|
Lead Mountain (Maine)
Lead Mountain, at high is a peak in eastern Maine. Lead Mountain is located north of the town of Beddington on the border of Hancock and Washington counties in Downeast Maine. The isolation of Lead Mountain is 35.73 miles, and it is easily visible from miles away along Maine state routes 9 and 193 The southern slopes of Lead Mountain are the location of the Bear Brook Watershed in Maine, a long-term research site dedicated to studying the effects of acid deposition on a landscape. Likewise, the southeast slopes of the mountain are drained by Bear Brook. The bedrock of the area contains small blebs of pyrrhotite, which may be mistaken for lead. Lead Mountain is located on private land, but can be hiked by the public. The primary route to Lead Mountain begins just north of the at the gated end of a dirt road southeast of the peak. The route follows the dirt road beyond the gate before turning up a path that ascends southeast of the summit before continuing up the east side of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hancock County, Maine
Hancock County is a county located in the U.S. state of Maine. As of the 2020 census, the population was 55,478. Its county seat is Ellsworth. The county was incorporated on June 25, 1789, and named for John Hancock, the first governor of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts. Geography According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of , of which is land and (32%) is water. The county high point is Cadillac Mountain, 1527 feet, the highest summit on the U.S. Atlantic seaboard. Adjacent counties * Penobscot County — north * Washington County — northeast *Waldo County — west * Knox County — southwest Demographics 2000 census As of the census of 2000, there were 51,791 people, 21,864 households, and 14,233 families living in the county. The population density was 33 people per square mile (13/km2). There were 33,945 housing units at an average density of 21 per square mile (8/km2). The racial makeup of the county was 97.61% White, 0.25% Bla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acid Deposition
Acid rain is rain or any other form of precipitation that is unusually acidic, meaning that it has elevated levels of hydrogen ions (low pH). Most water, including drinking water, has a neutral pH that exists between 6.5 and 8.5, but acid rain has a pH level lower than this and ranges from 4–5 on average. The more acidic the acid rain is, the lower its pH is. Acid rain can have harmful effects on plants, aquatic animals, and infrastructure. Acid rain is caused by emissions of sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxide, which react with the water molecules in the atmosphere to produce acids. Acid rain has been shown to have adverse impacts on forests, freshwaters, soils, microbes, insects and aquatic life-forms. In ecosystems, persistent acid rain reduces tree bark durability, leaving flora more susceptible to environmental stressors such as drought, heat/cold and pest infestation. Acid rain is also capable of detrimenting soil composition by stripping it of nutrients such as ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lead Mountain Wm1
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cut, lead is a shiny gray with a hint of blue. It tarnishes to a dull gray color when exposed to air. Lead has the highest atomic number of any stable element and three of its isotopes are endpoints of major nuclear decay chains of heavier elements. Lead is toxic, even in small amounts, especially to children. Lead is a relatively unreactive post-transition metal. Its weak metallic character is illustrated by its amphoteric nature; lead and lead oxides react with acids and bases, and it tends to form covalent bonds. Compounds of lead are usually found in the +2 oxidation state rather than the +4 state common with lighter members of the carbon group. Exceptions are mostly limited to organolead compounds. Like the lighter members of the group, lea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Lead Mountain Pond
Upper Lead Mountain Pond is a lake in Hancock County, Maine, United States. It is located less than west of the Lead Mountain and north of Maine State Route 9 near the town of Beddington. The inflow to Bear Pond comes from several small stream, and it drains via a small stream to Middle/Lower Lead Mountain Pond. Several unpaved roads provide access to the lake and private residences surrounding it. The Lake is surrounded by forest and supports several fish, including landlocked Atlantic salmon, brook trout, white perch, yellow perch, and chain pickerel The chain pickerel (''Esox niger'') is a species of freshwater fish in the pike family (family Esocidae) of order Esociformes. The chain pickerel and the American pickerel (''E. americanus'') belong to the ''Esox'' genus of pike. Taxonomy French .... References Lakes of Hancock County, Maine Glacial lakes of the United States Lakes of Maine {{Maine-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bear Pond (Hancock County, Maine)
Bear Pond is a lake in Hancock County, Maine, United States. It is located less than west of the Washington County border, approximately southeast of the summit of Lead Mountain, and northwest of Maine State Route 9 near the town of Beddington Beddington is a suburban settlement in the London Borough of Sutton on the boundary with the London Borough of Croydon. Beddington is formed from a village of the same name which until early the 20th century still included land which became t .... The inflow to Bear Pond comes primarily from Bear Brook, which drains the southeastern slopes of Lead Mountain, which comprises primarily the Bear Brook Watershed in Maine (BBWM), an experimental forest. There are two USGS stream gauges on the East and West Branches of Bear Brook. An unpaved road provides access to the BBWM from state route 9 and passes about from the eastern end of the pond. Bear Pond is surrounded by forest and is drained at its western end by the Little Narraguag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulf Of Maine
The Gulf of Maine is a large gulf of the Atlantic Ocean on the east coast of North America. It is bounded by Cape Cod at the eastern tip of Massachusetts in the southwest and by Cape Sable Island at the southern tip of Nova Scotia in the northeast. The gulf includes the entire coastlines of the U.S. states of New Hampshire and Maine, as well as Massachusetts north of Cape Cod, and the southern and western coastlines of the provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Nova Scotia, respectively. The gulf was named for the adjoining English colonial Province of Maine, which was in turn likely named by early explorers after the Maine (province), province of Maine in France. Massachusetts Bay, Penobscot Bay, Passamaquoddy Bay, and the Bay of Fundy are all arms of the Gulf of Maine. Geography and hydrography The Gulf of Maine is a roughly rectangular depression with a surface area of around , enclosed to the west and north by the North American mainland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
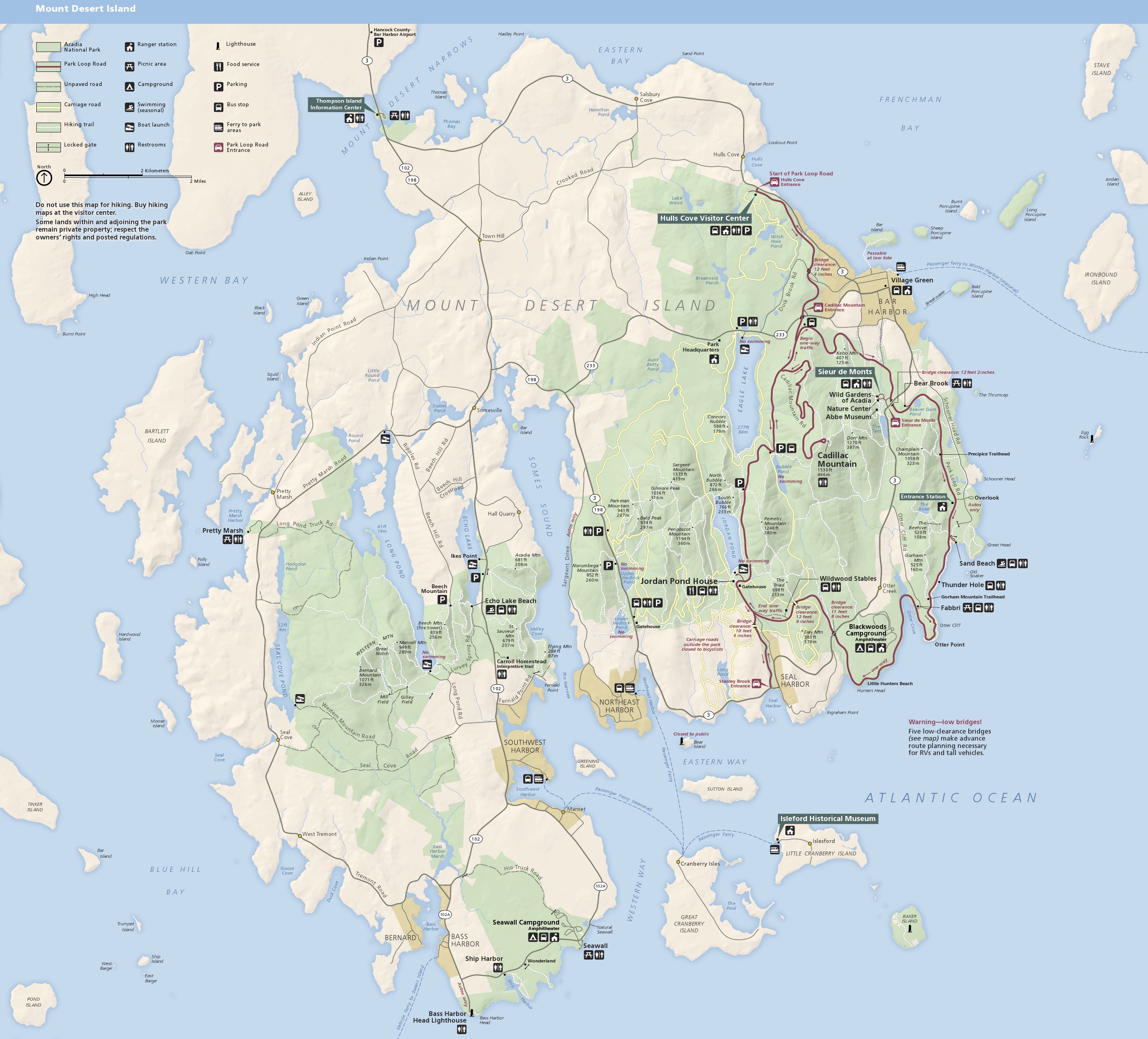
Acadia National Park
Acadia National Park is an American national park located along the mid-section of the Maine coast, southwest of Bar Harbor. The park preserves about half of Mount Desert Island, part of the Isle au Haut, the tip of the Schoodic Peninsula, and portions of 16 smaller outlying islands. It protects the natural beauty of the rocky headlands, including the highest mountains along the Atlantic coast. Acadia boasts a glaciated coastal and island landscape, an abundance of habitats, a high level of biodiversity, clean air and water, and a rich cultural heritage. The park contains the tallest mountain on the Atlantic Coast of the United States (Cadillac Mountain), exposed granite domes, glacial erratics, U-shaped valleys, and cobble beaches. Its mountains, lakes, streams, wetlands, forests, meadows, and coastlines contribute to a diversity of plants and animals. Weaved into this landscape is a historic carriage road system financed by John D. Rockefeller Jr. In total, it encompasses . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dirt Road
A dirt road or track is a type of unpaved road not paved with asphalt, concrete, brick, or stone; made from the native material of the land surface through which it passes, known to highway engineers as subgrade material. Dirt roads are suitable for vehicles; a narrower path for pedestrians, animals, and possibly small vehicles would be called a dirt track—the distinction is not well-defined. Unpaved roads with a harder surface made by the addition of material such as gravel and aggregate (stones), might be referred to as dirt roads in common usage but are distinguished as improved roads by highway engineers. (Improved unpaved roads include gravel roads, laterite roads, murram roads and macadamized roads.) Compared to a gravel road, a dirt road is not usually graded regularly to produce an enhanced camber to encourage rainwater to drain off the road, and drainage ditches at the sides may be absent. They are unlikely to have embankments through low-lying areas. This lea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrrhotite
Pyrrhotite is an iron sulfide mineral with the formula Fe(1-x)S (x = 0 to 0.2). It is a nonstoichiometric variant of FeS, the mineral known as troilite. Pyrrhotite is also called magnetic pyrite, because the color is similar to pyrite and it is weakly magnetic. The magnetism decreases as the iron content increases, and troilite is non-magnetic.Vaughan, D. J.; Craig, J. R. "Mineral Chemistry of Metal Sulfides" Cambridge University Press, Cambridge: 1978. . Structure Pyrrhotite exists as a number of polytypes of hexagonal or monoclinic crystal symmetry; several polytypes often occur within the same specimen. Their structure is based on the NiAs unit cell. As such, Fe occupies an octahedral site and the sulfide centers occupy trigonal prismatic sites. Materials with the NiAs structure often are non-stoichiometric because they lack up to 1/8th fraction of the metal ions, creating vacancies. One of such structures is pyrrhotite-4C (Fe7S8). Here "4" indicates that iron vacancies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bleb (mineralogy)
In geology, mineralogy, and petrology, a bleb is a small bubble-like inclusion of one mineral within a larger mineral. An example is a bleb of sylvite within chlorite The chlorite ion, or chlorine dioxide anion, is the halite with the chemical formula of . A chlorite (compound) is a compound that contains this group, with chlorine in the oxidation state of +3. Chlorites are also known as salts of chlorous ac .... Blebs tend to be brightly coloured. References *Kamenetsky VS et al. Chloride and carbonate immiscible liquids at the closure of the kimberlite magma evolution (Udachnaya-East kimberlite, Siberia) ''Chemical Geology'', Volume 237, Issues 3-4, 5 March 2007, Pages 384-400 DOI: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2006.07.010 Mineralogy {{geology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bear Brook Watershed In Maine
The Bear Brook Watershed in Maine (BBWM) is an experimental forest operated by the University of Maine in Hancock County, Maine, United States. The BBWM focuses around the two small first order branches of Bear Brook on the southeastern slopes of Lead Mountain above Bear Pond. Two years of monitoring studies began in 1987, after which the two watersheds of East and West Bear Brook were determined to be nearly identical. The West Bear Brook watershed was experimentally acidified with ammonium sulfate every other month from November 1989 until August 2016 to study the effects of sulfur and nitrogen acid deposition. East Bear Brook has been used as an untreated reference. Related research topics at BBWM include climate change, carbon sequestration Carbon sequestration is the process of storing carbon in a carbon pool. Carbon dioxide () is naturally captured from the atmosphere through biological, chemical, and physical processes. These changes can be accelerated through cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maine
Maine () is a state in the New England and Northeastern regions of the United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Quebec to the northeast and northwest, respectively. The largest state by total area in New England, Maine is the 12th-smallest by area, the 9th-least populous, the 13th-least densely populated, and the most rural of the 50 U.S. states. It is also the northeasternmost among the contiguous United States, the northernmost state east of the Great Lakes, the only state whose name consists of a single syllable, and the only state to border exactly one other U.S. state. Approximately half the area of Maine lies on each side of the 45th parallel north in latitude. The most populous city in Maine is Portland, while its capital is Augusta. Maine has traditionally been known for its jagged, rocky Atlantic Ocean and bayshore coastlines; smoothly contoured mountains; heavily f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)

