|
Legionnaire
The French Foreign Legion (french: Légion étrangère) is a corps of the French Army which comprises several specialties: infantry, cavalry, engineers, airborne troops. It was created in 1831 to allow foreign nationals into the French Army. It formed part of the Armée d’Afrique, the French Army's units associated with France's colonial project in Africa, until the end of the Algerian war in 1962. Legionnaires are highly trained soldiers and the Legion is unique in that it is open to foreign recruits willing to serve in the French Armed Forces. The Legion is today known as a unit whose training focuses on traditional military skills and on its strong esprit de corps, as its men and women come from different countries with different cultures. Consequently, training is often described as not only physically challenging, but also very stressful psychologically. French citizenship may be applied for after three years' service. Any soldier who is wounded during a battle for France ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Le Boudin
"Le Boudin" (), officially "Marche de la Légion Étrangère" (English "March of the Foreign Legion"), is the official march of the Foreign Legion. "Le Boudin" is a reference to boudin, a type of blood sausage or black pudding. "Le boudin" colloquially meant the gear (rolled up in a blanket) that used to be carried atop the backpacks of Legionnaires. Overview The song relates the Legion's feat of arms in Tuyên Quang (1884–1885) and in Camerone (1863), the date of which (April 30) is celebrated as the Legion's anniversary. While the tune was composed prior to the Legion's departure for Mexico in the 1860s, the lyrics were progressively composed after the Franco-Prussian War since Alsatians and Lorrains flocked to the legion after the regions were annexed by Germany.Fabienne Fischer, ''Alsaciens Et Lorrains En Algérie: Histoire D'Une Migration, 1830–1914'', p.12/ref> The song makes also repeated reference to the fact that the Belgium, Belgians are "lazy shirkers", wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rif War
The Rif War () was an armed conflict fought from 1921 to 1926 between Spain (joined by History of France, France in 1924) and the Berbers, Berber tribes of the mountainous Rif region of northern Morocco. Led by Abd el-Krim, the Riffians at first inflicted several defeats on the Spanish forces by using guerrilla tactics and captured European weapons. After France's military intervention against Abd el-Krim's forces and the major landing of Spanish troops at Alhucemas landing, Al Hoceima, considered the first amphibious landing in history to involve the use of tanks and aircraft, Abd el-Krim surrendered and was taken into exile. In July 1909, Spanish workers constructing a rail-bridge providing access to iron mines near Melilla were attacked by Rifian tribesmen. This incident led to the summoning of reinforcements from Spain itself. A series of skirmishes over the following weeks cost the Spanish over a thousand casualties. By September, the Spanish Army had 40,000 troops in n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foreign Legion Command
The Foreign Legion Command (french: Commandement de la Légion Étrangère, (COMLE)) (official) is the Command of the Foreign Legion in the French Army. The Legion is led by a French general, a Legion officer (french: Officier de Légion) who is usually a general who spent his entire career in Legion units. COMLE also includes the general staff headquarters of the foreign legion command (french: L’Etat-major du COMLE) L'Etat-major du Commandement de la Légion Étrangère (general staff headquarters of the foreign legion command)(official), led by another senior officer, chief of the general staff headquarters of the foreign legion command (french: Chef de L’Etat-major du COMLE) (official). As of 2017, the general staff headquarters of the foreig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Army
The French Army, officially known as the Land Army (french: Armée de Terre, ), is the land-based and largest component of the French Armed Forces. It is responsible to the Government of France, along with the other components of the Armed Forces. The current Chief of Staff of the French Army (CEMAT) is General , a direct subordinate of the Chief of the Defence Staff (CEMA). General Schill is also responsible to the Ministry of the Armed Forces for organization, preparation, use of forces, as well as planning and programming, equipment and Army future acquisitions. For active service, Army units are placed under the authority of the Chief of the Defence Staff (CEMA), who is responsible to the President of France for planning for, and use of forces. All French soldiers are considered professionals, following the suspension of French military conscription, voted in parliament in 1997 and made effective in 2001. , the French Army employed 118,600 personnel (including the Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Honneur Et Fidélité
''Honneur et Fidélité'' ("Honour and Fidelity") is the motto of the Foreign Legion in the French Armed Forces. It has been inscribed on Legion flags instead of the ''Honneur et Patrie'' (Honour and Fatherland) inscribed on flags of the regular French Army of the French Republic. Nevertheless, both mottos share a similar past. History This motto of ''Honneur et Fidélité'' was the one written on the banners of Swiss Military units, notably the Swiss Line Infantry Regiments of the Kingdom of France during the Ancien Regime. Originally formed as the Régiment de Salis (french: Régiment de Salis) (Swiss regiment at the service of France; 12 companies of 170 men) in 1690, Régiment de Diesbach (french: Régiment de Diesbach), becoming then the 85th Line Infantry Regiment (french: 85e régiment d'infanterie) of the French Army in 1791. The 3rd Foreign Regiment ( before the creation of the Foreign Legion), throughout all the campaign battles of the Empire, would remain loyal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Franco-Dahomean War
The Second Franco-Dahomean War, which raged from 1892 to 1894, was a major conflict between France, led by General Alfred-Amédée Dodds, and Dahomey under King Béhanzin. The French emerged triumphant and incorporated Dahomey into their growing colonial territory of French West Africa. Background In 1890, the Fon kingdom of Dahomey and the French Third Republic had gone to war in what was remembered as the First Franco-Dahomean War over the former's rights to certain territories, specifically those in the Ouémé Valley. The Fon ceased hostilities with the French after two military defeats, withdrawing their forces and signing a treaty conceding to all of France's demands. However, Dahomey remained a potent force in the area and quickly re-armed with modern weapons in anticipation of a second, decisive conflict. ''Casus belli'' After re-arming and regrouping, the Fon returned to raiding the Ouémé Valley, the same valley fought over in the first war with France. Vic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grenade (insignia)
A grenade insignia is a form of emblem which represents a stylized old style of hand grenade, with a rising flame. This symbol is used as a charge (heraldry), charge in heraldry and is also featured on the uniforms of numerous military units. Military usage The insignia is featured on the uniforms of such military units as the: *French French Foreign Legion, Foreign Legion *Italian Carabinieri *Italian Fanteria *Italian Cavalleria *Italian Trasmissioni *Italian Granatieri di Sardegna *Italian Trasporti e Materiali *Italian Engineers Corps *Italian Bersaglieri *Dutch Koninklijke Marechaussee *Finnish Defence Forces, Finnish artillery *The Grenadiers Regiment of the Indian Army *British and Commonwealth Grenadier Guards Regiments *British Royal Regiment of Fusiliers *Royal Canadian Engineers *Commissioned Officers of the British Royal Engineers *Commissioned Officers of the British Honourable Artillery Company *Commissioned Officers of the British Royal Artillery (collar badge) *No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Campaign Against Korea
The French expedition to Korea (french: Expédition française en Corée, ) was an 1866 punitive expedition undertaken by the Second French Empire against Joseon Korea in retaliation for the execution of seven French Catholic missionaries. The encounter over Ganghwa Island lasted nearly six weeks. The result was an eventual French retreat, and a check on French influence in the region. The encounter also confirmed Korea in its isolationism for another decade, until Japan forced it to open up to trade in 1876 through the Treaty of Ganghwa. In contemporary South Korea it is known as the ''Byeong-in yangyo'', or "Western disturbance of the ''byeong-in'' year". Background Throughout the history of the Joseon dynasty, Korea maintained a policy of strict isolationism from the outside world (with the exceptions being interaction with the Qing dynasty and occasional trading with Japan through the island of Tsushima). However, it did not succeed entirely in sealing itself off fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sino-French War
The Sino-French War (, french: Guerre franco-chinoise, vi, Chiến tranh Pháp-Thanh), also known as the Tonkin War and Tonquin War, was a limited conflict fought from August 1884 to April 1885. There was no declaration of war. The Chinese armies performed better than its List of Chinese wars and battles#Qing dynasty (1644–1912), other nineteenth-century wars and the war ended with French retreat on land and the momentum in China's favor. However lack of foreign support, French naval supremacy, and northern threats posed by Russia and Japan forced China to enter negotiations. China ceded its sphere of influence in Tonkin (northern Vietnam) to France and recognized all the French treaties with Annam (French protectorate), Annam turning it into a French protectorate. The war strengthened the dominance of Empress Dowager Cixi over the Chinese government, but brought down the government of Prime Minister Jules Ferry in Paris. Both sides ratified the Treaty of Tientsin (1885), Trea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Madagascar Expedition
The Second Madagascar expedition was a French military intervention which took place in 1894–95, sealing the conquest of the Merina Kingdom on the island of Madagascar by France. It was the last phase of the Franco-Hova War and followed the First Madagascar expedition of 1883–85. Background Madagascar was at the time an independent country, ruled from the capital of Antananarivo by the Merina dynasty from the central highlands. The French invasion was triggered by the refusal of Queen Ranavalona III to accept a protectorate treaty from France, despite the signature of the Franco- Hova Treaty of 1885 following the First Madagascar expedition. Resident-general Charles Le Myre de Vilers broke negotiation and effectively declared war on the Malagasy monarchy. The expedition An expeditionary corps was sent under General Jacques Duchesne. First, the harbor of Toamasina on the east coast, and Mahajanga on the west coast, were bombarded and occupied in December 1894 and Janua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
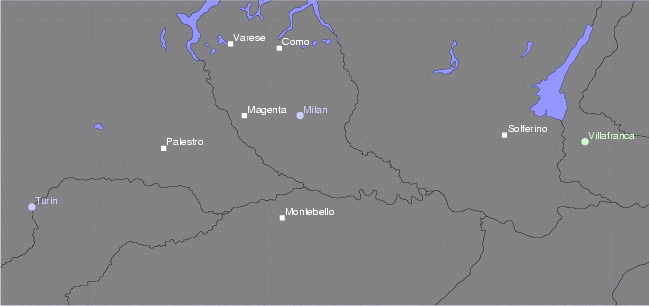
Second Italian War Of Independence
The Second Italian War of Independence, also called the Franco-Austrian War, the Austro-Sardinian War or Italian War of 1859 ( it, Seconda guerra d'indipendenza italiana; french: Campagne d'Italie), was fought by the Second French Empire and the Savoyard Kingdom of Sardinia against the Austrian Empire in 1859 and played a crucial part in the process of Italian Unification. A year prior to the war, in the Plombières Agreement, France agreed to support Sardinia's efforts to expel Austria from Italy in return for territorial compensation in the form of the Duchy of Savoy and the County of Nice. The two states signed a military alliance in January 1859. Sardinia mobilised its army on 9 March 1859, and Austria mobilized on 9 April. On 23 April, Austria delivered an ultimatum to Sardinia demanding its demobilization. Upon Sardinia's refusal, the war began on 26 April. Austria invaded Sardinia three days later, and France declared war on Austria on 3 May. The Austrian invasion wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_-_Fondo_Car-Kutxa_Fototeka.jpg)