokkien, but is often spelled as "Lee" in Hong Kong, Macau, Taiwan and many overseas Chinese communities. In Macau, it is also spelled as "Lei". In Indonesia it is commonly spelled as "Lie". The common Korean name#Family names, Korean surname, "Lee (Korean surname), Lee" (also romanized as "I", "Yi", "Ri", or "Rhee"), and the Vietnamese name#Family name, Vietnamese surname, "Lý (Vietnamese name), Lý", are both derived f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tang Dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an Zhou dynasty (690–705), interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. Historians generally regard the Tang as a high point in Chinese civilization, and a Golden age (metaphor), golden age of cosmopolitan culture. Tang territory, acquired through the military campaigns of its early rulers, rivaled that of the Han dynasty. The House of Li, Lǐ family () founded the dynasty, seizing power during the decline and collapse of the Sui Empire and inaugurating a period of progress and stability in the first half of the dynasty's rule. The dynasty was formally interrupted during 690–705 when Empress Wu Zetian seized the throne, proclaiming the Zhou dynasty (690–705), Wu Zhou dynasty and becoming the only legitimate Chinese empress regnant. The devast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empress Dou (Wen)
Empress Dou (; died 135 BC), formally Empress Xiaowen (孝文皇后), was an empress of the Chinese Han dynasty who greatly influenced the reigns of her husband Emperor Wen and her son Emperor Jing with her adherence to Taoist philosophy; she was the main support for the Huang-Lao school.Ssu-ma Ch'ien. Shmuel N. Eisenstadt 2016 p. 262. The Grand Scribe's Records: Volume X: The Memoirs of Han China, Part 3. https://books.google.com/books?id=s3E6DAAAQBAJ&pg=PA280 She therefore contributed greatly to the ''Rule of Wen and Jing'', commonly considered one of the golden ages of Chinese history. She even continued her considerable influence in the reign of her grandson Emperor Wu, and even her influence in the reign of Emperor Wu was so great that the young emperor did not have the power to decide for himself even one day. As a result, according to her influence, the Taoist laws were in force until her death over the empire. Early life Empress Dou was born into a family in Qinghe C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liu Wu, Prince Of Liang
Liu Wu (刘武) (–144 BC), posthumously named Prince Xiao of Liang, was a Han prince. He was a son of Emperor Wen and Empress Xiaowen, and a younger brother of Emperor Jing. He played a prominent role in the suppression of the Rebellion of the Seven Princes. He was also responsible for the assassination of the minister Yuan Ang.Sima Qian. ''Records of the Grand Historian'' in ang Xiuliang 'Shiji Cidian'' p. 698. Shandong Jiaoyu Chubanshe (Jinan), 1991 in Theobald, Ulrich. ''China Knowledge''. "Persons in Chinese HistoryLiang Xiaowang Liu Wu . 2011. Accessed 29 November 2013.Ban Biao & al. ''Book of Han'' in ang Xiuliang 'Hanshu Cidian'' p. 946. Shandong Jiaoyu Chubanshe (Jinan), 1991 in Theobald, Ulrich. ''China Knowledge''. "Persons in Chinese HistoryLiang Xiaowang Liu Wu . 2011. Accessed 29 November 2013. Life Liu Wu was initially created prince of Dai () in 178 BC. In 176, he became prince of Huaiyang () instead and his brother Liu Can () repl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Jing Of Han
Emperor Jing of Han (Liu Qi (劉啟); 188 BC – 9 March 141 BC) was the sixth emperor of the Chinese Han dynasty from 157 to 141 BC. His reign saw the limiting of the power of the feudal kings/princes which resulted in the Rebellion of the Seven States in 154 BC. Emperor Jing managed to crush the revolt and princes were thereafter denied rights to appoint ministers for their fiefs. This move helped to consolidate central power which paved the way for the long reign of his son Emperor Wu of Han. Emperor Jing had a complicated personality. He continued his father Emperor Wen's policy of general non-interference with the people, reduced tax and other burdens, and promoted government thrift. He continued and magnified his father's policy of reduction in criminal sentences. His light governance of the people was due to the Taoist influences of his mother, Empress Dou. Still, during his reign he arrested and imprisoned Zhou Yafu, and he was generally ungrateful to his wife Empress ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhou Yafu
Zhou may refer to: Chinese history * King Zhou of Shang () (1105 BC–1046 BC), the last king of the Shang dynasty * Predynastic Zhou (), 11th-century BC precursor to the Zhou dynasty * Zhou dynasty () (1046 BC–256 BC), a dynasty of China ** Western Zhou () (1046 BC–771 BC) ** Eastern Zhou () (770 BC–256 BC) * Western Zhou (state) () (440 BC–256 BC) * Eastern Zhou (state) () (367 BC–249 BC) * Northern Zhou () (557–581), one of the Northern dynasties during the Northern and Southern dynasties period * Wu Zhou () (690–705), an imperial dynasty established by Wu Zetian * Later Zhou () (951–960), the last of the Five dynasties during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period * Zhou (Zhang Shicheng's kingdom) () (1354–1367), a state founded by Zhang Shicheng during the Red Turban Rebellion * Zhou (Qing period state) () (1678–1681), a state founded by Wu Sangui during the Qing dynasty Other uses *Zhou (surname) (), Chinese surname *Zhou (country subdivision) (), a po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rebellion Of The Seven States
The Rebellion of the Seven States or Revolt of the Seven Kingdoms () took place in 154 BC against the Han dynasty of China by its regional semi-autonomous kings, to resist the emperor's attempt to centralize the government further. Background At the beginning of the Han dynasty, Liu Bang—Emperor Gaozu of Han—created princely titles for many of his relatives in certain territories that accounted for between approximately one-third to one-half of the empire. This was an attempt to consolidate Liu family rule over the parts of China that were not ruled directly from the capital under the commandery () system. During the reign of Emperor Wen, these princes were still setting their own laws, but in addition they were minting their own coins (albeit with Emperor Wen's approval) and collecting their own taxes. Many princes were effectively ignoring the imperial government's authority within their own principalities. When Emperor Jing became emperor in 157 BC, the rich principali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
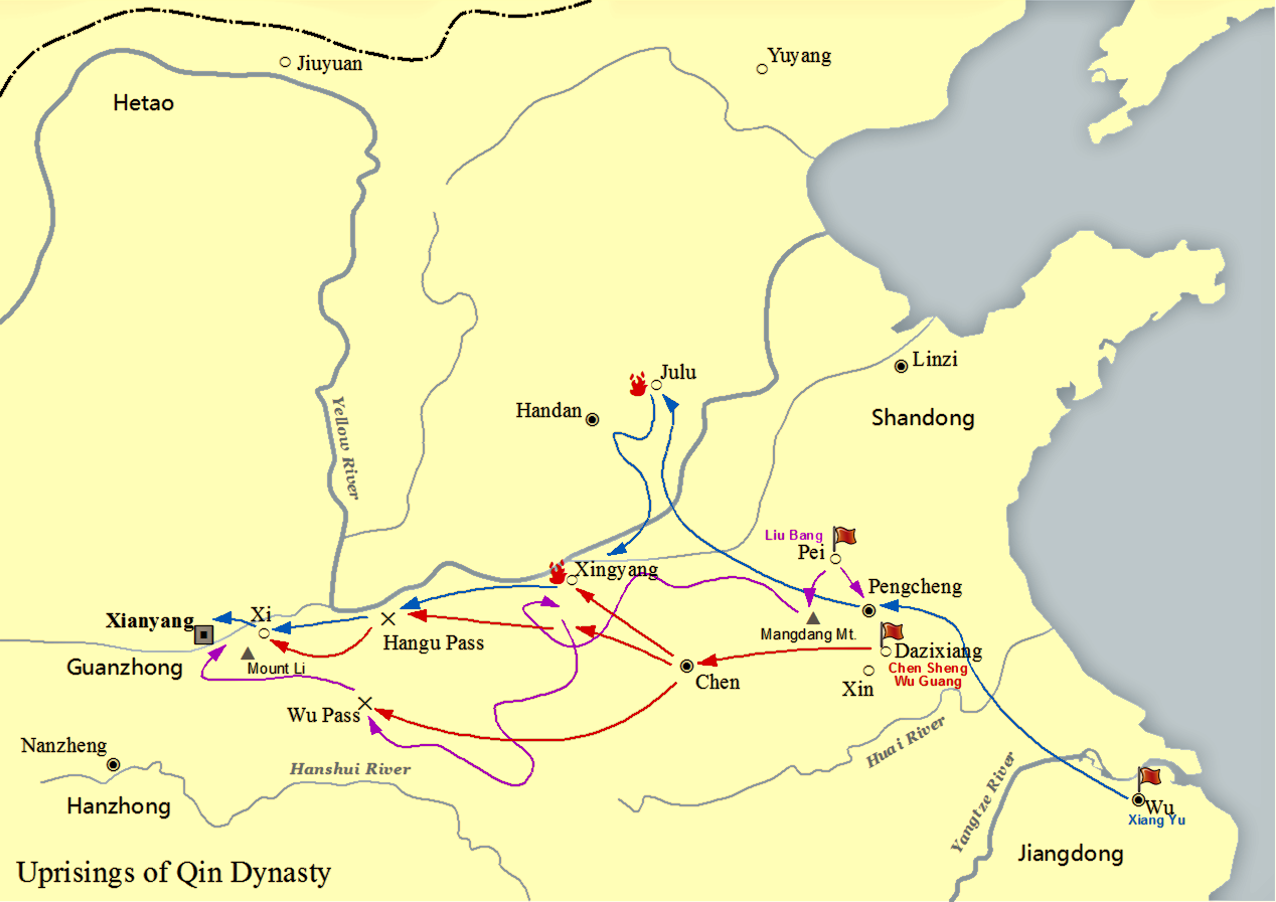
Liu Bang
Emperor Gaozu of Han (256 – 1 June 195 BC), born Liu Bang () with courtesy name Ji (季), was the founder and first emperor of the Han dynasty, reigning in 202–195 BC. His temple name was "Taizu" while his posthumous name was Emperor Gao, or Gaodi; "Gaozu of Han", derived from the ''Records of the Grand Historian'', is the common way of referring to this sovereign even though he was not accorded the temple name "Gaozu", which literally means "High Founder". Liu Bang was one of the few dynasty founders in Chinese history who was born into a peasant family. Prior to coming to power, Liu Bang initially served for the Qin dynasty as a minor law enforcement officer in his home town Pei County, within the conquered state of Chu. With the First Emperor's death and the Qin Empire's subsequent political chaos, Liu Bang renounced his civil service position and became an anti-Qin rebel leader. He won the race against fellow rebel leader Xiang Yu to invade the Qin heartland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Wen Of Han
Emperor Wen of Han (; 203/202 – 6 July 157 BCE), born Liu Heng (), was the fifth emperor of the Western Han dynasty in China from 180 to his death in 157 BCE. The son of Emperor Gao and Consort Bo, his reign provided a much needed stability after the unstable and violent regency of Empress Lü. The prosperous reigns of Wen and his son Emperor Jing are highly regarded by historians, being referred to as the Rule of Wen and Jing. When Emperor Gaozu suppressed the rebellion of Dai, he made Liu Heng Prince of Dai. Since Emperor Gaozu's death, power had been in the hands of his wife, Empress Lü, who became the empress dowager. After Empress Dowager Lü's death, the officials eliminated the powerful Lü clan, and deliberately chose the Prince of Dai as the emperor, since his mother, Consort Bo, had no powerful relatives, and her family was known for its humility and thoughtfulness. His reign brought a much needed political stability that laid the groundwork for prosperity under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huo Qubing
Huo Qubing (140 BC – 117 BC) was a Chinese military general and politician of the Western Han dynasty during the reign of Emperor Wu of Han. He was the nephew of the general Wei Qing and Empress Wei Zifu (Emperor Wu's wife), and the half-brother of the statesman Huo Guang. The Records of the Grand Historian by the ancient scholar Sima Qian also list him as a male favorite (i.e., lover) of the Emperor. Along with Wei Qing, he led a campaign into the Gobi Desert of what is now Mongolia to defeat the Xiongnu nomadic confederation, winning decisive victories such as the Battle of Mobei in 119 BC. Early life Huo Qubing was an illegitimate son from the love affair between Wei Shaoer (), the daughter of a lowly maid from the household of Princess Pingyang (Emperor Wu's older sister), and Huo Zhongru (), a low-ranking civil servant employed there at the time. However, Huo Zhongru did not want to marry a lower class serf girl like Wei Shaoer, so he abandoned her and went away to m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archery
Archery is the sport, practice, or skill of using a bow to shoot arrows.Paterson ''Encyclopaedia of Archery'' p. 17 The word comes from the Latin ''arcus'', meaning bow. Historically, archery has been used for hunting and combat. In modern times, it is mainly a competitive sport and recreational activity. A person who practices archery is typically called an archer, bowman, or toxophilite. History Origins and ancient archery The oldest known evidence of the bow and arrow comes from South African sites such as Sibudu Cave, where the remains of bone and stone arrowheads have been found dating approximately 72,000 to 60,000 years ago.Backwell L, d'Errico F, Wadley L.(2008). Middle Stone Age bone tools from the Howiesons Poort layers, Sibudu Cave, South Africa. Journal of Archaeological Science, 35:1566–1580. Backwell L, Bradfield J, Carlson KJ, Jashashvili T, Wadley L, d'Errico F.(2018). The antiquity of bow-and-arrow technology: evidence from Middle Stone Age layers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Records Of The Grand Historian
''Records of the Grand Historian'', also known by its Chinese name ''Shiji'', is a monumental history of China that is the first of China's 24 dynastic histories. The ''Records'' was written in the early 1st century by the ancient Chinese historian Sima Qian, whose father Sima Tan had begun it several decades earlier. The work covers a 2,500-year period from the age of the legendary Yellow Emperor to the reign of Emperor Wu of Han in the author's own time, and describes the world as it was known to the Chinese of the Western Han dynasty. The ''Records'' has been called a "foundational text in Chinese civilization". After Confucius and the First Emperor of Qin, "Sima Qian was one of the creators of Imperial China, not least because by providing definitive biographies, he virtually created the two earlier figures." The ''Records'' set the model for all subsequent dynastic histories of China. In contrast to Western historical works, the ''Records'' do not treat history as "a cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)