|
Laser Ultrasonics
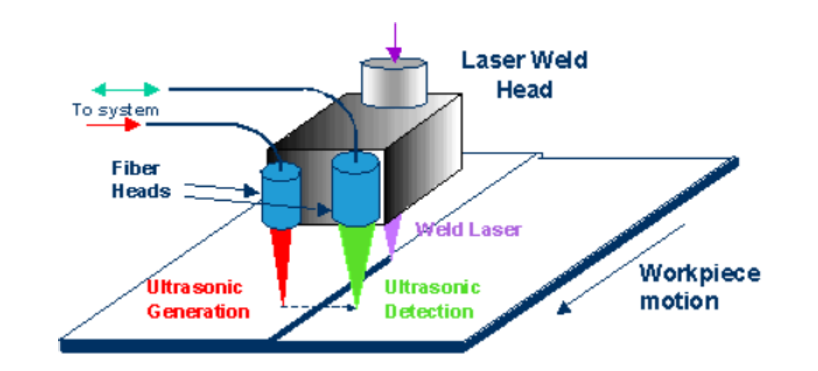
Laser-ultrasonics uses lasers to generate and detect ultrasonic waves.C.B. Scruby and L.E. Drain, Laser Ultrasonics, (Adam Hilger: Bristol), 1990. It is a non-contact technique used to measure materials thickness, detect flaws and carry out materials characterization. The basic components of a laser-ultrasonic system are a generation laser, a detection laser and a detector. Ultrasound generation by laser The generation lasers are short pulse (from tens of nanoseconds to femtoseconds) and high peak power lasers. Common lasers used for ultrasound generation are solid state Q-Switched Nd:YAG and gas lasers ( CO2 or Excimers). The physical principle is of thermal expansion (also called thermoelastic regime) or ablation. In the thermoelastic regime, the ultrasound is generated by the sudden thermal expansion due to the heating of a tiny surface of the material by the laser pulse. If the laser power is sufficient to heat the surface above the material boiling point, some material is ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lasers
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word "laser" is an acronym for "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation". The first laser was built in 1960 by Theodore H. Maiman at Hughes Research Laboratories, based on theoretical work by Charles Hard Townes and Arthur Leonard Schawlow. A laser differs from other sources of light in that it emits light which is coherence (physics), ''coherent''. Spatial coherence allows a laser to be focused to a tight spot, enabling applications such as laser cutting and Photolithography#Light sources, lithography. Spatial coherence also allows a laser beam to stay narrow over great distances (collimated light, collimation), enabling applications such as laser pointers and lidar (light detection and ranging). Lasers can also have high temporal coherence, which allows them to emit light with a very narrow frequency spectrum, spectr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Four Wave Mixing
Four-wave mixing (FWM) is an intermodulation phenomenon in nonlinear optics, whereby interactions between two or three wavelengths produce two or one new wavelengths. It is similar to the third-order intercept point in electrical systems. Four-wave mixing can be compared to the intermodulation distortion in standard electrical systems. It is a parametric nonlinear process, in that the energy of the incoming photons is conserved. FWM is a phase-sensitive process, in that the efficiency of the process is strongly affected by phase matching conditions. Mechanism When three frequencies (f1, f2, and f3) interact in a nonlinear medium, they give rise to a fourth frequency (f4) which is formed by the scattering of the incident photons, producing the fourth photon. Given inputs ''f1, f2,'' and ''f3'', the nonlinear system will produce : \pm f_ \pm f_ \pm f_ From calculations with the three input signals, it is found that 12 interfering frequencies are produced, three of which lie on o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laser Applications
Many scientific, military, medical and commercial laser applications have been developed since the invention of the laser in 1958. The coherency, high monochromaticity, and ability to reach extremely high powers are all properties which allow for these specialized applications. Scientific In science, lasers are used in many ways, including: * A wide variety of interferometric techniques'' * Raman spectroscopy * Laser induced breakdown spectroscopy * Atmospheric ''remote sensing'' * Investigating nonlinear optics phenomena * Holographic techniques employing lasers also contribute to a number of measurement techniques. * Laser based lidar (LIght raDAR) technology has application in geology, seismology, remote sensing and atmospheric physics. * Lasers have been used aboard spacecraft such as in the Cassini-Huygens mission. * In astronomy, lasers have been used to create artificial ''laser guide stars'', used as reference objects for adaptive optics telescopes. Lasers may als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transverse Wave
In physics, a transverse wave is a wave whose oscillations are perpendicular to the direction of the wave's advance. This is in contrast to a longitudinal wave which travels in the direction of its oscillations. Water waves are an example of transverse wave. A simple example is given by the waves that can be created on a horizontal length of string by anchoring one end and moving the other end up and down. Another example is the waves that are created on the membrane of a drum. The waves propagate in directions that are parallel to the membrane plane, but each point in the membrane itself gets displaced up and down, perpendicular to that plane. Light is another example of a transverse wave, where the oscillations are the electric and magnetic fields, which point at right angles to the ideal light rays that describe the direction of propagation. Transverse waves commonly occur in elastic solids due to the shear stress generated; the oscillations in this case are the displaceme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longitudinal Wave
Longitudinal waves are waves in which the vibration of the medium is parallel ("along") to the direction the wave travels and displacement of the medium is in the same (or opposite) direction of the wave propagation. Mechanical longitudinal waves are also called ''compressional'' or compression waves, because they produce compression and rarefaction when traveling through a medium, and pressure waves, because they produce increases and decreases in pressure. A wave along the length of a stretched Slinky toy, where the distance between coils increases and decreases, is a good visualization. Real-world examples include sound waves (vibrations in pressure, a particle of displacement, and particle velocity propagated in an elastic medium) and seismic P-waves (created by earthquakes and explosions). The other main type of wave is the transverse wave, in which the displacements of the medium are at right angles to the direction of propagation. Transverse waves, for instance, describe ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaporization
Vaporization (or vaporisation) of an element or compound is a phase transition from the liquid phase to vapor. There are two types of vaporization: evaporation and boiling. Evaporation is a surface phenomenon, whereas boiling is a bulk phenomenon. Evaporation is a phase transition from the liquid phase to vapor (a state of substance below critical temperature) that occurs at temperatures below the boiling temperature at a given pressure. Evaporation occurs ''on the surface''. Evaporation only occurs when the partial pressure of vapor of a substance is less than the equilibrium vapor pressure. For example, due to constantly decreasing pressures, vapor pumped out of a solution will eventually leave behind a cryogenic liquid. Boiling is also a phase transition from the liquid phase to gas phase, but boiling is the formation of vapor as bubbles of vapor ''below the surface'' of the liquid. Boiling occurs when the equilibrium vapor pressure of the substance is greater than or equa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ablation
Ablation ( la, ablatio – removal) is removal or destruction of something from an object by vaporization, chipping, erosion, erosive processes or by other means. Examples of ablative materials are described below, and include spacecraft material for ascent and atmospheric reentry, ice and snow in glaciology, biological tissues in medicine and passive fire protection materials. Artificial intelligence In artificial intelligence (AI), especially machine learning, Ablation (artificial intelligence), ablation is the removal of a component of an AI system. The term is by analogy with biology: removal of components of an organism. Biology Biological ablation is the removal of a biological structure or functionality. Genetic ablation is another term for gene silencing, in which gene expression is abolished through the alteration or deletion of genetic sequence information. In cell ablation, individual cells in a population or culture are destroyed or removed. Both can be used as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nondestructive Testing
Nondestructive testing (NDT) is any of a wide group of analysis techniques used in science and technology industry to evaluate the properties of a material, component or system without causing damage. The terms nondestructive examination (NDE), nondestructive inspection (NDI), and nondestructive evaluation (NDE) are also commonly used to describe this technology. Because NDT does not permanently alter the article being inspected, it is a highly valuable technique that can save both money and time in product evaluation, troubleshooting, and research. The six most frequently used NDT methods are eddy-current, magnetic-particle, liquid penetrant, radiographic, ultrasonic, and visual testing. NDT is commonly used in forensic engineering, mechanical engineering, petroleum engineering, electrical engineering, civil engineering, systems engineering, aeronautical engineering, medicine, and art. Innovations in the field of nondestructive testing have had a profound impact on medical im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultrasonic Laser
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hear it. This limit varies from person to person and is approximately 20 kilohertz (20,000 hertz) in healthy young adults. Ultrasound devices operate with frequencies from 20 kHz up to several gigahertz. Ultrasound is used in many different fields. Ultrasonic devices are used to detect objects and measure distances. Ultrasound imaging or sonography is often used in medicine. In the nondestructive testing of products and structures, ultrasound is used to detect invisible flaws. Industrially, ultrasound is used for cleaning, mixing, and accelerating chemical processes. Animals such as bats and porpoises use ultrasound for locating prey and obstacles. History Acoustics, the science of sound, starts as far back as Pythagoras in the 6th century BC, who wrote on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signal-to-noise Ratio
Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR or S/N) is a measure used in science and engineering that compares the level of a desired signal to the level of background noise. SNR is defined as the ratio of signal power to the noise power, often expressed in decibels. A ratio higher than 1:1 (greater than 0 dB) indicates more signal than noise. SNR, bandwidth, and channel capacity of a communication channel are connected by the Shannon–Hartley theorem. Definition Signal-to-noise ratio is defined as the ratio of the power of a signal (meaningful input) to the power of background noise (meaningless or unwanted input): : \mathrm = \frac, where is average power. Both signal and noise power must be measured at the same or equivalent points in a system, and within the same system bandwidth. Depending on whether the signal is a constant () or a random variable (), the signal-to-noise ratio for random noise becomes: : \mathrm = \frac where E refers to the expected value, i.e. in this case ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phonon Noise
Phonon noise, also known as thermal fluctuation noise, arises from the random exchange of energy between a thermal mass and its surrounding environment. This energy is quantized in the form of phonons. Each phonon has an energy of order k_\textT, where k_\text is the Boltzmann constant and T is the temperature. The random exchange of energy leads to fluctuations in temperature. This occurs even when the thermal mass and the environment are in thermal equilibrium, i.e. at the same time-average temperature. If a device has a temperature-dependent electrical resistance, then these fluctuations in temperature lead to fluctuations in resistance. Examples of devices where phonon noise is important include bolometers and Calorimeter (particle physics), calorimeters. The superconducting transition edge sensor (TES), which can be operated either as a bolometer or a calorimeter, is an example of a device for which phonon noise can significantly contribute to the total noise.K.D. Irwin and G. C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shot Noise
Shot noise or Poisson noise is a type of noise which can be modeled by a Poisson process. In electronics shot noise originates from the discrete nature of electric charge. Shot noise also occurs in photon counting in optical devices, where shot noise is associated with the particle nature of light. Origin In a statistical experiment such as tossing a fair coin and counting the occurrences of heads and tails, the numbers of heads and tails after many throws will differ by only a tiny percentage, while after only a few throws outcomes with a significant excess of heads over tails or vice versa are common; if an experiment with a few throws is repeated over and over, the outcomes will fluctuate a lot. From the law of large numbers, one can show that the relative fluctuations reduce as the reciprocal square root of the number of throws, a result valid for all statistical fluctuations, including shot noise. Shot noise exists because phenomena such as light and electric current co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |