|
Lateral Umbilical Fold
The lateral umbilical fold overlies the inferior epigastric artery (a branch of the external iliac artery) and its accompanying veins. Unlike the median and medial umbilical folds, the contents of the lateral umbilical fold remain functional after birth. It originates just medial to the deep inguinal ring to the arcuate line on the posterior surface of the anterior abdominal wall. Clinical significance The lateral umbilical fold is an important reference site with regards to hernia classification. A direct hernia occurs medial to the lateral umbilical fold, whereas an indirect hernia originates lateral to the fold. This latter case is due to the placement of the opening of the deep inguinal ring in the space lateral to the lateral umbilical fold, which allows the passage of the ductus deferens, testicular artery, and other components of the spermatic cord in men, or the round ligament of the uterus in women. Additional images File:Gray539.png, The arteries of the pelvis. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Epigastric Artery
In human anatomy, inferior epigastric artery refers to the artery that arises from the external iliac artery. It anastomoses with the superior epigastric artery. Along its course, it is accompanied by a similarly named vein, the inferior epigastric vein. These epigastric vessels form the lateral border of Hesselbach's triangle, which outlines the area through which direct inguinal hernias protrude. Structure Origin The inferior epigastric artery arises from the external iliac artery, immediately superior to the inguinal ligament. Course and relations It curves forward in the subperitoneal tissue, and then ascends obliquely along the medial margin of the abdominal inguinal ring; continuing its course upward, it pierces the transversalis fascia, and, passing in front of the linea semicircularis, ascends between the rectus abdominis muscle and the posterior lamella of its sheath. It finally divides into numerous branches, which anastomose, above the umbilicus, with the sup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
External Iliac Artery
The external iliac arteries are two major Artery, arteries which bifurcate off the common iliac arteries anterior to the sacroiliac joint of the pelvis. Structure The external iliac artery arises from the bifurcation of the common iliac artery. They proceed anterior and inferior along the medial border of the psoas major muscles. They exit the Pelvis, pelvic girdle posterior and inferior to the inguinal ligament. This occurs about one third laterally from the insertion point of the inguinal ligament on the pubic tubercle. At this point they are referred to as the femoral arteries. Branches Function The external iliac artery provides the main blood supply to the legs. It passes down along the brim of the pelvis and gives off two large branches - the "inferior epigastric artery" and a "deep circumflex artery." These vessels supply blood to the muscles and skin in the lower abdominal wall. The external iliac artery passes beneath the inguinal ligament in the lower part of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Median Umbilical Fold
In human anatomy, the median umbilical ligament is an unpaired midline ligamentous structure upon the lower inner surface of the anterior abdominal wall. It is covered by the median umbilical fold. The median umbilical ligament represents the remnant of the fetal urachus. It extends from the apex of the bladder to the umbilicus, on the deep surface of the anterior abdominal wall. The medial umbilical ligament represents one of the five ligaments of the internal anterior abdominal wall inferior to the umbilicus; laterally on either side of it are one medial umbilical ligament and finally one lateral umbilical ligament. Development The median umbilical ligament begins as the allantois in the embryonic period. It then becomes the urachus in the fetus. This later develops into the median umbilical ligament at birth. It is also formed from the cloaca in utero. Function The median umbilical ligament has no known function. Clinical significance The median umbilical ligament may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medial Umbilical Fold
The medial umbilical ligament (or cord of umbilical artery, or obliterated umbilical artery) is a paired structure found in human anatomy. It is on the deep surface of the anterior abdominal wall, and is covered by the medial umbilical folds (''plicae umbilicales mediales''). It is different from the median umbilical ligament, a structure that represents the remnant of the embryonic urachus. Origins It represents the remnant of the umbilical arteries, which serves no purpose in humans after birth, except for the initial part that becomes the adult superior vesical artery. The occluded part of umbilical artery becomes the medial umbilical ligament postnatal. The medial umbilical ligament arises from the anterior division of the internal iliac artery. Functions It may be used as a landmark for surgeons performing laparoscopic procedures to help identify and avoid damaging the inferior epigastric arteries during port placement. Other than this, it has no purpose in an adult and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep Inguinal Ring
The inguinal canals are the two passages in the anterior abdominal wall of humans and animals which in males convey the spermatic cords and in females the round ligament of the uterus. The inguinal canals are larger and more prominent in males. There is one inguinal canal on each side of the midline. Structure The inguinal canals are situated just above the medial half of the inguinal ligament. In both sexes the canals transmit the ilioinguinal nerves. The canals are approximately 3.75 to 4 cm long. , angled anteroinferiorly and medially. In males, its diameter is normally 2 cm (±1 cm in standard deviation) at the deep inguinal ring.The diameter has been estimated to be ±2.2cm ±1.08cm in Africans, and 2.1 cm ±0.41cm in Europeans. A first-order approximation is to visualize each canal as a cylinder. Walls To help define the boundaries, these canals are often further approximated as boxes with six sides. Not including the two rings, the remaining four sides are usually cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arcuate Line (anterior Abdominal Wall)
''Arcuate'' (Latin for "curved") can refer to: Anatomy * Arcuate fasciculus * Arcuate line (other) * Arcuate artery (other), several arteries * Arcuate nucleus * Arcuate nucleus (medulla) * Arcuate ligaments of the diaphragm * Arcuate vein * Arcuate vessels of uterus * Internal arcuate fibers of the brain Other * Arcuate architecture, employing its arches and beams * Arcuate delta, a type of river delta * Arcuate pocket a type of pocket used in clothing, especially jeans made by Levi Strauss Levi Strauss (; born Löb Strauß ; February 26, 1829 – September 26, 1902) was a German-born American businessman who founded the first company to manufacture blue jeans. His firm of Levi Strauss & Co. (Levi's) began in 1853 in San Francisco ... * Arcuate rack, a curved rack gear {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hernia
A hernia is the abnormal exit of tissue or an organ (anatomy), organ, such as the bowel, through the wall of the cavity in which it normally resides. Various types of hernias can occur, most commonly involving the abdomen, and specifically the groin. Groin hernias are most commonly of the inguinal hernia, inguinal type but may also be femoral hernia, femoral. Other types of hernias include Hiatal hernia, hiatus, incisional hernia, incisional, and umbilical hernias. Symptoms are present in about 66% of people with groin hernias. This may include pain or discomfort in the lower abdomen, especially with coughing, exercise, or Urination, urinating or Defecation, defecating. Often, it gets worse throughout the day and improves when lying down. A bulge may appear at the site of hernia, that becomes larger when bending down. Groin hernias occur more often on the right than left side. The main concern is Strangulation (bowel), bowel strangulation, where the blood supply to part of the bowe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
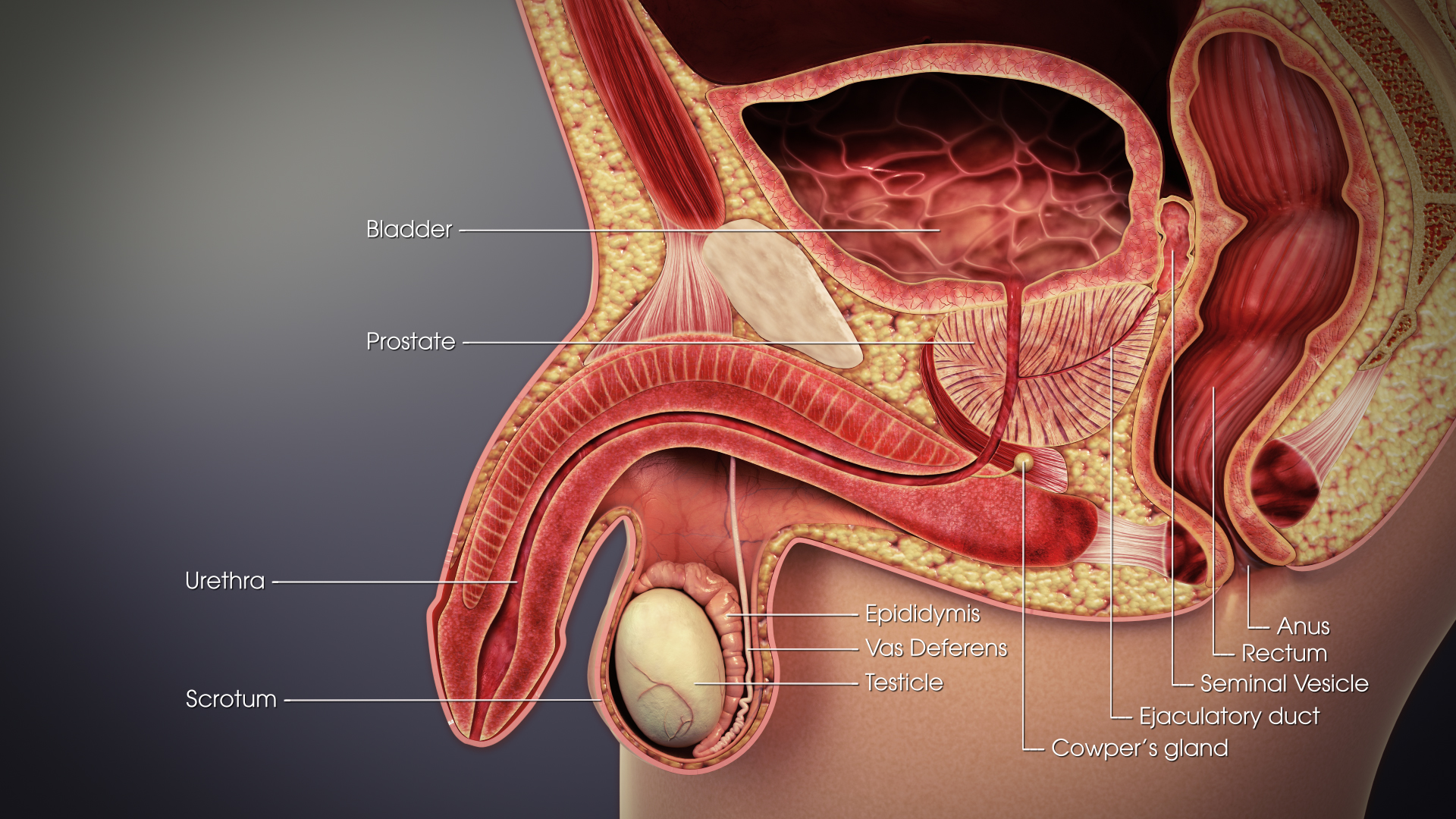
Ductus Deferens
The vas deferens or ductus deferens is part of the male reproductive system of many vertebrates. The ducts transport sperm from the epididymis to the ejaculatory ducts in anticipation of ejaculation. The vas deferens is a partially coiled tube which exits the abdominal cavity through the inguinal canal. Etymology ''Vas deferens'' is Latin, meaning "carrying-away vessel"; the plural version is ''vasa deferentia''. ''Ductus deferens'' is also Latin, meaning "carrying-away duct"; the plural version is ''ducti deferentes''. Structure There are two vasa deferentia, connecting the left and right epididymis with the seminal vesicles to form the ejaculatory duct in order to move spermatozoon, sperm. The (human) vas deferens measures 30–35 cm in length, and 2–3 mm in diameter. The vas deferens is continuous proximally with the tail of the epididymis. The vas deferens exhibits a tortuous, convoluted initial/proximal section (which measures 2–3 cm in length). Distall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Testicular Artery
The testicular artery (the male gonadal artery, also called the internal spermatic arteries in older texts) is a branch of the abdominal aorta that supplies blood to the testis. It is a paired artery, with one for each of the testes. It is the male equivalent of the ovarian artery. Because the testis is found in a different location than that of its female equivalent, it has a different course than the ovarian artery. They are two slender vessels of considerable length, and arise from the front of the aorta a little below the renal arteries. Each passes obliquely downward and lateralward behind the peritoneum, resting on the Psoas major, the right lying in front of the inferior vena cava and behind the middle colic and ileocolic arteries and the terminal part of the ileum, the left behind the left colic and sigmoid arteries and the iliac colon. Each crosses obliquely over the ureter and the lower part of the external iliac artery to reach the abdominal inguinal ring, through ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spermatic Cord
The spermatic cord is the cord-like structure in males formed by the vas deferens (''ductus deferens'') and surrounding tissue that runs from the deep inguinal ring down to each testicle. Its serosal covering, the tunica vaginalis, is an extension of the peritoneum that passes through the transversalis fascia. Each testicle develops in the lower thoracic and upper lumbar region and migrates into the scrotum. During its descent it carries along with it the vas deferens, its vessels, nerves etc. There is one on each side. Structure The spermatic cord is ensheathed in three layers of tissue: * ''external spermatic fascia'', an extension of the innominate fascia that overlies the aponeurosis of the external oblique muscle. * ''cremasteric muscle and fascia'', formed from a continuation of the internal oblique muscle and its fascia. * ''internal spermatic fascia'', continuous with the transversalis fascia. The normal diameter of the spermatic cord is about 16 mm (range 11 to 22 mm). It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Median Umbilical Ligament
In human anatomy, the median umbilical ligament is an unpaired midline ligamentous structure upon the lower inner surface of the anterior abdominal wall. It is covered by the median umbilical fold. The median umbilical ligament represents the remnant of the fetal urachus. It extends from the apex of the bladder to the umbilicus, on the deep surface of the anterior abdominal wall. The medial umbilical ligament represents one of the five ligaments of the internal anterior abdominal wall inferior to the umbilicus; laterally on either side of it are one medial umbilical ligament and finally one lateral umbilical ligament. Development The median umbilical ligament begins as the allantois in the embryonic period. It then becomes the urachus in the fetus. This later develops into the median umbilical ligament at birth. It is also formed from the cloaca in utero. Function The median umbilical ligament has no known function. Clinical significance The median umbilical ligament may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medial Umbilical Ligament
The medial umbilical ligament (or cord of umbilical artery, or obliterated umbilical artery) is a paired structure found in human anatomy. It is on the deep surface of the anterior abdominal wall, and is covered by the medial umbilical folds (''plicae umbilicales mediales''). It is different from the median umbilical ligament, a structure that represents the remnant of the embryonic urachus. Origins It represents the remnant of the umbilical arteries, which serves no purpose in humans after birth, except for the initial part that becomes the adult superior vesical artery. The occluded part of umbilical artery becomes the medial umbilical ligament postnatal. The medial umbilical ligament arises from the anterior division of the internal iliac artery. Functions It may be used as a landmark for surgeons performing laparoscopic procedures to help identify and avoid damaging the inferior epigastric arteries during port placement. Other than this, it has no purpose in an adult and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |