|
Lexical Approach
The lexical approach is a method of teaching foreign languages described by Michael Lewis in the early 1990s. The basic concept on which this approach rests is the idea that an important part of learning a language consists of being able to understand and produce lexical phrases as chunks. Students are taught to be able to perceive patterns of language (grammar) as well as have meaningful set uses of words at their disposal when they are taught in this way. In 2000, Norbert Schmitt, an American linguist and a Professor of Applied Linguistics at the University of Nottingham in the United Kingdom, contributed to a learning theory supporting the lexical approach he stated that "the mind stores and processes these exicalchunks as individual wholes." The short-term capacity of the brain is much more limited than long-term and so it is much more efficient for our brain to pull up a lexical chunk as if it were one piece of information as opposed to pulling up each word as separate pieces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Language Education
Language education – the process and practice of teaching a second or foreign language – is primarily a branch of applied linguistics, but can be an interdisciplinary field. There are four main learning categories for language education: communicative competencies, proficiencies, cross-cultural experiences, and multiple literacies. Need Increasing globalization has created a great need for people in the workforce who can communicate in multiple languages. Common languages are used in areas such as trade, tourism, diplomacy, technology, media, translation, interpretation and science. Many countries such as Korea (Kim Yeong-seo, 2009), Japan (Kubota, 1998) and China (Kirkpatrick & Zhichang, 2002) frame education policies to teach at least one foreign language at the primary and secondary school levels. However, some countries such as India, Singapore, Malaysia, Pakistan, and the Philippines use a second official language in their governments. According to GAO (2010), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
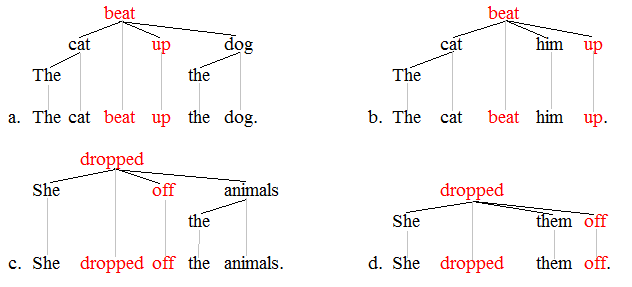
Lexical Phrase
In lexicography, a lexical item is a single word, a part of a word, or a chain of words (catena) that forms the basic elements of a language's lexicon (≈ vocabulary). Examples are ''cat'', ''traffic light'', ''take care of'', ''by the way'', and ''it's raining cats and dogs''. Lexical items can be generally understood to convey a single meaning, much as a lexeme, but are not limited to single words. Lexical items are like semes in that they are "natural units" translating between languages, or in learning a new language. In this last sense, it is sometimes said that language consists of grammaticalized lexis, and not lexicalized grammar. The entire store of lexical items in a language is called its lexis. Lexical items composed of more than one word are also sometimes called ''lexical chunks'', ''gambits'', ''lexical phrases'', ''lexicalized stems'', or ''speech formulae''. The term ''polyword listemes'' is also sometimes used. Types Common types of lexical items/chunks i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammar
In linguistics, the grammar of a natural language is its set of structure, structural constraints on speakers' or writers' composition of clause (linguistics), clauses, phrases, and words. The term can also refer to the study of such constraints, a field that includes domains such as phonology, morphology (linguistics), morphology, and syntax, often complemented by phonetics, semantics, and pragmatics. There are currently two different approaches to the study of grammar: traditional grammar and Grammar#Theoretical frameworks, theoretical grammar. Fluency, Fluent speakers of a variety (linguistics), language variety or ''lect'' have effectively internalized these constraints, the vast majority of which – at least in the case of one's First language, native language(s) – are language acquisition, acquired not by conscious study or language teaching, instruction but by hearing other speakers. Much of this internalization occurs during early childhood; learning a language later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norbert Schmitt
Norbert Schmitt (born 23 January 1956) is an American applied linguist and Emeritus Professor of Applied Linguistics at the University of Nottingham in the United Kingdom. He is known for his work on second-language vocabulary acquisition and second-language vocabulary teaching. He has published numerous books and papers on vocabulary acquisition. Research Norbert Schmitt began his career in 1988 as an EFL teacher in Japan and quickly became interested in how language learners acquire their second languages. During his Masters study at Temple University, Japan, he began researching how students learn vocabulary in particular. He extended this interest in vocabulary through his PhD research at the University of Nottingham in 1994. Upon completion of his PhD in 1997, he joined the University of Nottingham staff, and taught there until his retirement in September 2020. He is now Emeritus Professor of Applied Linguistics. Prof. Schmitt has researched second language vocabulary i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vocabulary
A vocabulary is a set of familiar words within a person's language. A vocabulary, usually developed with age, serves as a useful and fundamental tool for communication and acquiring knowledge. Acquiring an extensive vocabulary is one of the largest challenges in learning a second language. Definition and usage Vocabulary is commonly defined as "all the words known and used by a particular person". Productive and receptive knowledge The first major change distinction that must be made when evaluating word knowledge is whether the knowledge is productive (also called achieve or active) or receptive (also called receive or passive); even within those opposing categories, there is often no clear distinction. Words that are generally understood when heard or read or seen constitute a person's receptive vocabulary. These words may range from well known to barely known (see degree of knowledge below). A person's receptive vocabulary is usually the larger of the two. For exampl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English As A Foreign Or Second Language
English as a second or foreign language is the use of English by speakers with different native languages. Language education for people learning English may be known as English as a second language (ESL), English as a foreign language (EFL), English as an additional language (EAL), English as a New Language (ENL), or English for speakers of other languages (ESOL). The aspect in which ESL is taught is referred to as teaching English as a foreign language ( TEFL), teaching English as a second language (TESL) or teaching English to speakers of other languages (TESOL). Technically, TEFL refers to English language teaching in a country where English is not the official language, TESL refers to teaching English to non-native English speakers in a native English-speaking country and TESOL covers both. In practice, however, each of these terms tends to be used more generically across the full field. TEFL is more widely used in the UK and TESL or TESOL in the US. The term "ESL" ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |