|
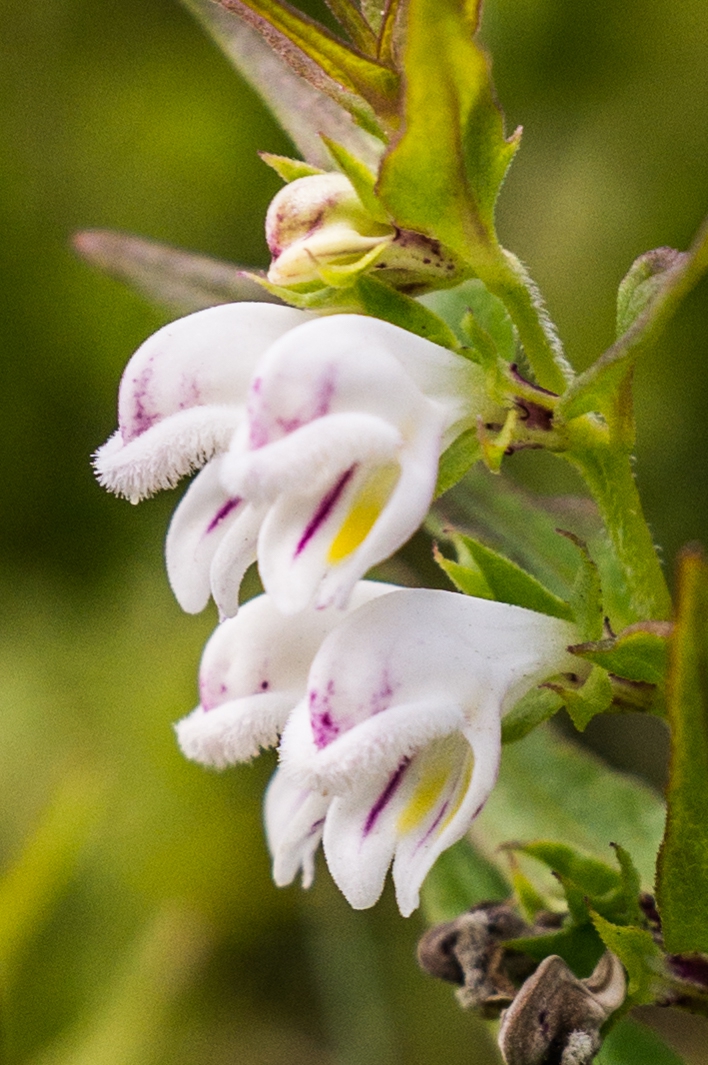
Lathraea Rhodopea
''Lathraea'' (toothwort) is a small genus of five to seven species of flowering plants, native to temperate Europe and Asia. They are parasitic plants on the roots of other plants, and are completely lacking chlorophyll. They are classified in the family Orobanchaceae. The toothwort is a protocarnivorous plant. Most of the plant consists of a branched whitish underground stem closely covered with thick fleshy colourless leaves, which are bent over so as to hide the under surface; irregular cavities communicating with the exterior are formed in the thickness of the leaf. On the inner walls of these chambers are stalked hairs, which when stimulated by the touch of an insect send out delicate filaments by means of which the insect is killed and digested. Etymology The genus name ''Lathraea'' derives from the ancient greek (), meaning "clandestine", which is a reference to the fact that it is inconspicuous until it flowers. Phylogeny The phylogeny of the genera of Rhinanthea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lathraea Squamaria
''Lathraea squamaria'', the common toothwort, is a species of flowering plant in the family Orobanchaceae. It is widely distributed in Europe and also occurs in Turkey. It is parasitic on the roots of hazel and alder, and occasionally other trees, and represents the second occasion on which a member of the family Orobanchaceae lost the ability to photosynthesize and became parasitic. It occurs in shady places such as deciduous woodland and hedge sides. The plant consists of a branched whitish underground stem closely covered with thick, fleshy, colourless leaves, which are bent over so as to hide under the surface. The only portions that appear above ground in April to May are the short flower-bearing shoots, which bear a spike of two-lipped dull purple flowers, but is also able to produce cleistogamic underground flowers which fertilise themselves. It is also able to regenerate from broken fragments of the underground stem. Description Toothwort is a perennial plant producing c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhinantheae
Rhinantheae is a tribe with less than 20 genera of herbaceous plants in the family Orobanchaceae. Phylogeny The phylogeny of the genera of Rhinantheae has been explored using DNA markers. Three assemblages can be distinguished in this tribe: * ''Rhinanthus'' is the sister genus to ''Lathraea'', and then to ''Rhynchocorys''. These taxa are closely related to the core Rhinanteae. * In the core Rhinantheae, ''Odontites'' sensu lato, including ''Bornmuellerantha'' and ''Bartsiella'', is the sister genus to ''Bellardia'', including ''Parentucellia'' and ''Bartsia canescens'' + ''B. mutica''. These taxa are closely related to ''Hedbergia'' (including ''Bartsia decurva'' + ''B. longiflora'') and ''Tozzia''. In turn, these genera share phylogenetic affinities with ''Euphrasia'', and then with ''Bartsia'' sensu stricto (''Bartsia alpina''). * ''Melampyrum'' occupies an isolated, deep-branching position. The median crown age of Rhinantheae was estimated to be ca. 30 Myr. Systematics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hazel
The hazel (''Corylus'') is a genus of deciduous trees and large shrubs native to the temperate Northern Hemisphere. The genus is usually placed in the birch family Betulaceae,Germplasmgobills Information Network''Corylus''Rushforth, K. (1999). ''Trees of Britain and Europe''. Collins .Huxley, A., ed. (1992). ''New RHS Dictionary of Gardening''. Macmillan . though some botanists split the hazels (with the hornbeams and allied genera) into a separate family Corylaceae. The fruit of the hazel is the hazelnut. Hazels have simple, rounded leaves with double-serrate margins. The flowers are produced very early in spring before the leaves, and are monoecious, with single-sex catkins. The male catkins are pale yellow and long, and the female ones are very small and largely concealed in the buds, with only the bright-red, 1-to-3 mm-long styles visible. The fruits are nuts long and 1–2 cm diameter, surrounded by an involucre (husk) which partly to fully encloses the nut. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
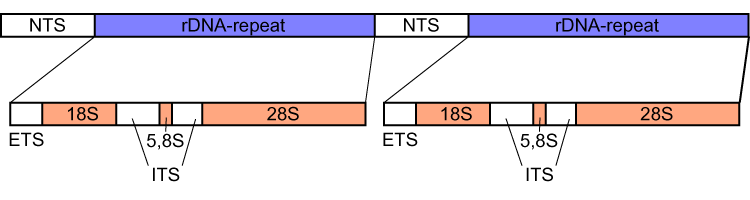
Internal Transcribed Spacer
Internal transcribed spacer (ITS) is the spacer DNA situated between the small-subunit ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and large-subunit rRNA genes in the chromosome or the corresponding transcribed region in the polycistronic rRNA precursor transcript. ITS across life domains In bacteria and archaea, there is a single ITS, located between the 16S and 23S rRNA genes. Conversely, there are two ITSs in eukaryotes: ITS1 is located between 18S and 5.8S rRNA genes, while ITS2 is between 5.8S and 28S (in opisthokonts, or 25S in plants) rRNA genes. ITS1 corresponds to the ITS in bacteria and archaea, while ITS2 originated as an insertion that interrupted the ancestral 23S rRNA gene. Organization In bacteria and archaea, the ITS occurs in one to several copies, as do the flanking 16S and 23S genes. When there are multiple copies, these do not occur adjacent to one another. Rather, they occur in discrete locations in the circular chromosome. It is not uncommon in bacteria to carry tRN ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloroplast DNA
Chloroplast DNA (cpDNA) is the DNA located in chloroplasts, which are photosynthetic organelles located within the cells of some eukaryotic organisms. Chloroplasts, like other types of plastid, contain a genome separate from that in the cell nucleus. The existence of chloroplast DNA was identified biochemically in 1959, and confirmed by electron microscopy in 1962. The discoveries that the chloroplast contains ribosomes and performs protein synthesis revealed that the chloroplast is genetically semi-autonomous. The first complete chloroplast genome sequences were published in 1986, ''Nicotiana tabacum'' (tobacco) by Sugiura and colleagues and ''Marchantia polymorpha'' (liverwort) by Ozeki et al. Since then, a great number of chloroplast DNAs from various species have been sequenced. Molecular structure Chloroplast DNAs are circular, and are typically 120,000–170,000 base pairs long. They can have a contour length of around 30–60 micrometers, and have a mass of about 80� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear DNA
Nuclear DNA (nDNA), or nuclear deoxyribonucleic acid, is the DNA contained within each cell nucleus of a eukaryotic organism. It encodes for the majority of the genome in eukaryotes, with mitochondrial DNA and plastid DNA coding for the rest. It adheres to Mendelian inheritance, with information coming from two parents, one male and one female—rather than matrilineally (through the mother) as in mitochondrial DNA. Structure Nuclear DNA is a nucleic acid, a polymeric biomolecule or biopolymer, found in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. Its structure is a double helix, with two strands wound around each other, a structure first described by Francis Crick and James D. Watson (1953) using data collected by Rosalind Franklin. Each strand is a long polymer chain of repeating nucleotides. Each nucleotide is composed of a five-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and an organic base. Nucleotides are distinguished by their bases: purines, large bases that include adenine and guanine; and pyr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melampyrum
''Melampyrum'' is a genus of about 20 species of herbaceous flowering plants in the family Orobanchaceae known commonly as cow wheat. They are native to temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere. They are hemiparasites on other plants, obtaining water and nutrients from host plants, though they are able to survive on their own without parasitising other plants.Kim, K. and S. Yun. (2012)A new species of ''Melampyrum'' (Orobanchaceae) from southern Korea.''Phytotaxa'' 42 48-50. ''Melampyrum'' species are used as food plants by the larvae of some Lepidoptera species, including the mouse moth (''Amphipyra tragopoginis''). Phylogeny The phylogeny of the genera of Rhinantheae has been explored using molecular characters. ''Melampyrum'' appears as a distant relative of other genera of Rhinantheae. It is the sister group of two clades: (i) ''Rhynchocorys'', ''Lathraea'', and ''Rhinanthus'' ; and (ii) the core Rhinantheae containing ''Bartsia'', ''Euphrasia'', ''Tozzia'', ''Hedbergi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odontites
''Odontites'' is a genus of flowering plants in the family Orobanchaceae. Phylogeny The phylogeny of the genera of Rhinantheae has been explored using molecular characters. ''Odontites'' belongs to the core Rhinantheae. It is the sister genus to ''Bellardia'', and then to ''Tozzia'' and ''Hedbergia''. These taxa are closely related to the genus ''Euphrasia''. In turn, these five genera share phylogenetic affinities with ''Bartsia''. Conservation One of the ''Odontites'' species, ''O. granatensis'', endemic to the Sierra Nevada in Spain , image_flag = Bandera de España.svg , image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg , national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond") , national_anthem = (English: "Royal March") , i ..., was so threatened that in 1993 only 1,500 plants survived in two locations. Due to conservation efforts the plant has made a comeback, numbering over 100,000 in 2006. References Oroban ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bellardia Trixago
''Bellardia trixago'' is a species of flowering plant in the family Orobanchaceae (it has been formerly classified in the family Scrophulariaceae). The only member of the monotypic genus ''Bellardia'', it is known as trixago bartsia or Mediterranean lineseed. This plant is native to the Mediterranean Basin, but it is known in other places with similar climates, such as California and parts of Chile, where it is an introduced species and noxious weed. Etymology The genus name ''Bellardia'' is a taxonomic patronym in honor of Carlo Antonio Lodovico Bellardi (1741-1826), an Italian botanist from Piedmont. The species name ''trixago'' has two possible etymologies. * It derives from the ancient Greek word (), meaning "hair", and the Latin suffix ''ago'' used to indicate a property, and refers to the glandular-hairy characteristic of the plant. * It derives from the ancient Greek word , , or (, , or ), meaning "triple", and refers to the trilobate lower lip of the flower. It is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hedbergia
''Hedbergia'' is a monotypic genus of flowering plants, initially classified in Scrophulariaceae, and now within the broomrape family Orobanchaceae. It contains a unique species, ''Hedbergia abyssinica''. It is an afromontane genus, widespread in grasslands and scrubs of the mountains of tropical Africa, and known from Ethiopia, Zaire, Uganda, Kenya, Tanzania, Malawi, Nigeria, and Cameroons. The genus name is a taxonomic patronym honoring the Swedish botanist Karl Olov Hedberg. Description ''Hedbergia abyssinica'' is a high, very hispid perennial plant, with subsessile thick leaves, and densely crowded, white to pink or magenta flowers. Phylogeny The phylogeny of the genera of Rhinantheae has been explored using molecular characters. ''Hedbergia'' belongs to the core Rhinantheae. ''Hedbergia'' is closely related to ''Odontites'', '' Bellardia'', and ''Tozzia''. In turn, these genera share phylogenetic affinities with ''Euphrasia'', and then with ''Bartsia ''Bartsia'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tozzia
''Tozzia'' is a monotypic genus of flowering plants within the broomrape family Orobanchaceae. It contains a unique species, ''Tozzia alpina''. While the plant in its young, vegetative stage is holoparasite, it becomes hemiparasite in its flowering stage. The originality of this species is therefore to combine half and full parasitism. The range of ''Tozzia alpina'' extends from the Pyrenees and the Alps to the Balkans and the Carpathians. Description Vegetative features ''Tozzia alpina'' is a herbaceous, perennial plant, reaching heights of . The quadrangular stem is hairless in the lower part, hairy on the edges in the middle and upper part. The simple, bright green leaves are broad, ovate, serrate, with a length of 1 to 3.5 centimeters, a rounded or slightly heart-shaped basis, and a sharp upper end. Reproductive features The flowering period is from June to August. The hermaphroditic zygomorph flowers are organized into a raceme inflorescence. The bracts have a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euphrasia
''Euphrasia'', or eyebright, is a genus of about 450 species of herbaceous flowering plants in the family Orobanchaceae (formerly included in the Scrophulariaceae), with a cosmopolitan distribution. They are semi-parasitic on grasses and other plants. The common name refers to the plant's use in treating eye infections. Many species are found in alpine or sub-alpine meadows where snow is common. Flowers usually are borne terminally, are zygomorphic, and have a lower petal shaped like a lip. The most common flower colours are purple, blue-white, and violet. Some species have yellow markings on the lower petal to act as a guide to pollinating insects. Alternative names, mainly in herbalism, are ''Augentrostkraut, Euphrasiae herba, Herba Euphrasiae'' and ''Herbe d'Euphraise''. Use in herbalism and medicine The plant was known to classical herbalists, but then was not referred to until mentioned again in 1305. Nicholas Culpeper assigned it to the Zodiac sign Leo, claiming that it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_IMG_7978.jpg)
