|
Les Illusions Perdues
''Illusions perdues'' — in English, ''Lost Illusions'' — is a serial novel written by the French writer Honoré de Balzac between 1837 and 1843. It consists of three parts, starting in provincial France, thereafter moving to Paris, and finally returning to the provinces. The book resembles another of Balzac's greatest novels, ''La Rabouilleuse'' (''The Black Sheep'', 1842), that is set in Paris and in the provinces. It forms part of the ''Scènes de la vie de province'' in ''La Comédie humaine''. Background The novel's main character, Lucien Chardon, works as a journalist, and his friend David Séchard is a printer. These were both professions with which Balzac himself had experience. Balzac had started a printing business in Paris in 1826, which went bankrupt in 1828. His experiences influenced his description of David Séchard's working life."Introduction" by Herbert J. Hunt from Penguin Classics edition of ''Lost Illusions'', 1971 Balzac had bought the newspaper ''La Chro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Novels
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is a Wikimedia movement affinity group for contributors with shared goals. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within sister projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by '' Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outside organizations relevant to the field at issue. For e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sonnet
A sonnet is a poetic form that originated in the poetry composed at the Court of the Holy Roman Emperor Frederick II in the Sicilian city of Palermo. The 13th-century poet and notary Giacomo da Lentini is credited with the sonnet's invention, and the Sicilian School of poets who surrounded him then spread the form to the mainland. The earliest sonnets, however, no longer survive in the original Sicilian language, but only after being translated into Tuscan dialect. The term "sonnet" is derived from the Italian word ''sonetto'' (lit. "little song", derived from the Latin word ''sonus'', meaning a sound). By the 13th century it signified a poem of fourteen lines that followed a strict rhyme scheme and structure. According to Christopher Blum, during the Renaissance, the sonnet became the "choice mode of expressing romantic love". During that period, too, the form was taken up in many other European language areas and eventually any subject was considered acceptable for writers o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
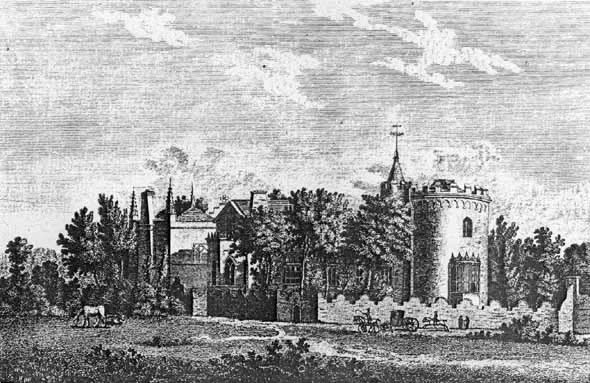
The Castle Of Otranto
''The Castle of Otranto'' is a novel by Horace Walpole. First published in 1764, it is generally regarded as the first gothic novel. In the second edition, Walpole applied the word 'Gothic' to the novel in the subtitle – ''A Gothic Story''. Set in a haunted castle, the novel merged medievalism and terror in a style that has endured ever since. The aesthetic of the book has shaped modern-day gothic books, films, art, music, and the goth subculture. Walpole was inspired to write the story after a nightmare he had at his Gothic Revival home, Strawberry Hill House, in southwest London. The novel initiated a literary genre that would become extremely popular in the later 18th and early 19th century, with authors such as Clara Reeve, Ann Radcliffe, William Thomas Beckford, Matthew Lewis, Mary Shelley, Bram Stoker, Edgar Allan Poe, Robert Louis Stevenson and George du Maurier. History ''The Castle of Otranto'' was written in 1764 during Horace Walpole's tenure as MP for King's Lyn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gothic Novel
Gothic fiction, sometimes called Gothic horror in the 20th century, is a loose literary aesthetic of fear and haunting. The name is a reference to Gothic architecture of the European Middle Ages, which was characteristic of the settings of early Gothic novels. The first work to call itself Gothic was Horace Walpole's 1764 novel ''The Castle of Otranto'', later subtitled "A Gothic Story". Subsequent 18th century contributors included Clara Reeve, Ann Radcliffe, William Beckford (novelist), William Thomas Beckford, and Matthew Gregory Lewis, Matthew Lewis. The Gothic influence continued into the early 19th century, works by the Romantic poetry, Romantic poets, and novelists such as Mary Shelley, Charles Maturin, Walter Scott and E. T. A. Hoffmann frequently drew upon gothic motifs in their works. The early Victorian literature, Victorian period continued the use of gothic, in novels by Charles Dickens and the Brontë family, Brontë sisters, as well as works by the American ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melodrama
A modern melodrama is a dramatic work in which the plot, typically sensationalized and for a strong emotional appeal, takes precedence over detailed characterization. Melodramas typically concentrate on dialogue that is often bombastic or excessively sentimental, rather than action. Characters are often flat, and written to fulfill stereotypes. Melodramas are typically set in the private sphere of the home, focusing on morality and family issues, love, and marriage, often with challenges from an outside source, such as a "temptress", a scoundrel, or an aristocratic villain. A melodrama on stage, filmed, or on television is usually accompanied by dramatic and suggestive music that offers cues to the audience of the drama being presented. In scholarly and historical musical contexts, ''melodramas'' are Victorian dramas in which orchestral music or song was used to accompany the action. The term is now also applied to stage performances without incidental music, novels, films, tel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In Medias Res
A narrative work beginning ''in medias res'' (, "into the middle of things") opens in the midst of the plot (cf. ''ab ovo'', ''ab initio''). Often, exposition is bypassed and filled in gradually, through dialogue, flashbacks or description of past events. For example, ''Hamlet'' begins after the death of Hamlet's father. Characters make reference to King Hamlet's death without the plot's first establishment of said fact. Since the play is about Hamlet and the revenge more so than the motivation, Shakespeare uses ''in medias res'' to bypass superfluous exposition. Works that employ ''in medias res'' often later use flashback and nonlinear narrative for exposition to fill in the backstory. In Homer's ''Odyssey'', the reader first learns about Odysseus's journey when he is held captive on Calypso's island. The reader then finds out, in Books IX through XII, that the greater part of Odysseus's journey precedes that moment in the narrative. In Homer's ''Iliad'' there are fewer flas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Cousine Bette
''La Cousine Bette'' (, ''Cousin Bette'') is an 1846 novel by French author Honoré de Balzac. Set in mid-19th-century Paris, it tells the story of an unmarried middle-aged woman who plots the destruction of her extended family. Bette works with Valérie Marneffe, an unhappily married young lady, to seduce and torment a series of men. One of these is Baron Hector Hulot, husband to Bette's cousin Adeline. He sacrifices his family's fortune and good name to please Valérie, who leaves him for a well-off merchant named Crevel. The book is part of the ''Scènes de la vie parisienne'' section of Balzac's novel sequence ''La Comédie humaine'' ("The Human Comedy"). In the 1840s, a serial format is known as the '' roman-feuilleton'' was highly popular in France, and the most acclaimed expression of it was the socialist writing of Eugène Sue. Balzac wanted to challenge Sue's supremacy, and prove himself the most capable ''feuilleton'' author in France. Writing quickly and with intense ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holy Ghost
For the majority of Christian denominations, the Holy Spirit, or Holy Ghost, is believed to be the third person of the Trinity, a Triune God manifested as God the Father, God the Son, and God the Holy Spirit, each entity itself being God.Grudem, Wayne A. 1994. ''Systematic Theology: An Introduction to Biblical Doctrine.'' Leicester, England: Inter-Varsity Press; Grand Rapids, MI: Zondervan page 226. Nontrinitarian Christians, who reject the doctrine of the Trinity, differ significantly from mainstream Christianity in their beliefs about the Holy Spirit. In Christian theology, pneumatology is the study of the Holy Spirit. Due to Christianity's historical relationship with Judaism, theologians often identify the Holy Spirit with the concept of the ''Ruach Hakodesh'' in Jewish scripture, on the theory that Jesus was expanding upon these Jewish concepts. Similar names, and ideas, include the ''Ruach Elohim'' (Spirit of God), ''Ruach YHWH'' (Spirit of Yahweh), and the ''Ruach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metropolis
A metropolis () is a large city or conurbation which is a significant economic, political, and cultural center for a country or region, and an important hub for regional or international connections, commerce, and communications. A big city belonging to a larger urban agglomeration, but which is not the core of that agglomeration, is not generally considered a metropolis but a part of it. The plural of the word is ''metropolises'', although the Latin plural is ''metropoles'', from the Greek ''metropoleis'' (). For urban centers outside metropolitan areas that generate a similar attraction on a smaller scale for their region, the concept of the regiopolis ("regio" for short) was introduced by urban and regional planning researchers in Germany in 2006. Etymology Metropolis (μητρόπολις) is a Greek word, coming from μήτηρ, ''mḗtēr'' meaning "mother" and πόλις, ''pólis'' meaning "city" or "town", which is how the Greek colonies of antiquity referred to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Splendeurs Et Misères Des Courtisanes
''Splendeurs et misères des courtisanes'', translated variously as ''The Splendors and Miseries of Courtesans'', ''A Harlot High and Low'', or as ''Lost Souls'', is an 1838-1847 novel by French novelist Honoré de Balzac, published in four initially separate parts: * ''Esther Happy'' (''Esther heureuse'', 1838) * ''What Love Costs an Old Man'' (''À combien l’amour revient aux vieillards'', 1843) * ''The End of Evil Ways'' (''Où mènent les mauvais chemins'', 1846) * ''The Last Incarnation of Vautrin'' (''La Dernière incarnation de Vautrin'', 1847) It continues the story of Lucien de Rubempré, who was a main character in ''Illusions perdues'', a preceding Balzac novel. ''Splendeurs et misères des courtisanes'' forms part of Balzac's ''La Comédie humaine''. Plot summary Lucien de Rubempré and the self-proclaimed abbey Carlos Herrera (Vautrin) have made a pact, in which Lucien will arrive at success in Paris if he agrees to follow Vautrin's instructions blindly. Esther v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Père Goriot
''Le Père Goriot'' (, ''"Old Goriot"'' or ''"Father Goriot"'') is an 1835 novel by French novelist and playwright Honoré de Balzac (1799–1850), included in the ''Scènes de la vie privée'' section of his novel sequence ''La Comédie humaine''. Set in Paris in 1819, it follows the intertwined lives of three characters: the elderly doting Goriot, a mysterious criminal-in-hiding named Vautrin and a naive law student named Eugène de Rastignac. Originally published in serial form during the winter of 1834–35, ''Le Père Goriot'' is widely considered Balzac's most important novel.Hunt, p. 95; Brooks (1998), p. ix; Kanes, p. 9. It marks the first serious use by the author of characters who had appeared in other books, a technique that distinguishes Balzac's fiction. The novel is also noted as an example of his realist style, using minute details to create character and subtext. The novel takes place during the Bourbon Restoration, which brought profound changes to French ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vautrin
Vautrin is a character from the novels of French writer Honoré de Balzac in the ''La Comédie humaine'' series. His real name is Jacques Collin . He appears in the novels '' Le Père Goriot'' (Father Goriot, 1834/35) under the name Vautrin, and in ''Illusions perdues'' (Lost illusions, 1837–1843) and ''Splendeurs et misères des courtisanes'' (Scenes from a Courtesan's Life, 1838–1844), the sequel of ''Illusions perdues'', under the name of Abbé Carlos Herrera. In prison, he got the nickname "Trompe-la-Mort" ("Dodgedeath" or "Cheats-Death"), because he managed to avoid the death sentence repeatedly. Background By the time the ''Comédie humaine'' series begins, Jacques Collin is an escaped convict and criminal mastermind fleeing from the police. The character first appears in the La Comédie humaine series using the name of Vautrin, so he is usually referred to in literary criticism under this name. Balzac was inspired to the character by Eugène François Vidocq (1775– ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |