|
Left Phrenic Nerve
The phrenic nerve is a mixed motor/sensory nerve which originates from the C3-C5 spinal nerves in the neck. The nerve is important for breathing because it provides exclusive motor control of the diaphragm, the primary muscle of respiration. In humans, the right and left phrenic nerves are primarily supplied by the C4 spinal nerve, but there is also contribution from the C3 and C5 spinal nerves. From its origin in the neck, the nerve travels downward into the chest to pass between the heart and lungs towards the diaphragm. In addition to motor fibers, the phrenic nerve contains sensory fibers, which receive input from the central tendon of the diaphragm and the mediastinal pleura, as well as some sympathetic nerve fibers. Although the nerve receives contributions from nerves roots of the cervical plexus and the brachial plexus, it is usually considered separate from either plexus. The name of the nerve comes from Ancient Greek ''phren'' 'diaphragm'. Structure The phrenic ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervical Plexus
The cervical plexus is a plexus of the anterior rami of the first four cervical spinal nerves which arise from C1 to C4 cervical segment in the neck. They are located laterally to the transverse processes between prevertebral muscles from the medial side and vertebral (m. scalenus, m. levator scapulae, m. splenius cervicis) from lateral side. There is anastomosis with accessory nerve, hypoglossal nerve and sympathetic trunk. It is located in the neck, deep to the sternocleidomastoid muscle. Nerves formed from the cervical plexus innervate the back of the head, as well as some neck muscles. The branches of the cervical plexus emerge from the posterior triangle at the nerve point, a point which lies midway on the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoid. Branches The cervical plexus has two types of branches: cutaneous and muscular. *Cutaneous (4 branches): **Lesser occipital nerve - innervates the skin and the scalp posterosuperior to the auricle (C2) **Great auricular nerve - ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subclavian Vein
The subclavian vein is a paired large vein, one on either side of the body, that is responsible for draining blood from the upper extremities, allowing this blood to return to the heart. The left subclavian vein plays a key role in the absorption of lipids, by allowing products that have been carried by lymph in the thoracic duct to enter the bloodstream. The diameter of the subclavian veins is approximately 1–2 cm, depending on the individual. Structure Each subclavian vein is a continuation of the axillary vein and runs from the outer border of the first rib to the medial border of anterior scalene muscle. From here it joins with the internal jugular vein to form the brachiocephalic vein (also known as "innominate vein"). The angle of union is termed the venous angle. The subclavian vein follows the subclavian artery and is separated from the subclavian artery by the insertion of anterior scalene. Thus, the subclavian vein lies anterior to the anterior scalene while the su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pain
Pain is a distressing feeling often caused by intense or damaging stimuli. The International Association for the Study of Pain defines pain as "an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with, or resembling that associated with, actual or potential tissue damage." In medical diagnosis, pain is regarded as a symptom of an underlying condition. Pain motivates the individual to withdraw from damaging situations, to protect a damaged body part while it heals, and to avoid similar experiences in the future. Most pain resolves once the noxious stimulus is removed and the body has healed, but it may persist despite removal of the stimulus and apparent healing of the body. Sometimes pain arises in the absence of any detectable stimulus, damage or disease. Pain is the most common reason for physician consultation in most developed countries. It is a major symptom in many medical conditions, and can interfere with a person's quality of life and general functioning. Simple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallbladder
In vertebrates, the gallbladder, also known as the cholecyst, is a small hollow organ where bile is stored and concentrated before it is released into the small intestine. In humans, the pear-shaped gallbladder lies beneath the liver, although the structure and position of the gallbladder can vary significantly among animal species. It receives and stores bile, produced by the liver, via the common hepatic duct, and releases it via the common bile duct into the duodenum, where the bile helps in the digestion of fats. The gallbladder can be affected by gallstones, formed by material that cannot be dissolved – usually cholesterol or bilirubin, a product of haemoglobin breakdown. These may cause significant pain, particularly in the upper-right corner of the abdomen, and are often treated with removal of the gallbladder (called a cholecystectomy). Cholecystitis, inflammation of the gallbladder, has a wide range of causes, including result from the impaction of gallstones, inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peritoneum
The peritoneum is the serous membrane forming the lining of the abdominal cavity or coelom in amniotes and some invertebrates, such as annelids. It covers most of the intra-abdominal (or coelomic) organs, and is composed of a layer of mesothelium supported by a thin layer of connective tissue. This peritoneal lining of the cavity supports many of the abdominal organs and serves as a conduit for their blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and nerves. The abdominal cavity (the space bounded by the vertebrae, abdominal muscles, diaphragm, and pelvic floor) is different from the intraperitoneal space (located within the abdominal cavity but wrapped in peritoneum). The structures within the intraperitoneal space are called "intraperitoneal" (e.g., the stomach and intestines), the structures in the abdominal cavity that are located behind the intraperitoneal space are called "retroperitoneal" (e.g., the kidneys), and those structures below the intraperitoneal space are called "subp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
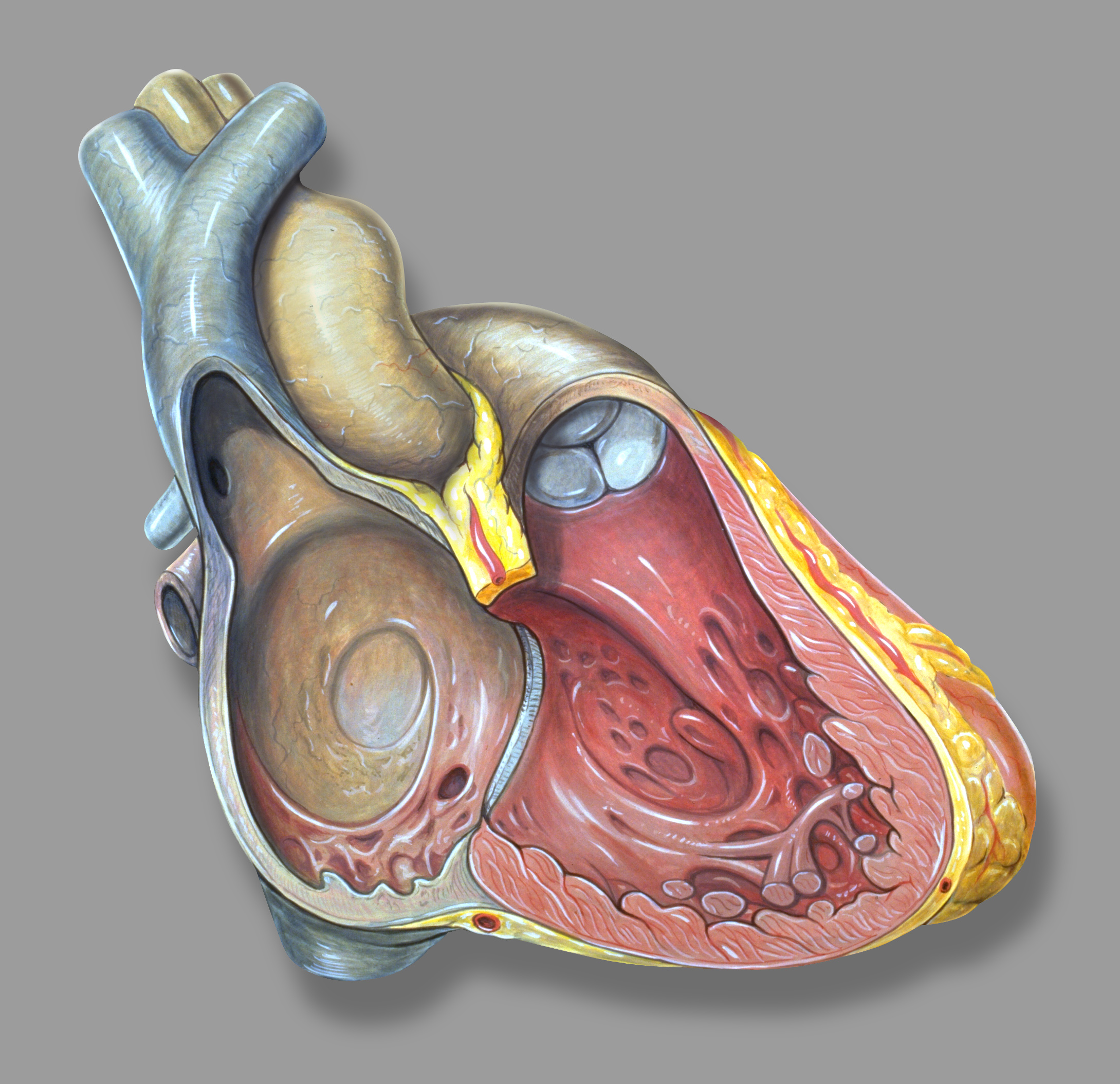
Pericardium
The pericardium, also called pericardial sac, is a double-walled sac containing the heart and the roots of the great vessels. It has two layers, an outer layer made of strong connective tissue (fibrous pericardium), and an inner layer made of serous membrane (serous pericardium). It encloses the pericardial cavity, which contains pericardial fluid, and defines the middle mediastinum. It separates the heart from interference of other structures, protects it against infection and blunt trauma, and lubricates the heart's movements. The English name originates from the Ancient Greek prefix "''peri-''" (περί; "around") and the suffix "''-cardion''" (κάρδιον; "heart"). Anatomy The pericardium is a tough fibroelastic sac which covers the heart from all sides except at the cardiac root (where the great vessels join the heart) and the bottom (where only the serous pericardium exists to cover the upper surface of the central tendon of diaphragm). The fibrous pericardiu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accessory Phrenic Nerve
The subclavian nerve, also known as the nerve to the subclavius, is small branch of the upper trunk of the brachial plexus. It contains axons from C5 and C6. The subclavian nerve innervates the subclavius muscle. Structure The subclavian nerve is a branch of the upper trunk of the brachial plexus. It contains axons derived from the ventral rami of the C5 and C6 cervical spinal nerves. Variation The subclavian nerve can variably give rise to a branch which innervates the diaphragm called the accessory phrenic nerve. The accessory phrenic nerve may rather branch from the C4 or C6 segments or ansa cervicalis. This nerve usually joins with the phrenic nerve before innervating the diaphragm, ventral to the subclavian vein. Function The subclavian nerve innervates the subclavius muscle The subclavius is a small triangular muscle, placed between the clavicle and the first rib. Along with the pectoralis major and pectoralis minor muscles, the subclavius muscle makes up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vascular Access
Vascular access refers to a rapid, direct method of introducing or removing devices or chemicals from the bloodstream. In hemodialysis, vascular access is used to remove the patient's blood so that it can be filtered through the dialyzer. Three primary methods are used to gain access to the blood: an intravenous catheter, an arteriovenous fistula (AV) or a synthetic graft. In the latter two, needles are used to puncture the graft or fistula each time dialysis is performed. The type of vascular access created for patients on hemodialysis is influenced by factors such as the expected time course of a patient's kidney failure and the condition of his or her vasculature. Patients may have multiple accesses, usually because an AV fistula or graft is maturing and a catheter is still being used. The creation of all these three major types of vascular accesses requires surgery. Catheter Catheter access, sometimes called a CVC (central venous catheter), consists of a plastic catheter wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pericardiacophrenic
The pericardiacophrenic artery is a long slender branch of the internal thoracic artery. It anastomoses with the musculophrenic and superior phrenic arteries. Location The pericardiacophrenic artery branches from the internal thoracic artery. It accompanies the phrenic nerve between the pleura and pericardium, to the diaphragm. This is where both the artery and the phrenic nerve are distributed. Function The pericardiacophrenic arteries travel through the thoracic cavity, and are located within and supply the fibrous pericardium. Along with the musculophrenic arteries, they also provide arterial supply to the diaphragm. References External links * - "Pleural Cavities and Lungs: Structures Beneath the Left Mediastinal pleura The pulmonary pleurae (''sing.'' pleura) are the two opposing layers of serous membrane overlying the lungs and the inside of the surrounding chest walls. The inner pleura, called the visceral pleura, covers the surface of each lung and dips b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Left Ventricle
A ventricle is one of two large chambers toward the bottom of the heart that collect and expel blood towards the peripheral beds within the body and lungs. The blood pumped by a ventricle is supplied by an atrium, an adjacent chamber in the upper heart that is smaller than a ventricle. Interventricular means between the ventricles (for example the interventricular septum), while intraventricular means within one ventricle (for example an intraventricular block). In a four-chambered heart, such as that in humans, there are two ventricles that operate in a double circulatory system: the right ventricle pumps blood into the pulmonary circulation to the lungs, and the left ventricle pumps blood into the systemic circulation through the aorta. Structure Ventricles have thicker walls than atria and generate higher blood pressures. The physiological load on the ventricles requiring pumping of blood throughout the body and lungs is much greater than the pressure generated by the atria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Right Atrium
The atrium ( la, ātrium, , entry hall) is one of two upper chambers in the heart that receives blood from the circulatory system. The blood in the atria is pumped into the heart ventricles through the atrioventricular valves. There are two atria in the human heart – the left atrium receives blood from the pulmonary circulation, and the right atrium receives blood from the venae cavae of the systemic circulation. During the cardiac cycle the atria receive blood while relaxed in diastole, then contract in systole to move blood to the ventricles. Each atrium is roughly cube-shaped except for an ear-shaped projection called an atrial appendage, sometimes known as an auricle. All animals with a closed circulatory system have at least one atrium. The atrium was formerly called the 'auricle'. That term is still used to describe this chamber in some other animals, such as the ''Mollusca''. They have thicker muscular walls than the atria do. Structure Humans have a four-chambered h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |