|
Laura Ruetsche
Laura Ruetsche is an American philosopher focusing on the foundations of quantum physics, feminist philosophy and philosophy of science. Ruetsche is a Professor and Chair of the department of philosophy at the University of Michigan. Her book, ''Interpreting Quantum Theories: The Art of the Possible ''was published in 2011 and received the 2013 Lakatos Award. She has also published on a diverse array of topics, exploring, among other things, philosophically salient differences between non-relativistic quantum mechanics and quantum field theory, modal semantics for quantum physics and virtue-epistemological theories of warrant. She is the partner of Gordon Beloalso at the philosophy department of the University of Michigan. Education and career Ruetsche graduated with a Bachelor of Arts, B.A. in Physics and Philosophy with a minor in Classical Greek from Carleton College. She went on to earn her B.Phil. in Philosophy at the University of Oxford, writing her thesis o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Citizen
Citizenship of the United States is a legal status that entails Americans with specific rights, duties, protections, and benefits in the United States. It serves as a foundation of fundamental rights derived from and protected by the Constitution and laws of the United States, such as freedom of expression, due process, the rights to vote (however, not all citizens have the right to vote in all federal elections, for example, those living in Puerto Rico), live and work in the United States, and to receive federal assistance. There are two primary sources of citizenship: birthright citizenship, in which persons born within the territorial limits of the United States are presumed to be a citizen, or—providing certain other requirements are met—born abroad to a United States citizen parent, and naturalization, a process in which an eligible legal immigrant applies for citizenship and is accepted. The first of these two pathways to citizenship is specified in the Citizenship Cla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
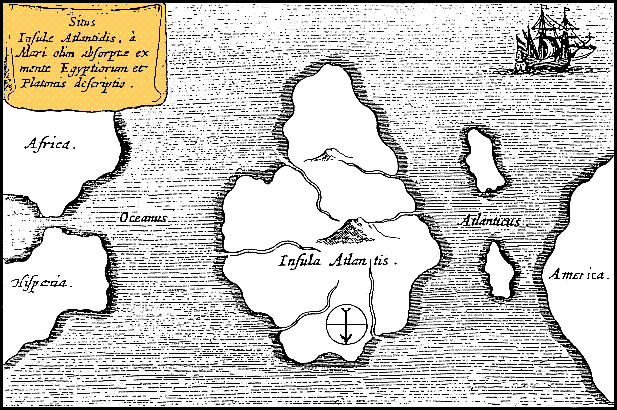
Timaeus (dialogue)
''Timaeus'' (; grc-gre, Τίμαιος, Timaios, ) is one of Plato's dialogues, mostly in the form of long monologues given by Critias and Timaeus, written 360 BC. The work puts forward reasoning on the possible nature of the physical world and human beings and is followed by the dialogue ''Critias''. Participants in the dialogue include Socrates, Timaeus, Hermocrates, and Critias. Some scholars believe that it is not the Critias of the Thirty Tyrants who appears in this dialogue, but his grandfather, who is also named Critias. It has been suggested from some traditions (Diogenes Laertius (VIII 85) from Hermippus of Smyrna (3rd century BC) and Timon of Phlius ( 320 – 235 BC)) that ''Timaeus'' was influenced by a book about Pythagoras, written by Philolaus, although this assertion is generally considered false. Introduction The dialogue takes place the day after Socrates described his ideal state. In Plato's works, such a discussion occurs in the ''Republic''. Socrates fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandra Harding
Sandra G. Harding (born 1935) is an American philosopher of feminist and postcolonial theory, epistemology, research methodology, and philosophy of science. She directed the UCLA Center for the Study of Women from 1996 to 2000, and co-edited '' Signs: Journal of Women in Culture and Society'' from 2000 to 2005. She is currently a Distinguished Professor Emeritus of Education and Gender Studies at UCLA and a Distinguished Affiliate Professor of Philosophy at Michigan State University. In 2013 she was awarded the John Desmond Bernal Prize by the Society for the Social Studies of Science (4S). Education and career Sandra Harding received her undergraduate degree from Douglass College of Rutgers University in 1956. After 12 years working as legal researcher, editor, and fifth-grade math teacher in New York City and Poughkeepsie, N.Y., she returned to graduate school and earned a doctorate from the Department of Philosophy at New York University in 1973. Harding's first u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenomenological Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics is a branch of physics that deals with heat, work, and temperature, and their relation to energy, entropy, and the physical properties of matter and radiation. The behavior of these quantities is governed by the four laws of thermodynamics which convey a quantitative description using measurable macroscopic physical quantities, but may be explained in terms of microscopic constituents by statistical mechanics. Thermodynamics applies to a wide variety of topics in science and engineering, especially physical chemistry, biochemistry, chemical engineering and mechanical engineering, but also in other complex fields such as meteorology. Historically, thermodynamics developed out of a desire to increase the efficiency of early steam engines, particularly through the work of French physicist Sadi Carnot (1824) who believed that engine efficiency was the key that could help France win the Napoleonic Wars. Scots-Irish physicist Lord Kelvin was the first to formulate a co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ontological Commitments
In metaphysics, ontology is the philosophical study of being, as well as related concepts such as existence, becoming, and reality. Ontology addresses questions like how entities are grouped into categories and which of these entities exist on the most fundamental level. Ontologists often try to determine what the categories or highest kinds are and how they form a system of categories that encompasses classification of all entities. Commonly proposed categories include substances, properties, relations, states of affairs and events. These categories are characterized by fundamental ontological concepts, including particularity and universality, abstractness and concreteness, or possibility and necessity. Of special interest is the concept of ontological dependence, which determines whether the entities of a category exist on the most fundamental level. Disagreements within ontology are often about whether entities belonging to a certain category exist and, if so, h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Realism
Scientific realism is the view that the universe described by science is real regardless of how it may be interpreted. Within philosophy of science, this view is often an answer to the question "how is the success of science to be explained?" The discussion on the success of science in this context centers primarily on the status of unobservable entities apparently talked about by scientific theories. Generally, those who are scientific realists assert that one can make valid claims about unobservables (viz., that they have the same ontological status) as observables, as opposed to instrumentalism. Main features Scientific realism involves two basic positions. First, it is a set of claims about the features of an ideal scientific theory; an ideal theory is the sort of theory science aims to produce. Second, it is the commitment that science will eventually produce theories very much like an ideal theory and that science has done pretty well thus far in some domains. It is imp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Degrees Of Freedom (physics And Chemistry)
In physics and chemistry, a degree of freedom is an independent physical parameter in the formal description of the state of a physical system. The set of all states of a system is known as the system's phase space, and the degrees of freedom of the system are the dimensions of the phase space. The location of a particle in three-dimensional space requires three position coordinates. Similarly, the direction and speed at which a particle moves can be described in terms of three velocity components, each in reference to the three dimensions of space. If the time evolution of the system is deterministic (where the state at one instant uniquely determines its past and future position and velocity as a function of time) such a system has six degrees of freedom. If the motion of the particle is constrained to a lower number of dimensions – for example, the particle must move along a wire or on a fixed surface – then the system has fewer than six degrees of freedom. On the oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematical Formulation Of Quantum Mechanics
The mathematical formulations of quantum mechanics are those mathematical formalisms that permit a rigorous description of quantum mechanics. This mathematical formalism uses mainly a part of functional analysis, especially Hilbert spaces, which are a kind of linear space. Such are distinguished from mathematical formalisms for physics theories developed prior to the early 1900s by the use of abstract mathematical structures, such as infinite-dimensional Hilbert spaces ( ''L''2 space mainly), and operators on these spaces. In brief, values of physical observables such as energy and momentum were no longer considered as values of functions on phase space, but as eigenvalues; more precisely as spectral values of linear operators in Hilbert space. These formulations of quantum mechanics continue to be used today. At the heart of the description are ideas of ''quantum state'' and ''quantum observables'', which are radically different from those used in previous models of physical r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hilbert Space
In mathematics, Hilbert spaces (named after David Hilbert) allow generalizing the methods of linear algebra and calculus from (finite-dimensional) Euclidean vector spaces to spaces that may be infinite-dimensional. Hilbert spaces arise naturally and frequently in mathematics and physics, typically as function spaces. Formally, a Hilbert space is a vector space equipped with an inner product that defines a distance function for which the space is a complete metric space. The earliest Hilbert spaces were studied from this point of view in the first decade of the 20th century by David Hilbert, Erhard Schmidt, and Frigyes Riesz. They are indispensable tools in the theories of partial differential equations, quantum mechanics, Fourier analysis (which includes applications to signal processing and heat transfer), and ergodic theory (which forms the mathematical underpinning of thermodynamics). John von Neumann coined the term ''Hilbert space'' for the abstract concept that under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rutgers University
Rutgers University (; RU), officially Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey, is a Public university, public land-grant research university consisting of four campuses in New Jersey. Chartered in 1766, Rutgers was originally called Queen's College, and was affiliated with the Reformed Church in America, Dutch Reformed Church. It is the eighth-oldest college in the United States, the second-oldest in New Jersey (after Princeton University), and one of the nine U.S. colonial colleges that were chartered before the American Revolution.Stoeckel, Althea"Presidents, professors, and politics: the colonial colleges and the American revolution", ''Conspectus of History'' (1976) 1(3):45–56. In 1825, Queen's College was renamed Rutgers College in honor of Colonel Henry Rutgers, whose substantial gift to the school had stabilized its finances during a period of uncertainty. For most of its existence, Rutgers was a Private university, private liberal arts college but it has evolved int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornell University
Cornell University is a private statutory land-grant research university based in Ithaca, New York. It is a member of the Ivy League. Founded in 1865 by Ezra Cornell and Andrew Dickson White, Cornell was founded with the intention to teach and make contributions in all fields of knowledge—from the classics to the sciences, and from the theoretical to the applied. These ideals, unconventional for the time, are captured in Cornell's founding principle, a popular 1868 quotation from founder Ezra Cornell: "I would found an institution where any person can find instruction in any study." Cornell is ranked among the top global universities. The university is organized into seven undergraduate colleges and seven graduate divisions at its main Ithaca campus, with each college and division defining its specific admission standards and academic programs in near autonomy. The university also administers three satellite campuses, two in New York City and one in Education City, Qatar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middlebury College
Middlebury College is a private liberal arts college in Middlebury, Vermont. Founded in 1800 by Congregationalists, Middlebury was the first operating college or university in Vermont. The college currently enrolls 2,858 undergraduates from all 50 states and 74 countries and offers 44 majors in the arts, humanities, literature, foreign languages, social sciences, and natural sciences, as well as joint engineering programs with Columbia University, Dartmouth College, and Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute. In addition to its undergraduate liberal arts program, the school also has graduate schools, the Middlebury College Language Schools, the Bread Loaf School of English, and the Middlebury Institute of International Studies at Monterey, as well as its C.V. Starr-Middlebury Schools Abroad international programs. It is the among the ''Little Ivies'', an unofficial group of academically selective liberal arts colleges, mostly in the northeastern United States. Middlebury is known f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |