|
Latent Dirichlet Allocation
In natural language processing, Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) is a generative statistical model that explains a set of observations through unobserved groups, and each group explains why some parts of the data are similar. The LDA is an example of a topic model. In this, observations (e.g., words) are collected into documents, and each word's presence is attributable to one of the document's topics. Each document will contain a small number of topics. History In the context of population genetics, LDA was proposed by J. K. Pritchard, M. Stephens and P. Donnelly in 2000. LDA was applied in machine learning by David Blei, Andrew Ng and Michael I. Jordan in 2003. Overview Evolutionary biology and bio-medicine In evolutionary biology and bio-medicine, the model is used to detect the presence of structured genetic variation in a group of individuals. The model assumes that alleles carried by individuals under study have origin in various extant or past populations. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Language Processing
Natural language processing (NLP) is an interdisciplinary subfield of linguistics, computer science, and artificial intelligence concerned with the interactions between computers and human language, in particular how to program computers to process and analyze large amounts of natural language data. The goal is a computer capable of "understanding" the contents of documents, including the contextual nuances of the language within them. The technology can then accurately extract information and insights contained in the documents as well as categorize and organize the documents themselves. Challenges in natural language processing frequently involve speech recognition, natural-language understanding, and natural-language generation. History Natural language processing has its roots in the 1950s. Already in 1950, Alan Turing published an article titled "Computing Machinery and Intelligence" which proposed what is now called the Turing test as a criterion of intelligence, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computational Musicology
Computational musicology is an interdisciplinary research area between musicology and computer science. Computational musicology includes any disciplines that use computers in order to study music. It includes sub-disciplines such as mathematical music theory, computer music, systematic musicology, music information retrieval, computational musicology, digital musicology, sound and music computing, and music informatics. As this area of research is defined by the tools that it uses and its subject matter, research in computational musicology intersects with both the humanities and the sciences. The use of computers in order to study and analyze music generally began in the 1960s, although musicians have been using computers to assist them in the composition of music beginning in the 1950s. Today, computational musicology encompasses a wide range of research topics dealing with the multiple ways music can be represented. History This history of computational musicology generall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latent Variable
In statistics, latent variables (from Latin: present participle of ''lateo'', “lie hidden”) are variables that can only be inferred indirectly through a mathematical model from other observable variables that can be directly observed or measured. Such ''latent variable models'' are used in many disciplines, including political science, demography, engineering, medicine, ecology, physics, machine learning/artificial intelligence, bioinformatics, chemometrics, natural language processing, management and the social sciences. Latent variables may correspond to aspects of physical reality. These could in principle be measured, but may not be for practical reasons. In this situation, the term ''hidden variables'' is commonly used (reflecting the fact that the variables are meaningful, but not observable). Other latent variables correspond to abstract concepts, like categories, behavioral or mental states, or data structures. The terms ''hypothetical variables'' or ''hypothetical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Observable Variable
In physics, an observable is a physical quantity that can be measured. Examples include position and momentum. In systems governed by classical mechanics, it is a real-valued "function" on the set of all possible system states. In quantum physics, it is an operator, or gauge, where the property of the quantum state can be determined by some sequence of operations. For example, these operations might involve submitting the system to various electromagnetic fields and eventually reading a value. Physically meaningful observables must also satisfy transformation laws that relate observations performed by different observers in different frames of reference. These transformation laws are automorphisms of the state space, that is bijective transformations that preserve certain mathematical properties of the space in question. Quantum mechanics In quantum physics, observables manifest as linear operators on a Hilbert space representing the state space of quantum states. The ei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smoothed LDA
In statistics and image processing, to smooth a data set is to create an approximating function that attempts to capture important patterns in the data, while leaving out noise or other fine-scale structures/rapid phenomena. In smoothing, the data points of a signal are modified so individual points higher than the adjacent points (presumably because of noise) are reduced, and points that are lower than the adjacent points are increased leading to a smoother signal. Smoothing may be used in two important ways that can aid in data analysis (1) by being able to extract more information from the data as long as the assumption of smoothing is reasonable and (2) by being able to provide analyses that are both flexible and robust. Many different algorithms are used in smoothing. Smoothing may be distinguished from the related and partially overlapping concept of curve fitting in the following ways: * curve fitting often involves the use of an explicit function form for the result, wherea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Probabilistic Graphical Model
A graphical model or probabilistic graphical model (PGM) or structured probabilistic model is a probabilistic model for which a graph expresses the conditional dependence structure between random variables. They are commonly used in probability theory, statistics—particularly Bayesian statistics—and machine learning. Types of graphical models Generally, probabilistic graphical models use a graph-based representation as the foundation for encoding a distribution over a multi-dimensional space and a graph that is a compact or factorized representation of a set of independences that hold in the specific distribution. Two branches of graphical representations of distributions are commonly used, namely, Bayesian networks and Markov random fields. Both families encompass the properties of factorization and independences, but they differ in the set of independences they can encode and the factorization of the distribution that they induce. Undirected Graphical Model The undire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
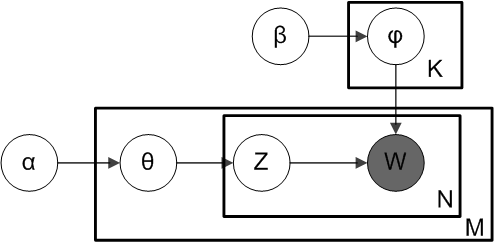
Plate Notation
In Bayesian inference, plate notation is a method of representing variables that repeat in a graphical model. Instead of drawing each repeated variable individually, a plate or rectangle is used to group variables into a subgraph that repeat together, and a number is drawn on the plate to represent the number of repetitions of the subgraph in the plate. The assumptions are that the subgraph is duplicated that many times, the variables in the subgraph are indexed by the repetition number, and any links that cross a plate boundary are replicated once for each subgraph repetition. Example In this example, we consider Latent Dirichlet allocation, a Bayesian network that models how documents in a corpus are topically related. There are two variables not in any plate; ''α'' is the parameter of the uniform Dirichlet prior on the per-document topic distributions, and ''β'' is the parameter of the uniform Dirichlet prior on the per-topic word distribution. The outermost plate represen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latent Dirichlet Allocation
In natural language processing, Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) is a generative statistical model that explains a set of observations through unobserved groups, and each group explains why some parts of the data are similar. The LDA is an example of a topic model. In this, observations (e.g., words) are collected into documents, and each word's presence is attributable to one of the document's topics. Each document will contain a small number of topics. History In the context of population genetics, LDA was proposed by J. K. Pritchard, M. Stephens and P. Donnelly in 2000. LDA was applied in machine learning by David Blei, Andrew Ng and Michael I. Jordan in 2003. Overview Evolutionary biology and bio-medicine In evolutionary biology and bio-medicine, the model is used to detect the presence of structured genetic variation in a group of individuals. The model assumes that alleles carried by individuals under study have origin in various extant or past populations. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MapReduce
MapReduce is a programming model and an associated implementation for processing and generating big data sets with a parallel, distributed algorithm on a cluster. A MapReduce program is composed of a ''map'' procedure, which performs filtering and sorting (such as sorting students by first name into queues, one queue for each name), and a ''reduce'' method, which performs a summary operation (such as counting the number of students in each queue, yielding name frequencies). The "MapReduce System" (also called "infrastructure" or "framework") orchestrates the processing by marshalling the distributed servers, running the various tasks in parallel, managing all communications and data transfers between the various parts of the system, and providing for redundancy and fault tolerance. The model is a specialization of the ''split-apply-combine'' strategy for data analysis. It is inspired by the map and reduce functions commonly used in functional programming,"Our abstraction is in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
K-means Clustering
''k''-means clustering is a method of vector quantization, originally from signal processing, that aims to partition ''n'' observations into ''k'' clusters in which each observation belongs to the cluster with the nearest mean (cluster centers or cluster centroid), serving as a prototype of the cluster. This results in a partitioning of the data space into Voronoi cells. ''k''-means clustering minimizes within-cluster variances (squared Euclidean distances), but not regular Euclidean distances, which would be the more difficult Weber problem: the mean optimizes squared errors, whereas only the geometric median minimizes Euclidean distances. For instance, better Euclidean solutions can be found using k-medians and k-medoids. The problem is computationally difficult (NP-hard); however, efficient heuristic algorithms converge quickly to a local optimum. These are usually similar to the expectation-maximization algorithm for mixtures of Gaussian distributions via an iterative refine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Probabilistic Latent Semantic Analysis
Probabilistic latent semantic analysis (PLSA), also known as probabilistic latent semantic indexing (PLSI, especially in information retrieval circles) is a statistical technique for the analysis of two-mode and co-occurrence data. In effect, one can derive a low-dimensional representation of the observed variables in terms of their affinity to certain hidden variables, just as in latent semantic analysis, from which PLSA evolved. Compared to standard latent semantic analysis which stems from linear algebra and downsizes the occurrence tables (usually via a singular value decomposition), probabilistic latent semantic analysis is based on a mixture decomposition derived from a latent class model. Model Considering observations in the form of co-occurrences (w,d) of words and documents, PLSA models the probability of each co-occurrence as a mixture of conditionally independent multinomial distributions: : P(w,d) = \sum_c P(c) P(d, c) P(w, c) = P(d) \sum_c P(c, d) P(w, c) with c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expectation Maximization
Expectation or Expectations may refer to: Science * Expectation (epistemic) * Expected value, in mathematical probability theory * Expectation value (quantum mechanics) * Expectation–maximization algorithm, in statistics Music * ''Expectation'' (album), a 2013 album by Girl's Day * ''Expectation'', a 2006 album by Matt Harding * ''Expectations'' (Keith Jarrett album), 1971 * ''Expectations'' (Dance Exponents album), 1985 * ''Expectations'' (Hayley Kiyoko album), 2018 **"Expectations/Overture", a song from the album * ''Expectations'' (Bebe Rexha album), 2018 * ''Expectations'' (Katie Pruitt album), 2020 **"Expectations", a song from the album * "Expectation" (waltz), a 1980 waltz composed by Ilya Herold Lavrentievich Kittler * "Expectation" (song), a 2010 song by Tame Impala * "Expectations" (song), a 2018 song by Lauren Jauregui * "Expectations", a song by Three Days Grace from ''Transit of Venus'', 2012 See also *''Great Expectations'', a novel by Charles Dickens *''X ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |