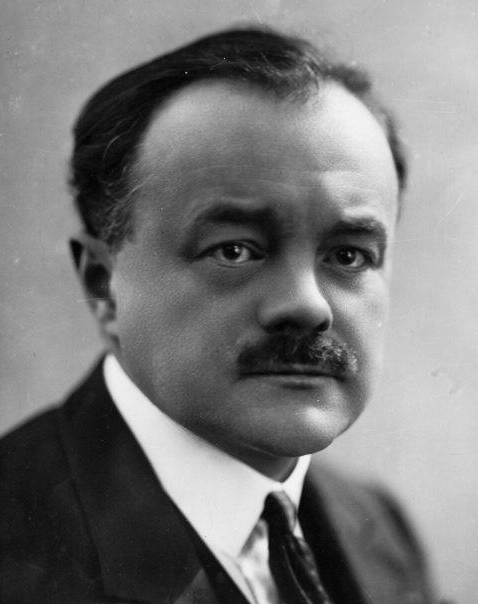|
Le Petit Elfe Ferme-l'œil
''Le Petit Elfe Ferme-l'œil'' (Op. 73) is an orchestral suite by Florent Schmitt adapted from his music for the homonymous ballet ("divertissement chorégraphique") after a tale by Hans Christian Andersen. on litteratureaudio.com The concert suite developed from a suite written in 1912 entitled ''une semaine de Petit Elfe ferme-l'œil'' was premiered on 1 December 1923 at the |
Suite (music)
A suite, in Western classical music, is an ordered set of instrumental or orchestral/concert band pieces. It originated in the late 14th century as a pairing of dance tunes; and grew in scope so that by the early 17th century it comprised up to five dances, sometimes with a Prelude (music), prelude. The separate Movement (music), movements were often thematically and tonally linked. The term can also be used to refer to similar forms in other musical traditions, such as the Ottoman Classical Music, Turkish fasıl and the Arab music, Arab nuubaat. In the Baroque music, Baroque era, the suite was an important musical form, also known as ''Suite de danses'', ''Ordre'' (the term favored by François Couperin), ''Partita'', or ''Ouverture'' (after the theatrical "overture" which often included a series of dances) as with the orchestral suites of Christoph Graupner, Georg Philipp Telemann, Telemann and Johann Sebastian Bach, J.S. Bach. During the 18th century, the suite fell out of fav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarabande
The sarabande (from ) is a dance in triple metre, or the music written for such a dance. History The Sarabande evolved from a Spanish dance with Arab influences, danced by a lively double line of couples with castanets. A dance called ''zarabanda'' is first mentioned in 1539 in Central America in the poem ''Vida y tiempo de Maricastaña'', written in Panama by Fernando de Guzmán Mejía. In 1596, Alonso López, "el Pinciano", traces its origins even to the cult of Dionysus. The dance seems to have been especially popular in the 16th and 17th centuries, initially in Spain and in the Spanish colonies. The Jesuit priest Juan de Mariana thought it indecent, describing it in his ''Tratato contra los juegos públicos'' (Treatise Against Public Amusements, 1609) as "a dance and song so loose in its words and so ugly in its motions that it is enough to excite bad emotions in even very decent people".Jane Bellingham, "Sarabande", ''The Oxford Companion to Music'', edited by Alison ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orchestral Suites
An orchestra (; ) is a large instrumental ensemble typical of classical music, which combines instruments from different families. There are typically four main sections of instruments: * String instruments, such as the violin, viola, cello, and double bass * Woodwinds, such as the flute, oboe, clarinet, bassoon, and occasional saxophone * Brass instruments, such as the French horn (commonly known as the "horn"), trumpet, trombone, cornet, and tuba, and sometimes euphonium * Percussion instruments, such as the timpani, snare drum, bass drum, cymbals, triangle, tambourine, tam-tam and mallet percussion instruments Other instruments such as the piano, harpsichord, pipe organ, and celesta may sometimes appear in a fifth keyboard section or may stand alone as soloist instruments, as may the concert harp and, for performances of some modern compositions, electronic instruments, and guitars. A full-size Western orchestra may sometimes be called a or philharmonic orchestra (fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compositions By Florent Schmitt
Composition or Compositions may refer to: Arts and literature *Composition (dance), practice and teaching of choreography *Composition (language), in literature and rhetoric, producing a work in spoken tradition and written discourse, to include visuals and digital space *Composition (visual arts), the plan, placement or arrangement of the elements of art in a work * ''Composition'' (Peeters), a 1921 painting by Jozef Peeters *Composition studies, the professional field of writing instruction * ''Compositions'' (album), an album by Anita Baker *Digital compositing, the practice of digitally piecing together a still image or video *Musical composition, an original piece of music, or the process of creating a new piece Computer science *Compose key, a key on a computer keyboard *Compositing window manager a component of a computer's graphical user interface that draws windows and/or their borders *Function composition (computer science), an act or mechanism to combine simple functi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data
Data ( , ) are a collection of discrete or continuous values that convey information, describing the quantity, quality, fact, statistics, other basic units of meaning, or simply sequences of symbols that may be further interpreted formally. A datum is an individual value in a collection of data. Data are usually organized into structures such as tables that provide additional context and meaning, and may themselves be used as data in larger structures. Data may be used as variables in a computational process. Data may represent abstract ideas or concrete measurements. Data are commonly used in scientific research, economics, and virtually every other form of human organizational activity. Examples of data sets include price indices (such as the consumer price index), unemployment rates, literacy rates, and census data. In this context, data represent the raw facts and figures from which useful information can be extracted. Data are collected using technique ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fayard
Fayard (complete name: ''Librairie Arthème Fayard'') is a French Paris-based publishing house established in 1857. Fayard is controlled by Hachette Livre. In 1999, Éditions Pauvert became part of Fayard. Claude Durand was director of Fayard from 1980 until his retirement in 2009. He was replaced by Olivier Nora, previously head of Éditions Grasset & Fasquelle another division of the Hachette group. On 6 November 2013, Nora was replaced by Sophie de Closets, who officially took over at the beginning of 2014. In December 2009, Hachette Littérature (publisher of the ''Pluriel'' pocket collection) was absorbed by Fayard. Isabelle Seguin, the director of Hachette Littérature, became literary director of Fayard. Imprints Fayard has three imprints: * Editions Mille et Une Nuits * Editions Mazarine * Pauvert Works published Works published by Editions Fayard include: *''Dictionnaire de la France médiévale'' by French historian Jean Favier * ''Les Égarés'' by French writ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
François-René Tranchefort
François-René Tranchefort (30 June 1933 – 22 May 2019) was a contemporary French musicologist. Biography Tranchefort has written, edited or directed, alone or in collaboration with other musicologists, a number of reference works on a wide range of themes related to classical music: chamber music, symphonic music, piano, harpsichord, opera, sacred music, choral, and musical instruments. on Amazon. Among others, he has collaborated with Harry Halbreich
Harry Halbreich (Berlin, 9 February 1931 – Brussels, 27 June 2016) was a Belgian musi ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentatonic Scale
A pentatonic scale is a musical scale with five notes per octave, in contrast to heptatonic scales, which have seven notes per octave (such as the major scale and minor scale). Pentatonic scales were developed independently by many ancient civilizations and are still used in various musical styles to this day. As Leonard Bernstein put it: "The universality of this scale is so well known that I'm sure you could give me examples of it, from all corners of the earth, as from Scotland, or from China, or from Africa, and from American Indian cultures, from East Indian cultures, from Central and South America, Australia, Finland ...now, that is a true musico-linguistic universal." There are two types of pentatonic scales: Those with semitones (hemitonic) and those without (anhemitonic). Types Hemitonic and anhemitonic Musicology commonly classifies pentatonic scales as either ''hemitonic'' or ''anhemitonic''. Hemitonic scales contain one or more semitones and anhemitonic s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert Wolff (conductor)
Albert Louis Wolff (19 January 1884 – 20 February 1970) was a French conductor and composer of Dutch descent. Most of his career was spent in European venues, with the exception of two years that he spent as a conductor at the Metropolitan Opera and a few years in Buenos Aires during the Second World War. He is most known for holding the position of principal conductor with the Opéra-Comique in Paris for several years. He was married to the French mezzo-soprano Simone Ballard. Biography Early life and education Wolff was born in Paris, of Dutch parents, though he was a French citizen from birth, never lived in the Netherlands, and never had a Dutch passport. When only 12 years old, he began his musical education at the Paris Conservatoire. There, he studied with such teachers as André Gedalge, Xavier Leroux, and Paul Antonin Vidal. At the same time he played the piano in cabarets and was organist at the Église Saint-Thomas-d'Aquin (Paris) for four years. Upon graduat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Florent Schmitt
Florent Schmitt (; 28 September 187017 August 1958) was a French composer. He was part of the group known as Les Apaches. His most famous pieces are ''La tragédie de Salome'' and ''Psaume XLVII'' ( Psalm 47). He has been described as "one of the most fascinating of France's lesser-known classical composers". Biography Early life and career Born in Meurthe-et-Moselle, Schmitt took music lessons in Nancy with the local composer Gustave Sandré. At the age of 19 he entered the Paris Conservatoire, where he studied with Gabriel Fauré, Jules Massenet, Théodore Dubois, and Albert Lavignac. In 1900 he won the Prix de Rome. During the 1890s he became friendly with Frederick Delius, who was living in Paris at the time, and Schmitt prepared vocal scores for four of Delius's operas: '' Irmelin'', ''The Magic Fountain'', '' Koanga'' and '' A Village Romeo and Juliet''. From 1929 to 1939 Schmitt worked as a music critic for ''Le Temps'', where he proved controversial. He was known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, largest city of France. With an estimated population of 2,048,472 residents in January 2025 in an area of more than , Paris is the List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, fourth-most populous city in the European Union and the List of cities proper by population density, 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2022. Since the 17th century, Paris has been one of the world's major centres of finance, diplomacy, commerce, culture, Fashion capital, fashion, and gastronomy. Because of its leading role in the French art, arts and Science and technology in France, sciences and its early adoption of extensive street lighting, Paris became known as the City of Light in the 19th century. The City of Paris is the centre of the Île-de-France region, or Paris Region, with an official estimated population of 12,271,794 inhabitants in January 2023, or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opéra-Comique
The Opéra-Comique () is a Paris opera company which was founded around 1714 by some of the popular Théâtre de la foire, theatres of the Parisian fairs. In 1762 the company was merged with – and for a time took the name of – its chief rival, the Comédie-Italienne at the Hôtel de Bourgogne (theatre), Hôtel de Bourgogne. It was also called the Théâtre-Italien up to about 1793, when it again became most commonly known as the Opéra-Comique. Today the company's official name is Théâtre national de l'Opéra-Comique, and its theatre, with a capacity of around 1,248 seats, sometimes referred to as the Salle Favart (the third on this site), is located at Place Boïeldieu in the 2nd arrondissement of Paris, not far from the Palais Garnier, one of the theatres of the Paris Opéra. The musicians and others associated with the Opéra-Comique have made important contributions to operatic history and tradition in France and to French opera. Its current mission is to reconnect with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |