|
Laparoscopic Stomach Surgery
Laparoscopy () is an operation performed in the abdomen or pelvis using small incisions (usually 0.5–1.5 cm) with the aid of a camera. The laparoscope aids diagnosis or therapeutic interventions with a few small cuts in the abdomen.MedlinePlus > Laparoscopy Update Date: 21 August 2009. Updated by: James Lee, MD // No longer valid Laparoscopic surgery, also called minimally invasive procedure, bandaid surgery, or keyhole surgery, is a modern surgical technique. There are a number of advantages to the patient with laparoscopic surgery versus an exploratory laparotomy. These include reduced pain due to smaller incisions, reduced hemorrhaging, and shorter recovery time. The key element is the use of a laparoscope, a long fiber optic cable system that allows viewing of the affected area by snaking the cable from a more distant, but more easily accessible location. Laparoscopic surgery includes operations within the abdominal or pelvic cavities, whereas keyhole surgery perform ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdomen
The abdomen (colloquially called the belly, tummy, midriff, tucky or stomach) is the part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis, in humans and in other vertebrates. The abdomen is the front part of the abdominal segment of the torso. The area occupied by the abdomen is called the abdominal cavity. In arthropods it is the posterior (anatomy), posterior tagma (biology), tagma of the body; it follows the thorax or cephalothorax. In humans, the abdomen stretches from the thorax at the thoracic diaphragm to the pelvis at the pelvic brim. The pelvic brim stretches from the lumbosacral joint (the intervertebral disc between Lumbar vertebrae, L5 and Vertebra#Sacrum, S1) to the pubic symphysis and is the edge of the pelvic inlet. The space above this inlet and under the thoracic diaphragm is termed the abdominal cavity. The boundary of the abdominal cavity is the abdominal wall in the front and the peritoneal surface at the rear. In vertebrates, the abdomen is a large body c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fiber Optic
An optical fiber, or optical fibre in Commonwealth English, is a flexible, transparent fiber made by drawing glass (silica) or plastic to a diameter slightly thicker than that of a human hair. Optical fibers are used most often as a means to transmit light between the two ends of the fiber and find wide usage in fiber-optic communications, where they permit transmission over longer distances and at higher bandwidths (data transfer rates) than electrical cables. Fibers are used instead of metal wires because signals travel along them with less loss; in addition, fibers are immune to electromagnetic interference, a problem from which metal wires suffer. Fibers are also used for illumination and imaging, and are often wrapped in bundles so they may be used to carry light into, or images out of confined spaces, as in the case of a fiberscope. Specially designed fibers are also used for a variety of other applications, some of them being fiber optic sensors and fiber lasers. Op ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nephrectomy
A nephrectomy is the surgical removal of a kidney, performed to treat a number of kidney diseases including kidney cancer. It is also done to remove a normal healthy kidney from a living or deceased donor, which is part of a kidney transplant procedure. History The first recorded nephrectomy was performed in 1861 by Erastus B. Wolcott in Wisconsin. The patient had had a large tumor and the operation was initially successful, but the patient died fifteen days later. The first planned nephrectomy was performed by the German surgeon Gustav Simon on August 2, 1869, in Heidelberg. Simon practiced the operation beforehand in animal experiments. He proved that one healthy kidney can be sufficient for urine excretion in humans. Indications There are various indications for this procedure, including renal cell carcinoma, a non-functioning kidney (which may cause high blood pressure) and a congenitally small kidney (in which the kidney is swelling, causing it to press on nerves, which ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colectomy
Colectomy ('' col-'' + '' -ectomy'') is bowel resection of the large bowel ( colon). It consists of the surgical removal of any extent of the colon, usually segmental resection (partial colectomy). In extreme cases where the entire large intestine is removed, it is called total colectomy, and proctocolectomy ('' procto-'' + ''colectomy'') denotes that the rectum is included. Indications Some of the most common indications for colectomy are: * Colon cancer * Diverticulitis and diverticular disease of the large intestine * Trauma * Inflammatory bowel disease such as ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease. Colectomy neither cures nor eliminates Crohn's disease, instead only removing part of the entire diseased large intestine. A colectomy is considered a "cure" for ulcerative colitis because the disease attacks only the large intestine and therefore will not be able to flare up again if the entire large intestine (cecum, ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon and si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
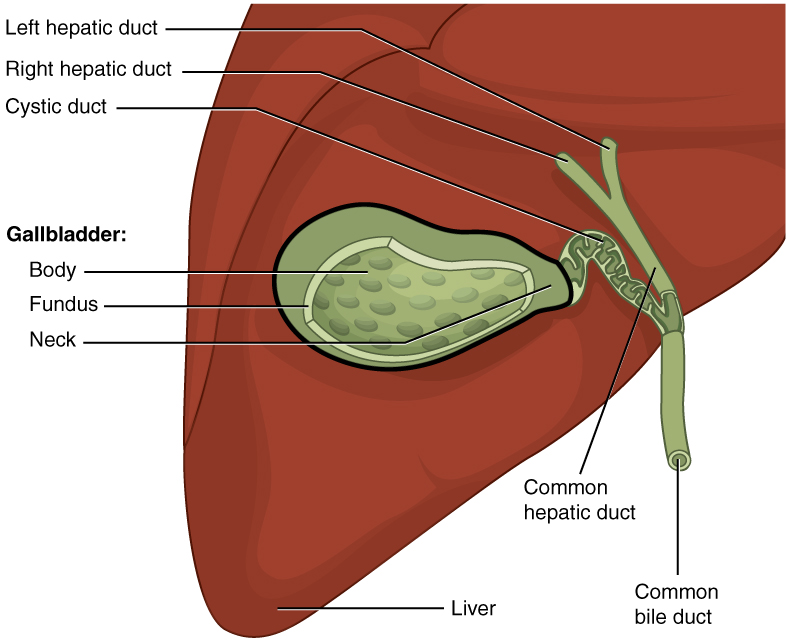
Gallbladder
In vertebrates, the gallbladder, also known as the cholecyst, is a small hollow organ where bile is stored and concentrated before it is released into the small intestine. In humans, the pear-shaped gallbladder lies beneath the liver, although the structure and position of the gallbladder can vary significantly among animal species. It receives and stores bile, produced by the liver, via the common hepatic duct, and releases it via the common bile duct into the duodenum, where the bile helps in the digestion of fats. The gallbladder can be affected by gallstones, formed by material that cannot be dissolved – usually cholesterol or bilirubin, a product of haemoglobin breakdown. These may cause significant pain, particularly in the upper-right corner of the abdomen, and are often treated with removal of the gallbladder (called a cholecystectomy). Cholecystitis, inflammation of the gallbladder, has a wide range of causes, including result from the impaction of gallstones, inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cholecystectomy
Cholecystectomy is the surgical removal of the gallbladder. Cholecystectomy is a common treatment of symptomatic gallstones and other gallbladder conditions. In 2011, cholecystectomy was the eighth most common operating room procedure performed in hospitals in the United States. Cholecystectomy can be performed either laparoscopically, or via an open surgical technique. The surgery is usually successful in relieving symptoms, but up to 10 percent of people may continue to experience similar symptoms after cholecystectomy, a condition called postcholecystectomy syndrome. Complications of cholecystectomy include bile duct injury, wound infection, bleeding, retained gallstones, abscess formation and stenosis (narrowing) of the bile duct. Medical use Pain and complications caused by gallstones are the most common reasons for removal of the gallbladder. The gallbladder can also be removed in order to treat biliary dyskinesia or gallbladder cancer. Gallstones are very common but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preload (cardiology)
In cardiac physiology, preload is the amount of sarcomere stretch experienced by cardiac muscle cells, called cardiomyocytes, at the end of ventricular filling during diastole. Preload is directly related to ventricular filling. As the relaxed ventricle fills during diastole, the walls are stretched and the length of sarcomeres increases. Sarcomere length can be approximated by the volume of the ventricle because each shape has a conserved surface-area-to-volume ratio. This is useful clinically because measuring the sarcomere length is destructive to heart tissue. It requires cutting out a piece of cardiac muscle to look at the sarcomeres under a microscope. It is currently not possible to directly measure preload in the beating heart of a living animal. Preload is estimated from end-diastolic ventricular pressure and is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg). Estimating preload Though not exactly equivalent to the strict definition of ''preload,'' end-diastolic volume is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trendelenburg Position
In the Trendelenburg position, the body is lain supine, or flat on the back on a 15–30 degree incline with the feet elevated above the head. The reverse Trendelenburg position, similarly, places the body supine on an incline but with the head now being elevated. The Trendelenburg position is used in surgery, especially of the abdomen and genitourinary system. It allows better access to the pelvic organs as gravity pulls the intra-abdominal organs away from the pelvis. Evidence does not support its use in hypovolaemic shock, with concerns for negative effects on the lungs and brain. The position was named for the German surgeon Friedrich Trendelenburg (1844–1924). Current uses *The Trendelenburg position can be used to treat a venous air embolism by placing the right ventricular outflow tract inferior to the right ventricular cavity, causing the air to migrate superiorly into a position within the right ventricle from which air is less likely to embolise. Most recently, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laparoscopic Stomach Surgery
Laparoscopy () is an operation performed in the abdomen or pelvis using small incisions (usually 0.5–1.5 cm) with the aid of a camera. The laparoscope aids diagnosis or therapeutic interventions with a few small cuts in the abdomen.MedlinePlus > Laparoscopy Update Date: 21 August 2009. Updated by: James Lee, MD // No longer valid Laparoscopic surgery, also called minimally invasive procedure, bandaid surgery, or keyhole surgery, is a modern surgical technique. There are a number of advantages to the patient with laparoscopic surgery versus an exploratory laparotomy. These include reduced pain due to smaller incisions, reduced hemorrhaging, and shorter recovery time. The key element is the use of a laparoscope, a long fiber optic cable system that allows viewing of the affected area by snaking the cable from a more distant, but more easily accessible location. Laparoscopic surgery includes operations within the abdominal or pelvic cavities, whereas keyhole surgery perform ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Dioxide
Carbon dioxide (chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is transparent to visible light but absorbs infrared radiation, acting as a greenhouse gas. It is a trace gas in Earth's atmosphere at 421 parts per million (ppm), or about 0.04% by volume (as of May 2022), having risen from pre-industrial levels of 280 ppm. Burning fossil fuels is the primary cause of these increased CO2 concentrations and also the primary cause of climate change.IPCC (2022Summary for policy makersiClimate Change 2022: Mitigation of Climate Change. Contribution of Working Group III to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA Carbon dioxide is soluble in water and is found in groundwater, lakes, ice caps, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insufflation (medicine)
Insufflation ( la, insufflare, lit=to blow into) is the act of blowing something (such as a gas, powder, or vapor) into a body cavity. Insufflation has many medical uses, most notably as a route of administration for various drugs. Medical uses Surgery Gases are often insufflated into a body cavity to inflate the cavity for more workroom, e.g. during laparoscopic surgery. The most common gas used in this manner is carbon dioxide, because it is non-flammable, colorless, and dissolves readily in blood. Diagnostics Gases can be insufflated into parts of the body to enhance radiological imaging or to gain access to areas for visual inspection (e.g. during colonoscopy). Respiratory assistance Oxygen can be insufflated into the nose by nasal cannulae to assist in respiration. Mechanical insufflation-exsufflation simulates a cough and assists airway mucus clearance. It is used with patients with neuromuscular disease and muscle weakness due to central nervous system injury. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trocar
A trocar (or trochar) is a medical or veterinary device that is made up of an awl (which may be a metal or plastic sharpened or non-bladed tip), a cannula (essentially a hollow tube), and a seal. Trocars are placed through the abdomen during laparoscopic surgery. The trocar functions as a portal for the subsequent placement of other instruments, such as graspers, scissors, staplers, etc. Trocars also allow the escape of gas or fluid from organs within the body. Etymology The word ''trocar'', less commonly ''trochar'', comes from French ''trocart'', ''trois-quarts'' (three-fourths), from ''trois'' 'three' and ''carre'' 'side, face of an instrument', first recorded in the ''Dictionnaire des Arts et des Sciences'', 1694, by Thomas Corneille, younger brother of Pierre Corneille. History Originally, doctors used trocars to relieve pressure build-up of fluids (edema) or gases (bloating). Patents for trocars appeared early in the 19th century, although their use dated back possibly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |