|
Latimer, Buckinghamshire
Latimer is a village that sits on the border between Buckinghamshire and Hertfordshire, England. In 2013, the civil parish of Latimer was renamed, Latimer and Ley Hill. The parish, forming part of the Buckinghamshire district of Chiltern, includes the villages of Latimer, Ley Hill and Tyler's Hill. History Latimer was originally joined with the adjacent village of Chenies. Both were anciently called Isenhampstead, at a time when there was a royal palace in the vicinity. However, in the reign of King Edward III of England the lands were split between two manorial barons: Thomas Cheyne in the village that later became known as 'Chenies', and William Latimer in this village. Latimer came into possession of the manor in 1326. At the time of the English Civil War Latimer belonged to the Earl of Devonshire. When Charles I was captured by the Parliamentarian forces he was brought to Latimer on his way to London. The triangular village green has two memorials. The first is a me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latimer And Ley Hill
Latimer and Ley Hill, formerly just Latimer, is a civil parish under Buckinghamshire Council Buckinghamshire Council is a unitary local authority in England, the area of which constitutes most of the ceremonial county of Buckinghamshire. It was created in April 2020 from the areas that were previously administered by Buckinghamshire Cou ..., in the ceremonial county of Buckinghamshire, England. The parish includes Latimer, Ley Hill and Tyler's Hill. As of 2020, it has a population of 986. Until 2020 it was in the Chiltern district. History The parish was renamed from "Latimer" to "Latimer and Ley Hill" on 9 April 2013. The parish council was also renamed from "Latimer Parish Council" to "Latimer and Ley Hill Parish Council" at the same time. It was felt that the name better reflected the area since Ley Hill ward accounted for 65% of the electors. References External linksParish council [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baron Latimer
The title Baron Latimer or Latymer has been created, by the definitions of modern peerage law, four times in the Peerage of England. Of these, one (of Snape) was restored from abeyance in 1913; one (of Braybrook) is forfeit; the other two (both of Corby) are dormant, although their heir is well known. Name and title All of these, and the title of Viscount Latimer, belong to the descendants of the same medieval family, whose surname was Latimer (''Latiner'' or "translator"); the fourteenth-century form of the name should therefore be ''le Latimer'', but it is often found as ''de Latimer'' as though it were a placename. Armorials The arms of Latimer appear originally to have been ''Gules, a cross patonce or''. The stems of a cross patonce should expand, as a cross pattée, then terminate more or less like a cross flory. The earliest surviving representation is on the seal of William Latimer, 1st Baron Latimer (died 1305), affixed to the Barons' Letter of 1301 to the Pope. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London Underground
The London Underground (also known simply as the Underground or by its nickname the Tube) is a rapid transit system serving Greater London and some parts of the adjacent counties of Buckinghamshire, Essex and Hertfordshire in England. The Underground has its origins in the Metropolitan Railway, the world's first underground passenger railway. Opened on 10 January 1863, it is now part of the Circle, District, Hammersmith & City and Metropolitan lines. The first line to operate underground electric traction trains, the City & South London Railway in 1890, is now part of the Northern line. The network has expanded to 11 lines, and in 2020/21 was used for 296 million passenger journeys, making it one of the world's busiest metro systems. The 11 lines collectively handle up to 5 million passenger journeys a day and serve 272 stations. The system's first tunnels were built just below the ground, using the cut-and-cover method; later, smaller, roughly circular tu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marylebone Station
Marylebone station ( ) is a Central London railway terminus and connected London Underground station in the Marylebone area of the City of Westminster. On the National Rail network it is also known as London Marylebone and is the southern terminus of the Chiltern Main Line to Birmingham. An accompanying Underground station is on the Bakerloo line between Edgware Road and in Transport for London's fare zone 1. The station opened on 15 March 1899 as the London terminus of the Great Central Main Line (GCML), the last major railway to open in Britain for 100 years, linking the capital to the cities of Leicester, Sheffield and Manchester. Marylebone was the last of London's main line termini to be built and is one of the smallest, opening with half of the platforms originally planned. There has been an interchange with the Bakerloo line since 1907, but not with any other lines. Traffic declined at Marylebone station from the mid-20th century, particularly after the GCML close ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aylesbury Railway Station
Aylesbury railway station is a railway station in Aylesbury, Buckinghamshire, England, on the London–Aylesbury line from via Amersham. It is from Aylesbury to Marylebone. A branch line from on the Chiltern Main Line terminates at the station. It was the terminus for London Underground's Metropolitan line until the service was cut back to Amersham in 1961. The station was also known as Aylesbury Town under the management of British Railways from until the 1960s. History The first station on the site was opened in 1863 by the Wycombe Railway, which in 1867 was taken over by the Great Western Railway. In 1868 the Aylesbury & Buckingham Railway (later part of the Metropolitan Railway) reached Aylesbury. When opened, the line to Aylesbury from Princes Risborough was broad gauge. To avoid mixed gauge track when the standard gauge Aylesbury and Buckingham arrived at the station in 1868, the section to Princes Risborough was converted to standard gauge, and therefore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London To Aylesbury Line
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a major settlement for two millennia. The City of London, its ancient core and financial centre, was founded by the Romans as ''Londinium'' and retains its medieval boundaries.See also: Independent city § National capitals The City of Westminster, to the west of the City of London, has for centuries hosted the national government and parliament. Since the 19th century, the name "London" has also referred to the metropolis around this core, historically split between the counties of Middlesex, Essex, Surrey, Kent, and Hertfordshire, which largely comprises Greater London, governed by the Greater London Authority.The Greater London Authority consists of the Mayor of London and the London Assembly. The London Mayor is distinguished from the Lord May ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Little Chalfont
Little Chalfont is a village and civil parish in south-east Buckinghamshire, England. It is one of a group of villages known collectively as The Chalfonts, which also comprises Chalfont St Giles and Chalfont St Peter. Little Chalfont is located around east of Amersham and northwest of Charing Cross, central London. History Little Chalfont is a 20th-century creation triggered by the coming of the Metropolitan Railway. A station called Chalfont Road was opened in 1889 at the northernmost point of Chalfont St Giles Parish where the parishes of Amersham, Chenies, and Chalfont St Giles met. At that time, the area was remote from the centres of the villages and towns, and consisted of isolated farms and cottages, and did not have a specific name. The coming of the railway eventually brought local housing development, and a community developed around the station, which was renamed Chalfont & Latimer station in 1915, a name which it retains today. The first appearance of the name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
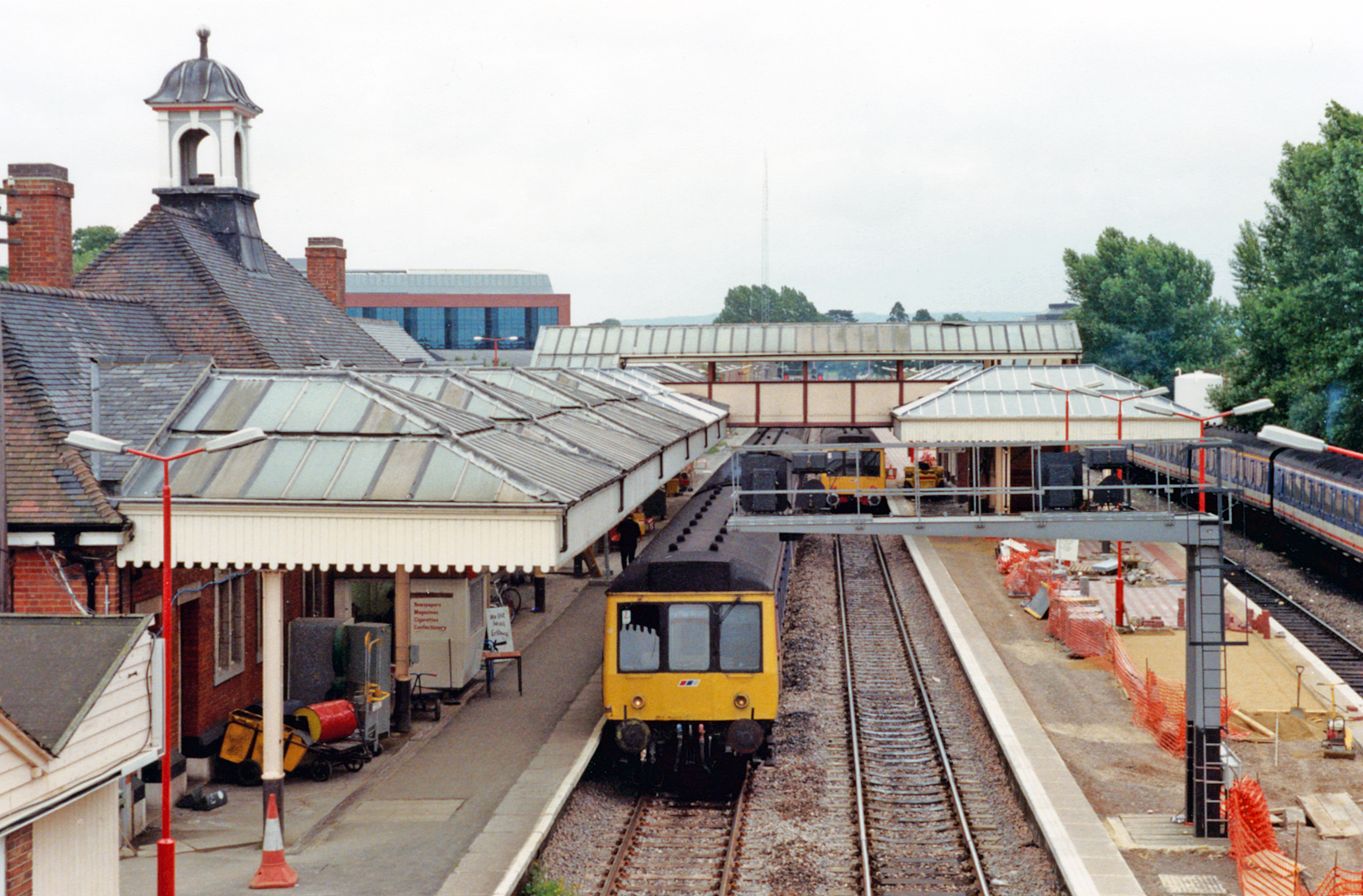
Chalfont & Latimer Station
Chalfont & Latimer is a London Underground and National Rail station in Travelcard Zone 8 (previously zone C) on the Metropolitan line, in Buckinghamshire. It also serves the Chiltern Railways line to Aylesbury. Chalfont & Latimer station is located just before the junction for trains to Chesham. The station serves Chalfont St Giles, Chalfont St Peter, Little Chalfont and Latimer. It is located in Little Chalfont. It opened as "Chalfont Road" on 8 July 1889 but changed to the present name from 1 November 1915. The station is a good location to alight from to explore the Chess Valley. History Chalfont & Latimer station was formerly served by steam–hauled Metropolitan line trains with a changeover to an electric locomotive at Rickmansworth. The electrification north of Rickmansworth to Amersham and Chesham was completed in 1960, with steam trains being finally withdrawn in 1961. British Railways took over the operation of the service north of Amersham at the same time, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir George Gilbert Scott
Sir George Gilbert Scott (13 July 1811 – 27 March 1878), known as Sir Gilbert Scott, was a prolific English Gothic Revival architect, chiefly associated with the design, building and renovation of churches and cathedrals, although he started his career as a leading designer of workhouses. Over 800 buildings were designed or altered by him. Scott was the architect of many iconic buildings, including the Midland Grand Hotel at St Pancras Station, the Albert Memorial, and the Foreign and Commonwealth Office, all in London, St Mary's Cathedral, Glasgow, the main building of the University of Glasgow, St Mary's Cathedral in Edinburgh and King's College Chapel, London. Life and career Born in Gawcott, Buckingham, Buckinghamshire, Scott was the son of the Reverend Thomas Scott (1780–1835) and grandson of the biblical commentator Thomas Scott. He studied architecture as a pupil of James Edmeston and, from 1832 to 1834, worked as an assistant to Henry Roberts. He also worked a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
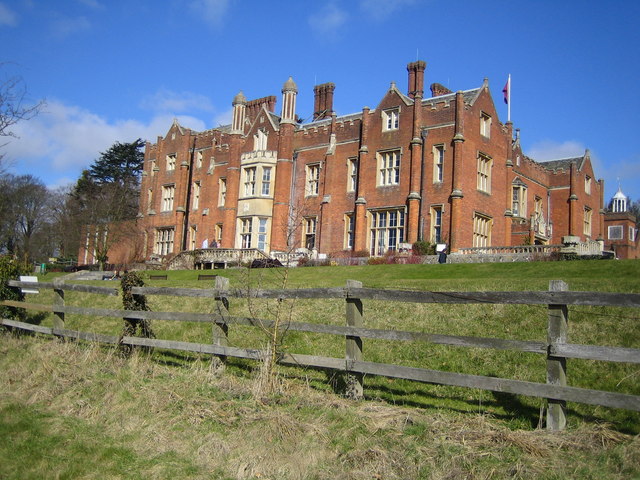
Latimer House
Latimer House is a large country house at Latimer, Buckinghamshire. It is now branded as De Vere Latimer Estate and functions as a countryside hotel used for country house weddings and conferences. Latimer Place has a small church, St Mary Magdalene, which was built by Lord Chesham, in the grounds. The Cavendish family Latimer House, a mansion on the hill on the edge of the village, was once a home of members of the Cavendish family who became the barons Chesham. During the 17th century, Latimer Manor was the home of Christian Cavendish, Countess of Devonshire, then later of William Cavendish, 3rd Earl of Devonshire, and his wife, the former Elizabeth Cecil because Chatsworth House had been sequestered by Parliament. Their daughter, Anne Cecil, Countess of Exeter was born at Latimer and would later marry John Cecil, 5th Earl of Exeter, known as Lord Burghley, and would go living at Burghley House. During the 18th century, the Manor was lived in by the wife of Elihu Yale, Cather ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a major settlement for two millennia. The City of London, its ancient core and financial centre, was founded by the Roman Empire, Romans as ''Londinium'' and retains its medieval boundaries.See also: Independent city#National capitals, Independent city § National capitals The City of Westminster, to the west of the City of London, has for centuries hosted the national Government of the United Kingdom, government and Parliament of the United Kingdom, parliament. Since the 19th century, the name "London" has also referred to the metropolis around this core, historically split between the Counties of England, counties of Middlesex, Essex, Surrey, Kent, and Hertfordshire, which largely comprises Greater London ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roundhead
Roundheads were the supporters of the Parliament of England during the English Civil War (1642–1651). Also known as Parliamentarians, they fought against King Charles I of England and his supporters, known as the Cavaliers or Royalists, who claimed rule by absolute monarchy and the principle of the divine right of kings. The goal of the Roundheads was to give to Parliament the supreme control over executive administration of the country/kingdom. Beliefs Most Roundheads sought constitutional monarchy in place of the absolute monarchy sought by Charles; however, at the end of the English Civil War in 1649, public antipathy towards the king was high enough to allow republican leaders such as Oliver Cromwell to abolish the monarchy completely and establish the Commonwealth of England. The Roundhead commander-in-chief of the first Civil War, Thomas Fairfax, remained a supporter of constitutional monarchy, as did many other Roundhead leaders such as Edward Montagu, 2nd Earl o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





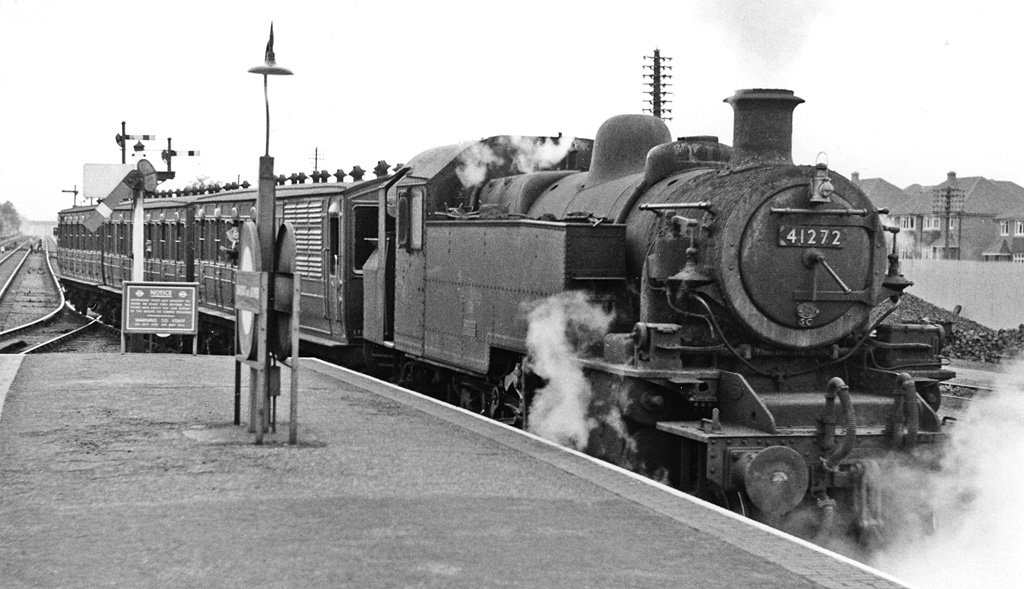

.jpg)
