|
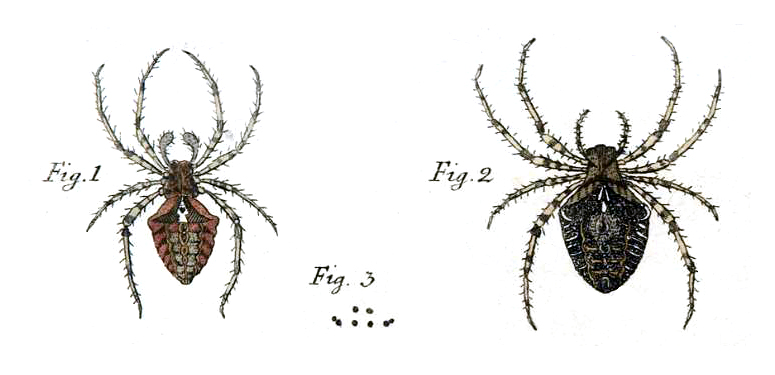
Larinioides Sclopetarius
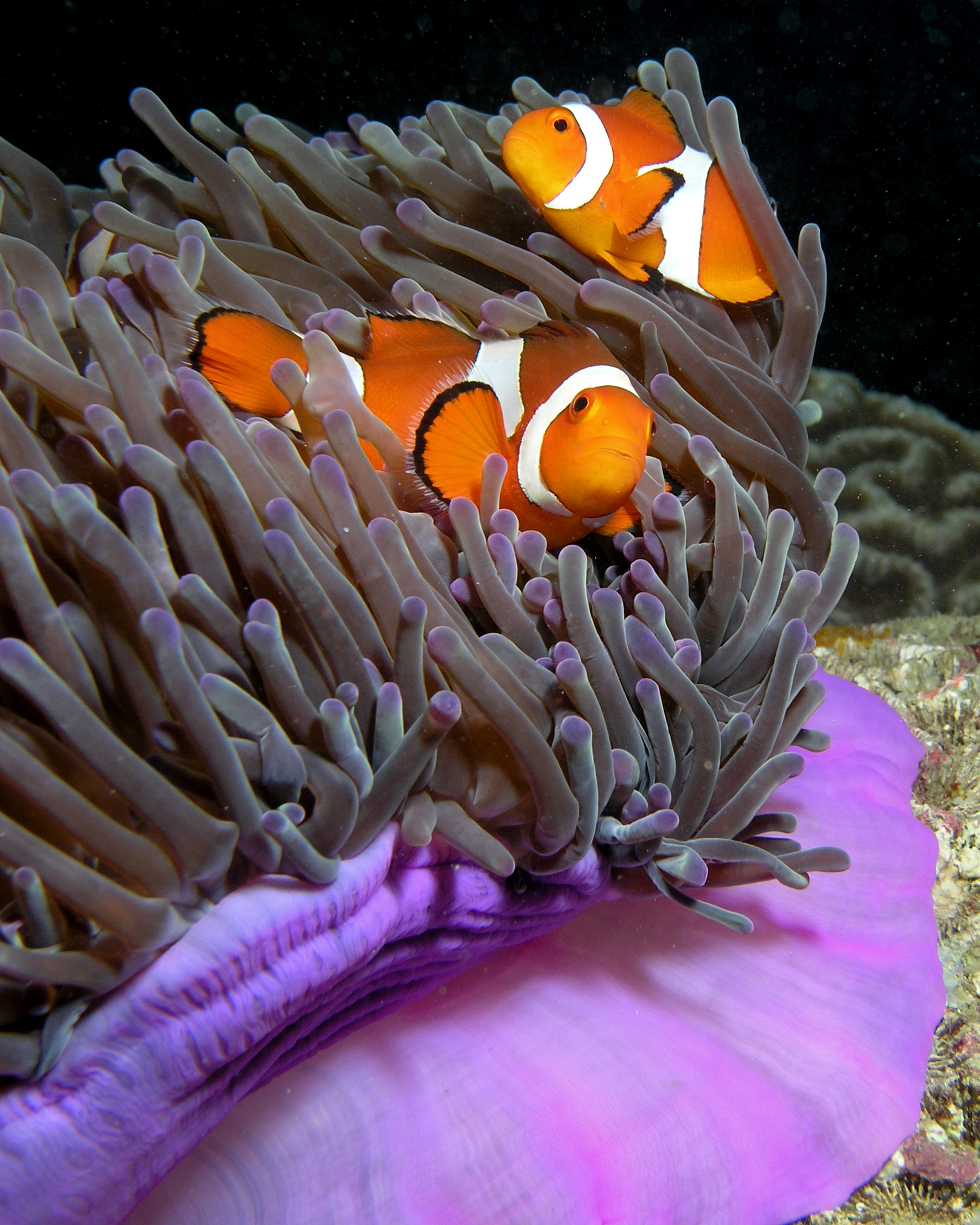
''Larinioides sclopetarius'', commonly called bridge-spider or gray cross-spider, is a relatively large orb-weaver spider with Holarctic distribution. These spiders are located in Europe and have been observed as south as the Mediterranean Coast and as north as Finland. They are often found on bridges, especially near light and over water.Roberts, Michael J. (1996) ''Collins Field Guide: Spiders of Britain and Northern Europe'', AND NORTHERN MICHIGAN Collins, , pp. 321–2 The species tends to live on steel objects and is seldom seen on vegetation. Females reach a body length of 10–14mm, and males 8–9mm. Their orb webs can have diameters of up to 70 cm. ''L. sclopetarius'' is attracted to light. Spiders found near light sources may be in better condition and have greater reproductive success than spiders living in unlit areas. Most of these lighted areas are found in cities or other metropolitan areas. As a result, many urban areas have become saturated with these spiders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Alexander Clerck
Carl Alexander Clerck (1709 – 22 July 1765) was a Sweden, Swedish entomologist and arachnology, arachnologist. Clerck came from a family in the petty Swedish nobility, nobility and entered the University of Uppsala in 1726. Little is known of his studies; although a contemporary of Carl Linnaeus, Linnaeus, it is unknown whether he had any contact with him during his time in Uppsala. His limited means forced him to leave university early and enter into government service, later ending up working in the administration of the City of Stockholm. His interest in natural history appears to have come at a more mature age, influenced by a lecture of Linnaeus he attended in Stockholm in 1739. In the following years he collected and categorized many spiders, published together with more general observations on the morphology and behaviour of spiders, in his ''Svenska Spindlar'' ("Swedish spiders", 1757, also known by its Latin subtitle, ''Aranei Suecici''). He also started the publication ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rensch's Rule
Rensch's rule is a biological rule on allometrics, concerning the relationship between the extent of sexual size dimorphism and which sex is larger. Across species within a lineage, size dimorphism increases with increasing body size when the male is the larger sex, and decreases with increasing average body size when the female is the larger sex. The rule was proposed by the evolutionary biologist Bernhard Rensch in 1950. After controlling for confounding factors such as evolutionary history, an increase in average body size makes the difference in body size larger if the species has larger males, and smaller if it has larger females. Some studies propose that this is due to sexual bimaturism, which causes male traits to diverge faster and develop for a longer period of time. The correlation between sexual size dimorphism and body size is hypothesized to be a result of an increase in male-male competition in larger species, a result of limited environmental resources, fuelling a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spiders Of Europe
Spiders ( order Araneae) are air-breathing arthropods that have eight legs, chelicerae with fangs generally able to inject venom, and spinnerets that extrude silk. They are the largest order of arachnids and rank seventh in total species diversity among all orders of organisms. Spiders are found worldwide on every continent except for Antarctica, and have become established in nearly every land habitat. , 50,356 spider species in 132 families have been recorded by taxonomists. However, there has been debate among scientists about how families should be classified, with over 20 different classifications proposed since 1900. Anatomically, spiders (as with all arachnids) differ from other arthropods in that the usual body segments are fused into two tagmata, the cephalothorax or prosoma, and the opisthosoma, or abdomen, and joined by a small, cylindrical pedicel, however, as there is currently neither paleontological nor embryological evidence that spiders ever had a separate t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holarctic Spiders
The Holarctic realm is a biogeographic realm that comprises the majority of habitats found throughout the continents in the Northern Hemisphere. It corresponds to the floristic Boreal Kingdom. It includes both the Nearctic zoogeographical region (which covers most of North America), and Alfred Wallace's Palearctic zoogeographical region (which covers North Africa, and all of Eurasia except for Southeast Asia, the Indian subcontinent, the southern Arabian Peninsula). These regions are further subdivided into a variety of ecoregions. Many ecosystems and the animal and plant communities that depend on them extend across a number of continents and cover large portions of the Holarctic realm. This continuity is the result of those regions’ shared glacial history. Major ecosystems Within the Holarctic realm, there are a variety of ecosystems. The type of ecosystem found in a given area depends on its latitude and the local geography. In the far north, a band of Arctic tundra en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Araneidae
Orb-weaver spiders are members of the spider family Araneidae. They are the most common group of builders of spiral wheel-shaped webs often found in gardens, fields, and forests. The English word "orb" can mean "circular", hence the English name of the group. Araneids have eight similar eyes, hairy or spiny legs, and no stridulating organs. The family has a cosmopolitan distribution, including many well-known large or brightly colored garden spiders. With 3,108 species in 186 genera worldwide, the Araneidae comprise the third-largest family of spiders (behind the Salticidae and Linyphiidae). Araneid webs are constructed in a stereotypical fashion, where a framework of nonsticky silk is built up before the spider adds a final spiral of silk covered in sticky droplets. Orb webs are also produced by members of other spider families. The long-jawed orb weavers (Tetragnathidae) were formerly included in the Araneidae; they are closely related, being part of the superfamily Araneo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Larinioides Sclopetarius
''Larinioides sclopetarius'', commonly called bridge-spider or gray cross-spider, is a relatively large orb-weaver spider with Holarctic distribution. These spiders are located in Europe and have been observed as south as the Mediterranean Coast and as north as Finland. They are often found on bridges, especially near light and over water.Roberts, Michael J. (1996) ''Collins Field Guide: Spiders of Britain and Northern Europe'', AND NORTHERN MICHIGAN Collins, , pp. 321–2 The species tends to live on steel objects and is seldom seen on vegetation. Females reach a body length of 10–14mm, and males 8–9mm. Their orb webs can have diameters of up to 70 cm. ''L. sclopetarius'' is attracted to light. Spiders found near light sources may be in better condition and have greater reproductive success than spiders living in unlit areas. Most of these lighted areas are found in cities or other metropolitan areas. As a result, many urban areas have become saturated with these spiders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trypoxylon
''Trypoxylon'' is a genus of wasps in the family Crabronidae. All ''Trypoxylon'' species that have been studied so far are active hunters of spiders, which they paralyse with a venomous sting, to provide as food to their developing larvae. Depending on the species, they will either construct their own nest from mud or find cavities that already exist. These cavities can range from keyholes to nail holes to previously abandoned nests, and are generally sealed with mud to create cells for their larvae. Worldwide distribution The 634 species in this most speciose genus are found worldwide being represented in the Palearctic, Nearctic, Afrotropic (largest number of species in the Old World), Neotropic (highest number of species), Australasia (poorly represented) and Indomalayan realm. Selected species Source *'' Trypoxylon albipes'' F. Smith 1856 *'' Trypoxylon attenuatum'' F. Smith 1851 *'' Trypoxylon beaumonti'' Antropov 1991 *'' Trypoxylon clavicerum'' Lepeletier & Serville ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phalacrotophora Epeirae
''Phalacrotophora epeirae'' is a species of scuttle flies (insects in the family Phoridae). References Further reading * Phoridae Articles created by Qbugbot Insects described in 1902 Diptera of North America Taxa named by Charles Thomas Brues {{Platypezoidea-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protandry
Sequential hermaphroditism (called dichogamy in botany) is a type of hermaphroditism that occurs in many fish, gastropods, and plants. Sequential hermaphroditism occurs when the individual changes its sex at some point in its life. In particular, a sequential hermaphrodite produces eggs (female gametes) and sperm (male gametes) at different stages in life. Species that can undergo these changes from one sex to another do so as a normal event within their reproductive cycle that is usually cued by either social structure or the achievement of a certain age or size. In animals, the different types of change are male to female (protandry or protandrous hermaphroditism), female to male (protogyny or protogynous hermaphroditism), bidirectional (serial or bidirectional hermaphroditism). Both protogynous and protandrous hermaphroditism allow the organism to switch between functional male and functional female. Bidirectional hermaphrodites have the capacity for sex change in either directi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kleptoparasitism
Kleptoparasitism (etymologically, parasitism by theft) is a form of feeding in which one animal deliberately takes food from another. The strategy is evolutionarily stable when stealing is less costly than direct feeding, which can mean when food is scarce or when victims are abundant. Many kleptoparasites are arthropods, especially bees and wasps, but including some true flies, dung beetles, bugs, and spiders. Cuckoo bees are specialized kleptoparasites which lay their eggs either on the pollen masses made by other bees, or on the insect hosts of parasitoid wasps. They are an instance of Emery's rule, which states that insect social parasites tend to be closely related to their hosts. The behavior occurs, too, in vertebrates including birds such as skuas, which persistently chase other seabirds until they disgorge their food, and carnivorous mammals such as spotted hyenas and lions. Other species opportunistically indulge in kleptoparasitism. Strategy Kleptoparasitism is a fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Larinioides Sclopetarius (Araneidae Sp
''Larinioides sclopetarius'', commonly called bridge-spider or gray cross-spider, is a relatively large orb-weaver spider with Holarctic distribution. These spiders originated in Europe, have been observed as south as the Mediterranean Coast and as north as Finland, and have been introduced to North America. They are often found on bridges, especially near light and over water.Roberts, Michael J. (1996) ''Collins Field Guide: Spiders of Britain and Northern Europe'', AND NORTHERN MICHIGAN Collins, , pp. 321–2 The species tends to live on steel objects and is seldom seen on vegetation. Females reach a body length of 10–14mm, and males 8–9mm. Their orb webs can have diameters of up to 70 cm. ''L. sclopetarius'' is attracted to light. Spiders found near light sources may be in better condition and have greater reproductive success than spiders living in unlit areas. Most of these lighted areas are found in cities or other metropolitan areas. As a result, many urban areas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Svenska Spindlar
The book ' or ' (Swedish and Latin, respectively, for "Swedish spiders") is one of the major works of the Swedish arachnologist and entomologist Carl Alexander Clerck and was first published in Stockholm in the year 1757. It was the first comprehensive book on the spiders of Sweden and one of the first regional monographs of a group of animals worldwide. The full title of the work is '' – '', ("Swedish spiders into their main genera separated, and as sixty and a few particular species described and with illuminated figures illustrated") and included 162 pages of text (eight pages were unpaginated) and six colour plates. It was published in Swedish, with a Latin translation printed in a slightly smaller font below the Swedish text. Clerck described in detail 67 species of Swedish spiders, and for the first time in a zoological work consistently applied binomial nomenclature as proposed by Carl Linnaeus. Linnaeus had originally invented this system for botanical names in his 1753 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_female%2C_Arnhem%2C_the_Netherlands_-_2.jpg)