|
Lessepsian Migrant
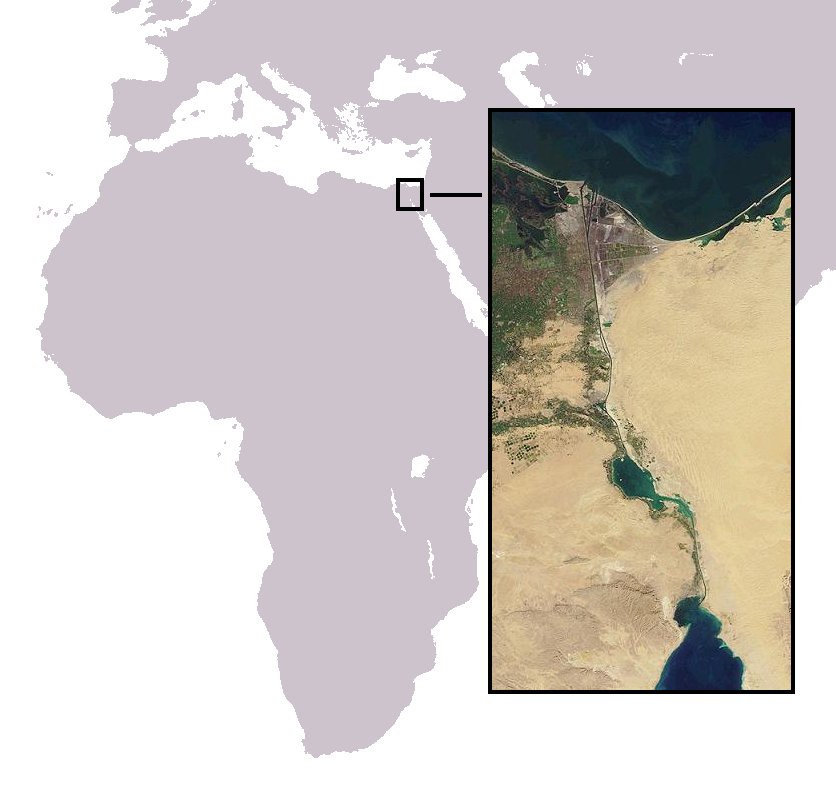
The Lessepsian migration (also called Erythrean invasion) is the migration of marine species across the Suez Canal, usually from the Red Sea to the Mediterranean Sea, and more rarely in the opposite direction. When the canal was completed in 1869, fish, crustaceans, mollusks, and other marine animals and plants were exposed to an artificial passage between the two naturally separate bodies of water, and cross-contamination was made possible between formerly isolated ecosystems. The phenomenon is still occurring today. It is named after Ferdinand de Lesseps, the French diplomat in charge of the canal's construction. The migration of invasive species through the Suez Canal from the Indo-Pacific region has been facilitated by many factors, both abiotic and anthropogenic, and presents significant implications for the ecological health and economic stability of the contaminated areas; of particular concern is the fisheries industry in the Eastern Mediterranean. Despite these threats, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canal De Suez
Canals or artificial waterways are waterways or engineered channels built for drainage management (e.g. flood control and irrigation) or for conveyancing water transport vehicles (e.g. water taxi). They carry free, calm surface flow under atmospheric pressure, and can be thought of as artificial rivers. In most cases, a canal has a series of dams and locks that create reservoirs of low speed current flow. These reservoirs are referred to as ''slack water levels'', often just called ''levels''. A canal can be called a ''navigation canal'' when it parallels a natural river and shares part of the latter's discharges and drainage basin, and leverages its resources by building dams and locks to increase and lengthen its stretches of slack water levels while staying in its valley. A canal can cut across a drainage divide atop a ridge, generally requiring an external water source above the highest elevation. The best-known example of such a canal is the Panama Canal. Man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annual Reviews (publisher)
Annual Reviews is an independent, non-profit academic publishing company based in San Mateo, California. As of 2021, it publishes 51 journals of review articles and ''Knowable Magazine'', covering the fields of life, biomedical, physical, and social sciences. Review articles are usually “peer-invited” solicited submissions, often planned one to two years in advance, which go through a peer-review process. The organizational structure has three levels: a volunteer board of directors, editorial committees of experts for each journal, and paid employees. Annual Reviews' stated mission is to synthesize and integrate knowledge "for the progress of science and the benefit of society". The first Annual Reviews journal, the ''Annual Review of Biochemistry'', was published in 1932 under the editorship of Stanford University chemist J. Murray Luck, who wanted to create a resource that provided critical reviews on contemporary research. The second journal was added in 1939. By ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annual Review Of Ecology, Evolution, And Systematics
The ''Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics'' is an annual scientific journal published by Annual Reviews. The journal was established in 1970 as the ''Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics'' and changed its name beginning in 2003. It publishes invited review articles on topics considered to be timely and important in the fields of ecology, evolutionary biology, and systematics. As of 2022, ''Journal Citation Reports'' gave the journal a 2021 impact factor of 14.340, ranking it third of 173 journals in the "Ecology" category and third of 51 journals in "Evolutionary Biology". History The ''Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics'' was first published in 1970, with Richard F. Johnston as its first editor. In 1975 it began publishing biographies of notable ecologists in the prefatory chapter. In 2003, its name was changed to its current form, the ''Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics''. It defines its scope as covering significant developments ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediterranean Science Commission
The Mediterranean Science Commission, or CIESM, (French: ''Commission Internationale pour l'Exploration Scientifique de la Méditerranée'') unites 24 Member States, hundreds of marine Institutes, and thousands of marine researchers from all shores of the Basin and adjacent seas, to exchange on the latest advances in oceanography. Created by an International Conference held in Madrid, Spain, in November 1919 the Commission promotes multilateral international research on marine sciences via the international use of national research stations and scientific exchange. Originally the organization was restricted to countries bordering the Mediterranean and the Black seas and is now open to other countries engaged in marine research in the broad region. Early years Two professors, the Italian Decio Vinciguerra and the German Otto Krümmel, thought it would be useful for the fishing industry to promote oceanographic exploration of the Mediterranean Sea. Based on Vinciguerra's prop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biogeography
Biogeography is the study of the distribution of species and ecosystems in geographic space and through geological time. Organisms and biological communities often vary in a regular fashion along geographic gradients of latitude, elevation, isolation and habitat area.Brown University, "Biogeography." Accessed February 24, 2014. . Phytogeography is the branch of biogeography that studies the distribution of plants. Zoogeography is the branch that studies distribution of animals. Mycogeography is the branch that studies distribution of fungi, such as mushrooms. Knowledge of spatial variation in the numbers and types of organisms is as vital to us today as it was to our early human ancestors, as we adapt to heterogeneous but geographically predictable environments. Biogeography is an integrative field of inquiry that unites concepts and information from ecology, evolutionary biology, taxonomy, geology, physical geography, palaeontology, and climatology.Dansereau, Pierre. 1957 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nile River
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered the longest river in the world, though this has been contested by research suggesting that the Amazon River is slightly longer.Amazon Longer Than Nile River, Scientists Say Of the world's major rivers, the Nile is one of the smallest, as measured by annual flow in cubic metres of water. About long, its covers eleven countries: the |
Aswan High Dam
The Aswan Dam, or more specifically since the 1960s, the Aswan High Dam, is one of the world's largest embankment dams, which was built across the Nile in Aswan, Egypt, between 1960 and 1970. Its significance largely eclipsed the previous Aswan Low Dam initially completed in 1902 downstream. Based on the success of the Low Dam, then at its maximum utilization, construction of the High Dam became a key objective of the government following the Egyptian Revolution of 1952; with its ability to better control flooding, provide increased water storage for irrigation and generate hydroelectricity, the dam was seen as pivotal to Egypt's planned industrialization. Like the earlier implementation, the High Dam has had a significant effect on the economy and culture of Egypt. Before the High Dam was built, even with the old dam in place, the annual flooding of the Nile during late summer had continued to pass largely unimpeded down the valley from its East African drainage basin. These floo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe and Asia from the "New World" of the Americas in the European perception of the World. The Atlantic Ocean occupies an elongated, S-shaped basin extending longitudinally between Europe and Africa to the east, and North and South America to the west. As one component of the interconnected World Ocean, it is connected in the north to the Arctic Ocean, to the Pacific Ocean in the southwest, the Indian Ocean in the southeast, and the Southern Ocean in the south (other definitions describe the Atlantic as extending southward to Antarctica). The Atlantic Ocean is divided in two parts, by the Equatorial Counter Current, with the North(ern) Atlantic Ocean and the South(ern) Atlantic Ocean split at about 8°N. Scientific explorations of the A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by the Southern Ocean or Antarctica, depending on the definition in use. Along its core, the Indian Ocean has some large marginal or regional seas such as the Arabian Sea, Laccadive Sea, Bay of Bengal, and Andaman Sea. Etymology The Indian Ocean has been known by its present name since at least 1515 when the Latin form ''Oceanus Orientalis Indicus'' ("Indian Eastern Ocean") is attested, named after Indian subcontinent, India, which projects into it. It was earlier known as the ''Eastern Ocean'', a term that was still in use during the mid-18th century (see map), as opposed to the ''Western Ocean'' (Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic) before the Pacific Ocean, Pacific was surmised. Conversely, Ming treasure voyages, Chinese explorers in the Indian Oce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salinity
Salinity () is the saltiness or amount of salt dissolved in a body of water, called saline water (see also soil salinity). It is usually measured in g/L or g/kg (grams of salt per liter/kilogram of water; the latter is dimensionless and equal to ‰). Salinity is an important factor in determining many aspects of the chemistry of natural waters and of biological processes within it, and is a thermodynamic state variable that, along with temperature and pressure, governs physical characteristics like the density and heat capacity of the water. A contour line of constant salinity is called an ''isohaline'', or sometimes ''isohale''. Definitions Salinity in rivers, lakes, and the ocean is conceptually simple, but technically challenging to define and measure precisely. Conceptually the salinity is the quantity of dissolved salt content of the water. Salts are compounds like sodium chloride, magnesium sulfate, potassium nitrate, and sodium bicarbonate which dissolve into ions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |