|
Lauenburg (district)
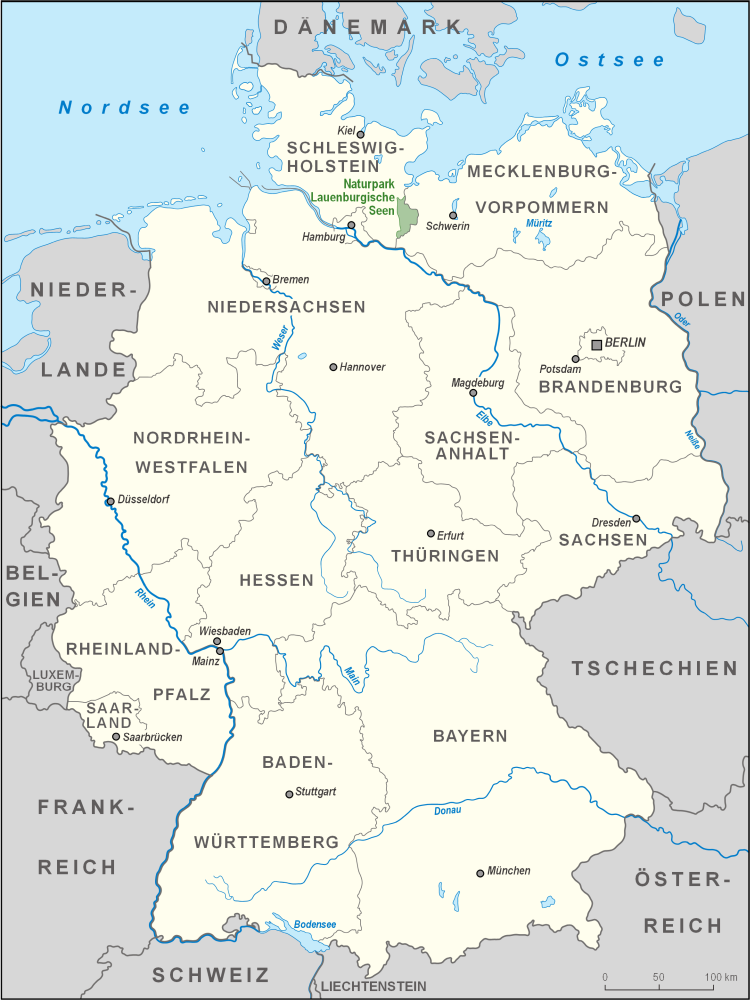
Herzogtum Lauenburg ( en, Duchy of Lauenburg; ) is the southernmost ''Kreis'', or Districts of Germany, district, officially called Kreis Herzogtum Lauenburg (), of Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. It is bordered by (from the west and clockwise) the district of Stormarn (district), Stormarn, the city of Lübeck, the state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern (districts of Nordwestmecklenburg and Ludwigslust-Parchim), the state of Lower Saxony (districts of Lüneburg (district), Lüneburg and Harburg (district), Harburg), and the city state of Hamburg. The district of Herzogtum Lauenburg is named after the former Duchy of Saxe-Lauenburg. Geography The district's territory comprises most of the former Duchy's territory north of the river Elbe, except of the Amt Neuhaus. All the former Saxe-Lauenburgian areas beyond the Elbe belong today to the Lower Saxony, Lower Saxon districts of Cuxhaven (district), Cuxhaven (Land of Hadeln), Harburg (district), Harburg and Lüneburg (district), Lüneburg. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amt Neuhaus
Amt Neuhaus is a municipality in the District of Lüneburg, in Lower Saxony, Germany. ''Amt'' means "municipal office" in German. The original "municipal office of ''Neuhaus''" existed since at least the 17th century until 1885, consecutively as part of Saxe-Lauenburg (which ceased to exist in 1689), Electorate of Hanover (1689-1810), Kingdom of Hanover (1814-1866), and the Prussian Province of Hanover (1866-1885). In 1885, Prussia dissolved the municipality of Neuhaus, while the area remained part of the Province of Hanover. However, in 1945 the area of the former municipality was annexed to Mecklenburg and thus became a part of the Soviet Occupation Zone due to lying on the right bank of the Elbe River, and thus along with the former County of Blankenburg and the municipality of Calvörde became one of a few small areas of the Province of Hanover (since 1946 Lower Saxony) that were part of East Germany from 1949 to 1990. After German reunification in 1990, the municipalities t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert I, Duke Of Saxony
Albert I (; c. 1175 – 7 October 1260) was a Duke of Saxony, Angria, and Westphalia; Lord of Nordalbingia; Count of Anhalt; and Prince-elector and Archmarshal of the Holy Roman Empire. Even though his grandfather Albert the Bear had held the Saxon dukedom between 1138 and 1142, this Albert is counted as the first. Biography A member of the House of Ascania, Albert was a younger son of Bernard III, Duke of Saxony, and Judith (Jutta) of Poland, daughter of Mieszko III the Old. After his father's death in 1212, the surviving sons of the late duke divided his lands according to the laws of the House of Ascania: The elder Henry received Anhalt and the younger Albert the Saxon duchy. Albert supported Otto IV, Holy Roman Emperor, in his wars against the Hohenstaufen. In 1218, Albert's maternal uncle Prince-Archbishop Valdemar of Denmark, who had been deposed from his Prince-Archbishopric of Bremen, found refuge in Saxony, before he joined the Loccum Abbey as monk. On 22 July 1227, Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John I, Duke Of Saxony
John I (1249 – 30 July 1285) ruled as duke of Saxony from 1260 until 1282. John was the elder son of Duke Albert I of Saxony and his third wife Helen, a daughter of Otto the Child. John and his younger brother Albert II jointly ruled the Duchy of Saxony after the death of their father Albert I in 1260. In 1269, 1272, and 1282 the brothers gradually divided their land within the three territorially unconnected Saxon areas (one called Land of Hadeln around Otterndorf, another around Lauenburg upon Elbe and the third around Wittenberg), thus preparing a partition. As part of this arrangement John I became Burgrave of Magdeburg in 1269. In the imperial election in 1273, Albert II represented the jointly ruling brothers. In 1270, John married Ingeborg Birgersdotter of Småland (*c. 1253–30 June 1302*, Mölln), a daughter or grandchild of Birger jarl. They had eight children, among them the following: * Helen (c. 1272–1337), married firstly to Count Günther IX of Schwarzbu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert II, Duke Of Saxony
Albert II of Saxony ( Wittenberg upon Elbe, ca. 1250 – 25 August 1298, near Aken) was a son of Duke Albert I of Saxony and his third wife Helen of Brunswick and Lunenburg, a daughter of Otto the Child. He supported Rudolph I of Germany at his election as Roman king and became his son-in-law. After the death of their father Albert I in 1260 Albert II jointly ruled the Duchy of Saxony with his elder brother John I, and thereafter with the latter's sons. Life In 1269, 1272 and 1282 the brothers gradually divided their governing competences within the three territorially unconnected Saxon areas (one called Land of Hadeln around Otterndorf, another around Lauenburg upon Elbe and the third around Wittenberg), thus preparing a partition. In the imperial election in 1273 Albert II represented the jointly ruling brothers. In return Rudolph I had married his daughter Agnes of Habsburg to Albert II. After John I had resigned in 1282 in favour of his three minor sons Eric I, John II and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Saxony
The Duchy of Saxony ( nds, Hartogdom Sassen, german: Herzogtum Sachsen) was originally the area settled by the Saxons in the late Early Middle Ages, when they were subdued by Charlemagne during the Saxon Wars from 772 and incorporated into the Carolingian Empire (Francia) by 804. Upon the 843 Treaty of Verdun, Saxony was one of the five German stem duchies of East Francia; Duke Henry the Fowler was elected German king in 919. Upon the deposition of the Welf duke Henry the Lion in 1180, the ducal title fell to the House of Ascania, while numerous territories split from Saxony, such as the Principality of Anhalt in 1218 and the Welf Duchy of Brunswick-Lüneburg in 1235. In 1296 the remaining lands were divided between the Ascanian dukes of Saxe-Lauenburg and Saxe-Wittenberg, the latter obtaining the title of Electors of Saxony by the Golden Bull of 1356. Geography The Saxon stem duchy covered the greater part of present-day Northern Germany, including the modern German states ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ratzeburger See
is a lake in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe .... At an elevation of 4 m, its surface area is 14.3 km². Amidst the lake is an island upon which the City of Ratzeburg is located, accessible from the mainland via three isthmuses. The island is home to the Old Town, including a cathedral - one of the oldest in Germany. At the end of the 17th century, the old castle at the western end of the island was completely destroyed and the site has since been degraded to a mere parking lot. External links * Lakes of Schleswig-Holstein Ratzeburg LRatzeburgerSee {{SchleswigHolstein-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lauenburg Lakes Nature Park
The Lauenburg Lakes Nature Park (german: Naturpark Lauenburgische Seen) at www.germany.travel. Retrieved 20 Apr 2020. was founded in and lies in the district of Lauenburg in the southeastern part of the German state of . It is right on the border with the state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern in the , a [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
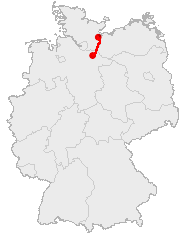
Stecknitz Canal
The Stecknitz Canal (german: Stecknitzfahrt) was an artificial waterway in northern Germany which connected Lauenburg and Lübeck on the Old Salt Route by linking the tiny rivers Stecknitz (a tributary of the Trave) and Delvenau (a tributary of the Elbe), thus establishing an inland water route across the drainage divide from the North Sea to the Baltic Sea. Built between 1391 and 1398, the Stecknitz Canal was the first European summit-level canal and one of the earliest artificial waterways in Europe. In the 1890s the canal was replaced by an enlarged and straightened waterway called the Elbe–Lübeck Canal, which includes some of the Stecknitz Canal's watercourse. The original artificial canal was deep and wide; the man-made segment ran for , with a total length of including the rivers it linked. The canal included seventeen wooden locks (of which the ''Palmschleuse'' at Lauenburg still exists) that managed the elevation difference between its endpoints and the highest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Salt Route
The Old Salt Route was a medieval trade route in Northern Germany, one of the ancient network of salt roads which were used primarily for the transport of salt and other staples. In Germany it was referred to as ''Alte Salzstraße''. Salt was very valuable at that time; it was sometimes referred to as "white gold." The vast majority of the salt transported on the road was produced from brine near Lüneburg, a city in the northern central part of the country and then transported to Lübeck, a major seaport on Germany's Baltic Sea coast. History Historians generally recognize the Old Salt Route as part of a much longer path, which functioned as an important connection between the northern and southern reaches of the country. One of the oldest documents that confirms Lüneburg and its role in refining and transporting salt dates from 956 A.D. According to that document, King Otto I the Great granted the St. Michaelis Monastery in Lüneburg the customs revenue from the saltworks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |