|
Least Squares Regression
Linear least squares (LLS) is the least squares approximation of linear functions to data. It is a set of formulations for solving statistical problems involved in linear regression, including variants for Ordinary least squares, ordinary (unweighted), Weighted least squares, weighted, and Generalized least squares, generalized (correlated) residuals (statistics), residuals. Numerical methods for linear least squares include inverting the matrix of the normal equations and matrix decomposition, orthogonal decomposition methods. Basic formulation Consider the linear equation where Real_number#Vocabulary_and_notation, A \in \mathbb^ and b \in \mathbb^m are given and x \in \mathbb^n is variable to be computed. When m > n, it is generally the case that () has no solution. For example, there is no value of x that satisfies \begin 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 1 \\ 1 & 1 \end x = \begin 1 \\ 1 \\ 0 \end, because the first two rows require that x = (1, 1), but then the third row is not satisf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Least Squares Approximation
The method of least squares is a mathematical optimization technique that aims to determine the best fit function by minimizing the sum of the squares of the differences between the observed values and the predicted values of the model. The method is widely used in areas such as regression analysis, curve fitting and data modeling. The least squares method can be categorized into linear and nonlinear forms, depending on the relationship between the model parameters and the observed data. The method was first proposed by Adrien-Marie Legendre in 1805 and further developed by Carl Friedrich Gauss. History Founding The method of least squares grew out of the fields of astronomy and geodesy, as scientists and mathematicians sought to provide solutions to the challenges of navigating the Earth's oceans during the Age of Discovery. The accurate description of the behavior of celestial bodies was the key to enabling ships to sail in open seas, where sailors could no longer rely on la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bias Of An Estimator
In statistics, the bias of an estimator (or bias function) is the difference between this estimator's expected value and the true value of the parameter being estimated. An estimator or decision rule with zero bias is called ''unbiased''. In statistics, "bias" is an property of an estimator. Bias is a distinct concept from consistency: consistent estimators converge in probability to the true value of the parameter, but may be biased or unbiased (see bias versus consistency for more). All else being equal, an unbiased estimator is preferable to a biased estimator, although in practice, biased estimators (with generally small bias) are frequently used. When a biased estimator is used, bounds of the bias are calculated. A biased estimator may be used for various reasons: because an unbiased estimator does not exist without further assumptions about a population; because an estimator is difficult to compute (as in unbiased estimation of standard deviation); because a biased esti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Percentage Least Squares
In mathematics, a percentage () is a number or ratio expressed as a fraction of 100. It is often denoted using the ''percent sign'' (%), although the abbreviations ''pct.'', ''pct'', and sometimes ''pc'' are also used. A percentage is a dimensionless number (pure number), primarily used for expressing proportions, but percent is nonetheless a unit of measurement in its orthography and usage. Examples For example, 45% (read as "forty-five percent") is equal to the fraction , or 0.45. Percentages are often used to express a proportionate part of a total. (Similarly, one can also express a number as a fraction of 1,000, using the term "per mille" or the symbol "".) Example 1 If 50% of the total number of students in the class are male, that means that 50 out of every 100 students are male. If there are 500 students, then 250 of them are male. Example 2 An increase of $0.15 on a price of $2.50 is an increase by a fraction of = 0.06. Expressed as a percentage, this is a 6% ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newton's Method
In numerical analysis, the Newton–Raphson method, also known simply as Newton's method, named after Isaac Newton and Joseph Raphson, is a root-finding algorithm which produces successively better approximations to the roots (or zeroes) of a real-valued function. The most basic version starts with a real-valued function , its derivative , and an initial guess for a root of . If satisfies certain assumptions and the initial guess is close, then x_ = x_0 - \frac is a better approximation of the root than . Geometrically, is the x-intercept of the tangent of the graph of at : that is, the improved guess, , is the unique root of the linear approximation of at the initial guess, . The process is repeated as x_ = x_n - \frac until a sufficiently precise value is reached. The number of correct digits roughly doubles with each step. This algorithm is first in the class of Householder's methods, and was succeeded by Halley's method. The method can also be extended t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Log-normal Distribution
In probability theory, a log-normal (or lognormal) distribution is a continuous probability distribution of a random variable whose logarithm is normal distribution, normally distributed. Thus, if the random variable is log-normally distributed, then has a normal distribution. Equivalently, if has a normal distribution, then the exponential function of , , has a log-normal distribution. A random variable which is log-normally distributed takes only positive real values. It is a convenient and useful model for measurements in exact and engineering sciences, as well as medicine, economics and other topics (e.g., energies, concentrations, lengths, prices of financial instruments, and other metrics). The distribution is occasionally referred to as the Galton distribution or Galton's distribution, after Francis Galton. The log-normal distribution has also been associated with other names, such as Donald MacAlister#log-normal, McAlister, Gibrat's law, Gibrat and Cobb–Douglas. A l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Template Fit
In mathematics, the term ''linear'' is used in two distinct senses for two different properties: * linearity of a '' function'' (or '' mapping''); * linearity of a ''polynomial''. An example of a linear function is the function defined by f(x)=(ax,bx) that maps the real line to a line in the Euclidean plane R2 that passes through the origin. An example of a linear polynomial in the variables X, Y and Z is aX+bY+cZ+d. Linearity of a mapping is closely related to '' proportionality''. Examples in physics include the linear relationship of voltage and current in an electrical conductor (Ohm's law), and the relationship of mass and weight. By contrast, more complicated relationships, such as between velocity and kinetic energy, are ''nonlinear''. Generalized for functions in more than one dimension, linearity means the property of a function of being compatible with addition and scaling, also known as the superposition principle. Linearity of a polynomial means that its degree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Total Least Squares
In applied statistics, total least squares is a type of errors-in-variables regression, a least squares data modeling technique in which observational errors on both dependent and independent variables are taken into account. It is a generalization of Deming regression and also of orthogonal regression, and can be applied to both linear and non-linear models. The total least squares approximation of the data is generically equivalent to the best, in the Frobenius norm, low-rank approximation of the data matrix. Linear model Background In the least squares method of data modeling, the objective function to be minimized, ''S'', is a quadratic form: :S=\mathbf, where ''r'' is the vector of residuals and ''W'' is a weighting matrix. In linear least squares the model contains equations which are linear in the parameters appearing in the parameter vector \boldsymbol\beta, so the residuals are given by :\mathbf. There are ''m'' observations in y and ''n'' parameters in β wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Instrumental Variables
In statistics, econometrics, epidemiology and related disciplines, the method of instrumental variables (IV) is used to estimate causal relationships when controlled experiments are not feasible or when a treatment is not successfully delivered to every unit in a randomized experiment. Intuitively, IVs are used when an explanatory variable of interest is correlated with the error term (endogenous), in which case ordinary least squares and ANOVA give biased results. A valid instrument induces changes in the explanatory variable (is correlated with the endogenous variable) but has no independent effect on the dependent variable and is not correlated with the error term, allowing a researcher to uncover the causal effect of the explanatory variable on the dependent variable. Instrumental variable methods allow for consistent estimation when the explanatory variables (covariates) are correlated with the error terms in a regression model. Such correlation may occur when: # changes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iteratively Reweighted Least Squares
The method of iteratively reweighted least squares (IRLS) is used to solve certain optimization problems with objective functions of the form of a ''p''-norm: \mathop_ \sum_^n \big, y_i - f_i (\boldsymbol\beta) \big, ^p, by an iterative method in which each step involves solving a weighted least squares problem of the form:C. Sidney Burrus, Iterative Reweighted Least Squares' \boldsymbol\beta^ = \underset \sum_^n w_i (\boldsymbol\beta^) \big, y_i - f_i (\boldsymbol\beta) \big, ^2. IRLS is used to find the maximum likelihood estimates of a generalized linear model, and in robust regression to find an M-estimator, as a way of mitigating the influence of outliers in an otherwise normally-distributed data set, for example, by minimizing the least absolute errors rather than the least square errors. One of the advantages of IRLS over linear programming and convex programming is that it can be used with Gauss–Newton and Levenberg–Marquardt numerical algorithms. Exam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
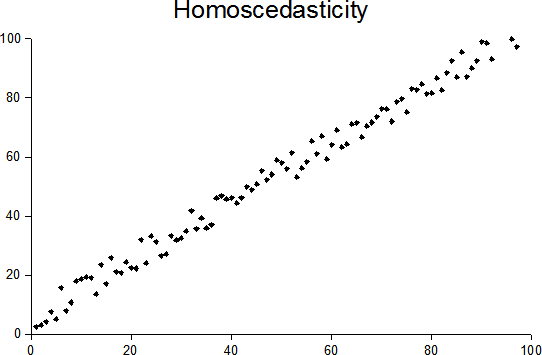
Heteroscedasticity
In statistics, a sequence of random variables is homoscedastic () if all its random variables have the same finite variance; this is also known as homogeneity of variance. The complementary notion is called heteroscedasticity, also known as heterogeneity of variance. The spellings ''homoskedasticity'' and ''heteroskedasticity'' are also frequently used. “Skedasticity” comes from the Ancient Greek word “skedánnymi”, meaning “to scatter”. Assuming a variable is homoscedastic when in reality it is heteroscedastic () results in unbiased but inefficient point estimates and in biased estimates of standard errors, and may result in overestimating the goodness of fit as measured by the Pearson coefficient. The existence of heteroscedasticity is a major concern in regression analysis and the analysis of variance, as it invalidates statistical tests of significance that assume that the modelling errors all have the same variance. While the ordinary least squares ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multicollinearity
In statistics, multicollinearity or collinearity is a situation where the predictors in a regression model are linearly dependent. Perfect multicollinearity refers to a situation where the predictive variables have an ''exact'' linear relationship. When there is perfect collinearity, the design matrix X has less than full rank, and therefore the moment matrix X^X cannot be inverted. In this situation, the parameter estimates of the regression are not well-defined, as the system of equations has infinitely many solutions. Imperfect multicollinearity refers to a situation where the predictive variables have a ''nearly'' exact linear relationship. Contrary to popular belief, neither the Gauss–Markov theorem nor the more common maximum likelihood justification for ordinary least squares relies on any kind of correlation structure between dependent predictors (although perfect collinearity can cause problems with some software). There is no justification for the pra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homoscedasticity
In statistics, a sequence of random variables is homoscedastic () if all its random variables have the same finite variance; this is also known as homogeneity of variance. The complementary notion is called heteroscedasticity, also known as heterogeneity of variance. The spellings ''homoskedasticity'' and ''heteroskedasticity'' are also frequently used. “Skedasticity” comes from the Ancient Greek word “skedánnymi”, meaning “to scatter”. Assuming a variable is homoscedastic when in reality it is heteroscedastic () results in Biased estimator, unbiased but Efficiency (statistics), inefficient point estimates and in biased estimates of standard errors, and may result in overestimating the goodness of fit as measured by the Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient, Pearson coefficient. The existence of heteroscedasticity is a major concern in regression analysis and the analysis of variance, as it invalidates statistical hypothesis testing, statistical tests ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |