|
Leves
''Leves'' (Singular: ''Levis'') were javelin-armed skirmishers in the army of the early Roman Republic. They were typically some of the youngest and poorest men in the legion, and could not afford much equipment. They were usually outfitted with just a number of light javelins and no other equipment. There were 300 leves in a legion, and unlike other infantry types they did not form their own units, but were assigned to units of ''hastati'' – heavier sword-armed troops. Their primary purpose on the battlefield was to harass the enemy with javelin fire and support the heavy infantry who fought in hand-to-hand combat. ''Accensi'' and ''rorarii'' were also light missile troops and had similar roles. History and deployment ''Leves'' appear to have evolved from the old poor classes of the army under the Etruscan kings when it was reformed by Marcus Furius Camillus ca. 386 BC. These soldiers stood at the rear of a very large phalanx and were equipped in a similar manner to ''leve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Velites
''Velites'' (singular: ) were a class of infantry in the Roman army of the mid-Republic from 211 to 107 BC. ''Velites'' were light infantry and skirmishers armed with javelins ( la, hastae velitares), each with a 75cm (30 inch) wooden shaft the diameter of a finger, with a 25cm (10 inch) narrow metal point, to fling at the enemy. They also carried short thrusting swords, or ''gladii'', for use in melee. They rarely wore armour as they were the youngest and poorest soldiers in the legion and could not afford much equipment. They did carry small wooden shields called ''parma'' for protection, and wore headdresses made from wolf skins so their brave deeds could be recognized. The ''velites'' were placed at the front partly for tactical reasons, and also so that they had the opportunity to secure glory for themselves in single combat. ''Velites'' did not form their own units; a number of them were attached to each ''maniple'' of ''hastati'', ''principes'' and ''triarii''. They were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
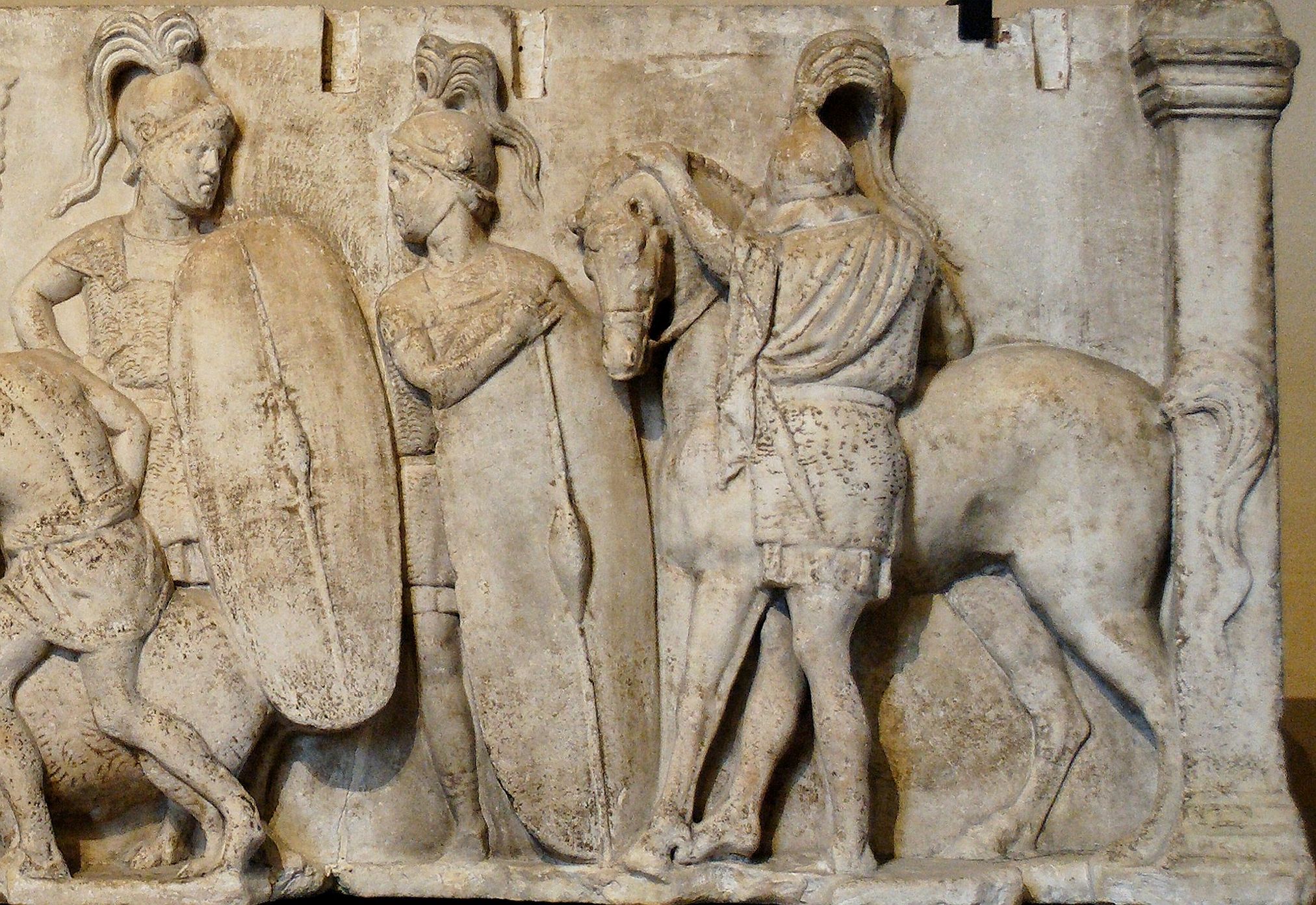
Hastati
''Hastati'' (singular: ''hastatus'') were a class of infantry employed in the armies of the early Roman Republic, who originally fought as spearmen and later as swordsmen. These soldiers were the staple unit after Rome threw off Etruscan rule. They were originally some of the poorest men in the legion, and could afford only modest equipment—light chainmail and other miscellaneous equipment. The Senate supplied their soldiers with only a short stabbing sword, the gladius, and their distinctive squared shield, the scutum. The ''hastatus'' was typically equipped with these, and one or two soft iron tipped throwing spears called pila. This doubled their effectiveness, not only as a strong leading edge to their maniple, but also as a stand-alone missile troop. Later, the ''hastati'' contained the younger men rather than just the poorer, though most men of their age were relatively poor. Their usual position was the first battle line. They fought in a quincunx formation, supported b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establishment of the Roman Empire, Rome's control rapidly expanded during this period—from the city's immediate surroundings to hegemony over the entire Mediterranean world. Roman society under the Republic was primarily a cultural mix of Latin and Etruscan societies, as well as of Sabine, Oscan, and Greek cultural elements, which is especially visible in the Roman Pantheon. Its political organization developed, at around the same time as direct democracy in Ancient Greece, with collective and annual magistracies, overseen by a senate. The top magistrates were the two consuls, who had an extensive range of executive, legislative, judicial, military, and religious powers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Legion
The Roman legion ( la, legiō, ) was the largest military unit of the Roman army, composed of 5,200 infantry and 300 equites (cavalry) in the period of the Roman Republic (509 BC–27 BC) and of 5,600 infantry and 200 auxilia in the period of the Roman Empire (27 BC – AD 476). Size The size of a typical legion varied throughout the history of ancient Rome, with complements ranging from 4,200 legionaries and 300 equites (drawn from the wealthier classes – in early Rome all troops provided their own equipment) in the Republican period of Rome (the infantry were split into 10 cohorts each of four maniples of 120 legionaries), to 4,800 legionaries (in 10 cohorts of 6 centuries of 80 legionaries) during Caesar's age, to 5,280 men plus 120 auxiliaries in the Imperial period (split into 10 cohorts, nine of 480 men each, with the first cohort being double-strength at 960 men). It should be noted the above numbers are typical field strengths while "paper strength" was sli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accensi
The term ''accensi'' (Singular: ''accensus'') is applied to two different groups. Originally, the ''accensi'' were light infantry in the armies of the early Roman Republic. They were the poorest men in the legion, and could not afford much equipment. They did not wear armour or carry shields, and their usual position was part of the third battle line. They fought in a loose formation, supporting the heavier troops. They were eventually phased out by the time of Second Punic War. In the later Roman Republic the term was used for civil servants who assisted the elected magistrates, particularly in the courts, where they acted as ushers and clerks. Infantry History and deployment ''Accensi'' appear to have evolved from the old fifth class of the army under the Etruscan kings when it was reformed by Marcus Furius Camillus. The fifth class was made up of the poorest soldiers in the legion who were equipped with slings and perhaps a small shield. They acted as skirmishers, screening ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Javelin
A javelin is a light spear designed primarily to be thrown, historically as a ranged weapon, but today predominantly for sport. The javelin is almost always thrown by hand, unlike the sling, bow, and crossbow, which launch projectiles with the aid of a hand-held mechanism. However, devices do exist to assist the javelin thrower in achieving greater distance, such as spear-throwers or the amentum. A warrior or soldier armed primarily with one or more javelins is a javelineer. The word javelin comes from Middle English and it derives from Old French ''javelin'', a diminutive of ''javelot'', which meant spear. The word ''javelot'' probably originated from one of the Celtic languages. Prehistory There is archaeological evidence that javelins and throwing sticks were already in use by the last phase of the Lower Paleolithic. Seven spear-like objects were found in a coal mine in the city of Schöningen, Germany. Stratigraphy, Stratigraphic dating indicates that the weapons are abo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structural History Of The Roman Military
The structural history of the Roman military concerns the major transformations in the organization and constitution of ancient Rome's armed forces, "the most effective and long-lived military institution known to history."''Encyclopædia Britannica'', Eleventh Edition (1911), ''The Roman Army'' From its origins around 800 BC to its final dissolution in AD 476 with the demise of the Western Roman Empire, Rome's military organization underwent substantial structural change. At the highest level of structure, the forces were split into the Roman army and the Roman navy, although these two branches were less distinct than in many modern national defense forces. Within the top levels of both army and navy, structural changes occurred as a result of both positive military reform and organic structural evolution. These changes can be divided into four distinct phases. ;Phase I: The army was derived from obligatory annual military service levied on the citizenry, as part of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Units And Formations Of The Roman Republic
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct military uniform. It may consist of one or more military branches such as an army, navy, air force, space force, marines, or coast guard. The main task of the military is usually defined as defence of the state and its interests against external armed threats. In broad usage, the terms ''armed forces'' and ''military'' are often treated as synonymous, although in technical usage a distinction is sometimes made in which a country's armed forces may include both its military and other paramilitary forces. There are various forms of irregular military forces, not belonging to a recognized state; though they share many attributes with regular military forces, they are less often referred to as simply ''military''. A nation's military may f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equites
The ''equites'' (; literally "horse-" or "cavalrymen", though sometimes referred to as "knights" in English) constituted the second of the property-based classes of ancient Rome, ranking below the senatorial class. A member of the equestrian order was known as an ''eques'' (). Description During the Roman kingdom and the first century of the Roman Republic, legionary cavalry was recruited exclusively from the ranks of the patricians, who were expected to provide six ''centuriae'' of cavalry (300 horses for each consular legion). Around 400BC, 12 more ''centuriae'' of cavalry were established and these included non-patricians (plebeians). Around 300 BC the Samnite Wars obliged Rome to double the normal annual military levy from two to four legions, doubling the cavalry levy from 600 to 1,200 horses. Legionary cavalry started to recruit wealthier citizens from outside the 18 ''centuriae''. These new recruits came from the first class of commoners in the Centuriate Assembly orga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polybius
Polybius (; grc-gre, Πολύβιος, ; ) was a Greek historian of the Hellenistic period. He is noted for his work , which covered the period of 264–146 BC and the Punic Wars in detail. Polybius is important for his analysis of the mixed constitution or the separation of powers in government, his in-depth discussion of checks and balances to limit power, and his introduction of "the people", which influenced Montesquieu's ''The Spirit of the Laws'', John Locke's ''Two Treatises of Government'', and the framers of the United States Constitution. The leading expert on Polybius for nearly a century was F. W. Walbank (1909–2008), who published studies related to him for 50 years, including a long commentary of his ''Histories'' and a biography. Early life Polybius was born around 200 BC in Megalopolis, Greece, Megalopolis, Arcadia (region), Arcadia, when it was an active member of the Achaean League. The town was revived, along with other Achaean states, a century before he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equites
The ''equites'' (; literally "horse-" or "cavalrymen", though sometimes referred to as "knights" in English) constituted the second of the property-based classes of ancient Rome, ranking below the senatorial class. A member of the equestrian order was known as an ''eques'' (). Description During the Roman kingdom and the first century of the Roman Republic, legionary cavalry was recruited exclusively from the ranks of the patricians, who were expected to provide six ''centuriae'' of cavalry (300 horses for each consular legion). Around 400BC, 12 more ''centuriae'' of cavalry were established and these included non-patricians (plebeians). Around 300 BC the Samnite Wars obliged Rome to double the normal annual military levy from two to four legions, doubling the cavalry levy from 600 to 1,200 horses. Legionary cavalry started to recruit wealthier citizens from outside the 18 ''centuriae''. These new recruits came from the first class of commoners in the Centuriate Assembly orga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
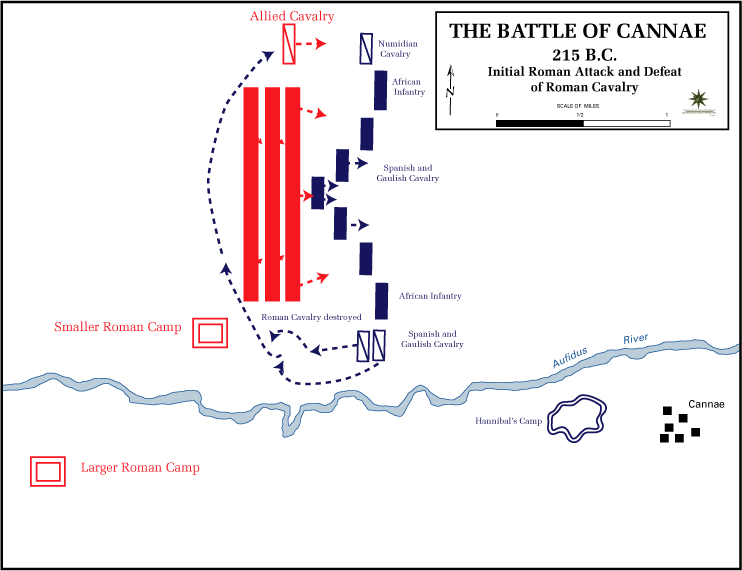
Pitched Battle
A pitched battle or set-piece battle is a battle in which opposing forces each anticipate the setting of the battle, and each chooses to commit to it. Either side may have the option to disengage before the battle starts or shortly thereafter. A pitched battle is not a chance encounter such as a meeting engagement, or where one side is forced to fight at a time not of its choosing such as happens in a siege or an ambush. Pitched battles are usually carefully planned, to maximize one's strengths against an opponent's weaknesses, and use a full range of deceptions, feints, and other manoeuvres. They are also planned to take advantage of terrain favourable to one's force. Forces strong in cavalry for example will not select swamp, forest, or mountain terrain for the planned struggle. For example, Carthaginian general Hannibal selected relatively flat ground near the village of Cannae for his great confrontation with the Romans, not the rocky terrain of the high Apennines. Likewise, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |