|
Leakage Reactance
Leakage inductance derives from the electrical property of an imperfectly-coupled transformer whereby each winding behaves as a self-inductance in series with the winding's respective ohmic resistance constant. These four winding constants also interact with the transformer's mutual inductance. The winding leakage inductance is due to leakage flux not linking with all turns of each imperfectly-coupled winding. Leakage reactance is usually the most important element of a power system transformer due to power factor, voltage drop, reactive power consumption and fault current considerations. Leakage inductance depends on the geometry of the core and the windings. Voltage drop across the leakage reactance results in often undesirable supply regulation with varying transformer load. But it can also be useful for harmonic isolation ( attenuating higher frequencies) of some loads. Leakage inductance applies to any imperfectly-coupled magnetic circuit device including motors. Leakag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transformer
A transformer is a passive component that transfers electrical energy from one electrical circuit to another circuit, or multiple circuits. A varying current in any coil of the transformer produces a varying magnetic flux in the transformer's core, which induces a varying electromotive force (EMF) across any other coils wound around the same core. Electrical energy can be transferred between separate coils without a metallic (conductive) connection between the two circuits. Faraday's law of induction, discovered in 1831, describes the induced voltage effect in any coil due to a changing magnetic flux encircled by the coil. Transformers are used to change AC voltage levels, such transformers being termed step-up or step-down type to increase or decrease voltage level, respectively. Transformers can also be used to provide galvanic isolation between circuits as well as to couple stages of signal-processing circuits. Since the invention of the first constant-potential transfo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Electrotechnical Commission
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC; in French: ''Commission électrotechnique internationale'') is an international standards organization that prepares and publishes international standards for all electrical, electronic and related technologies – collectively known as "electrotechnology". IEC standards cover a vast range of technologies from power generation, transmission and distribution to home appliances and office equipment, semiconductors, fibre optics, batteries, solar energy, nanotechnology and marine energy as well as many others. The IEC also manages four global conformity assessment systems that certify whether equipment, system or components conform to its international standards. All electrotechnologies are covered by IEC Standards, including energy production and distribution, electronics, magnetics and electromagnetics, electroacoustics, multimedia, telecommunication and medical technology, as well as associated general disciplines such as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voltage Regulation
In electrical engineering, particularly power engineering, voltage regulation is a measure of change in the voltage magnitude between the sending and receiving end of a component, such as a transmission or distribution line. Voltage regulation describes the ability of a system to provide near constant voltage over a wide range of load conditions. The term may refer to a passive property that results in more or less voltage drop under various load conditions, or to the active intervention with devices for the specific purpose of adjusting voltage. Electrical power systems In electrical power systems, voltage regulation is a dimensionless quantity defined at the receiving end of a transmission line as: :\text VR = \frac \times 100 where ''Vnl'' is voltage at no load and ''Vfl'' is voltage at full load. The percent voltage regulation of an ideal transmission line, as defined by a transmission line with zero resistance and reactance, would equal zero due to ''Vnl'' equaling ''Vfl'' a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
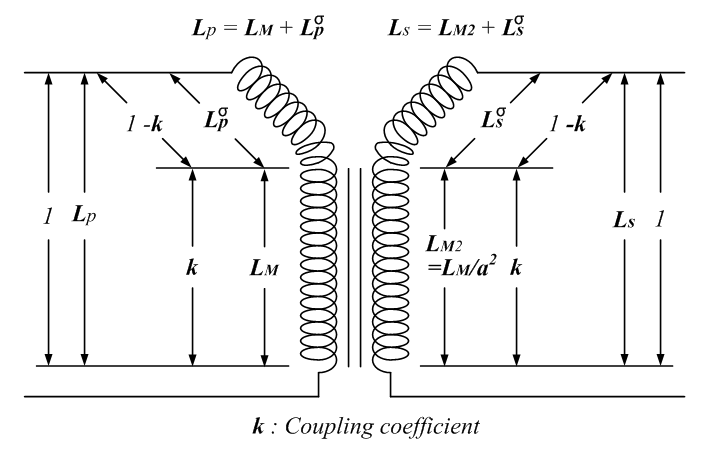
Main & Leakage Inductances
Main may refer to: Geography * Main River (other) **Most commonly the Main (river) in Germany * Main, Iran, a village in Fars Province *"Spanish Main", the Caribbean coasts of mainland Spanish territories in the 16th and 17th centuries *''The Main'', the diverse core running through Montreal, Quebec, Canada, also separating the Two Solitudes *Main (lunar crater), located near the north pole of the Moon *Main (Martian crater) People and organisations * Main (surname), a list of people with this family name *Ma'in, alternate spelling for the Minaeans, an ancient people of modern-day Yemen *Main (band), a British ambient band formed in 1991 * Chas. T. Main, an American engineering and hydroelectric company founded in 1893 *MAIN (Mountain Area Information Network), former operator of WPVM-LP (MAIN-FM) in Asheville, North Carolina, U.S. Ships * ''Main'' (ship), an iron sailing ship launched in 1884 * SS ''Main'', list of steamships with this name * ''Main'' (A515), a moder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equivalent Circuit
In electrical engineering and science, an equivalent circuit refers to a theoretical circuit that retains all of the electrical characteristics of a given circuit. Often, an equivalent circuit is sought that simplifies calculation, and more broadly, that is a simplest form of a more complex circuit in order to aid analysis. In its most common form, an equivalent circuit is made up of linear, passive elements. However, more complex equivalent circuits are used that approximate the nonlinear behavior of the original circuit as well. These more complex circuits often are called ''macromodels'' of the original circuit. An example of a macromodel is the Boyle circuit for the 741 operational amplifier. Examples Thévenin and Norton equivalents One of linear circuit theory's most surprising properties relates to the ability to treat any two-terminal circuit no matter how complex as behaving as only a source and an impedance, which have either of two simple equivalent circuit forms: * Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open-circuit Test
The open-circuit test, or no-load test, is one of the methods used in electrical engineering to determine the no-load impedance in the excitation branch of a transformer. The no load is represented by the open circuit, which is represented on the right side of the figure as the "hole" or incomplete part of the circuit. Method The secondary of the transformer is left open-circuited. A wattmeter is connected to the primary. An ammeter is connected in series with the primary winding. A voltmeter is optional since the applied voltage is the same as the voltmeter reading. Rated voltage is applied at primary. If the applied voltage is normal voltage then normal flux will be set up. Since iron loss is a function of applied voltage, normal iron loss will occur. Hence the iron loss is maximum at rated voltage. This maximum iron loss is measured using the wattmeter. Since the impedance of the series winding of the transformer is very small compared to that of the excitation branch, all o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Short-circuit Test
The purpose of a short-circuit test is to determine the series branch parameters of the equivalent circuit of a transformer. Method The test is conducted on the high-voltage (HV) side of the transformer where the low-voltage (LV) side (or the secondary) is short-circuited. A wattmeter is connected to the primary side. An ammeter is connected in series with the primary winding. A voltmeter is optional since the applied voltage is the same as the voltmeter reading. Now with the help of a variac, the applied voltage is slowly increased until the ammeter gives a reading equal to the rated current of the HV side. After reaching the rated current of the HV side, all three instruments reading (Voltmeter, Ammeter, and wattmeter readings) are recorded. The ammeter reading gives the primary equivalent of full load current IL. As the voltage applied for full load current in short circuit test on transformer is quite small compared to the rated primary voltage of the transformer, the ir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Derivative
In mathematics, the derivative of a function of a real variable measures the sensitivity to change of the function value (output value) with respect to a change in its argument (input value). Derivatives are a fundamental tool of calculus. For example, the derivative of the position of a moving object with respect to time is the object's velocity: this measures how quickly the position of the object changes when time advances. The derivative of a function of a single variable at a chosen input value, when it exists, is the slope of the tangent line to the graph of the function at that point. The tangent line is the best linear approximation of the function near that input value. For this reason, the derivative is often described as the "instantaneous rate of change", the ratio of the instantaneous change in the dependent variable to that of the independent variable. Derivatives can be generalized to functions of several real variables. In this generalization, the derivativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |