|
Languages Of Hungary
The languages spoken in Hungary include Hungarian, recognized minority languages, and other languages. Minority languages of Hungary Minority languages are spoken in a number of autochthonous settlements in Hungary. The country is a signatory of the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages, which was ratified at 26 April 1995 under which 14 minority languages are recognized and protected. Official linguistic rights of 13 recognized minorities are regulated by the Act on the Rights of National and Ethnic Minorities, which provides measures for development of cultural and educational autonomy. Levels of linguistic assimilation among Hungarian ethnic minorities are high. At the time of 2001 Census, out of the 314 059 citizens belonging to ethnic minorities, 135 787 stated minority language as their primary language. Under the terms of the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages, Hungary is providing special protection for the Armenian, Boyash, Bulgarian, Cro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hungarian Language
Hungarian () is an Uralic language spoken in Hungary and parts of several neighbouring countries. It is the official language of Hungary and one of the 24 official languages of the European Union. Outside Hungary, it is also spoken by Hungarian communities in southern Slovakia, western Ukraine (Subcarpathia), central and western Romania ( Transylvania), northern Serbia ( Vojvodina), northern Croatia, northeastern Slovenia ( Prekmurje), and eastern Austria. It is also spoken by Hungarian diaspora communities worldwide, especially in North America (particularly the United States and Canada) and Israel. With 17 million speakers, it is the Uralic family's largest member by number of speakers. Classification Hungarian is a member of the Uralic language family. Linguistic connections between Hungarian and other Uralic languages were noticed in the 1670s, and the family itself (then called Finno-Ugric) was established in 1717. Hungarian has traditionally been assigned to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
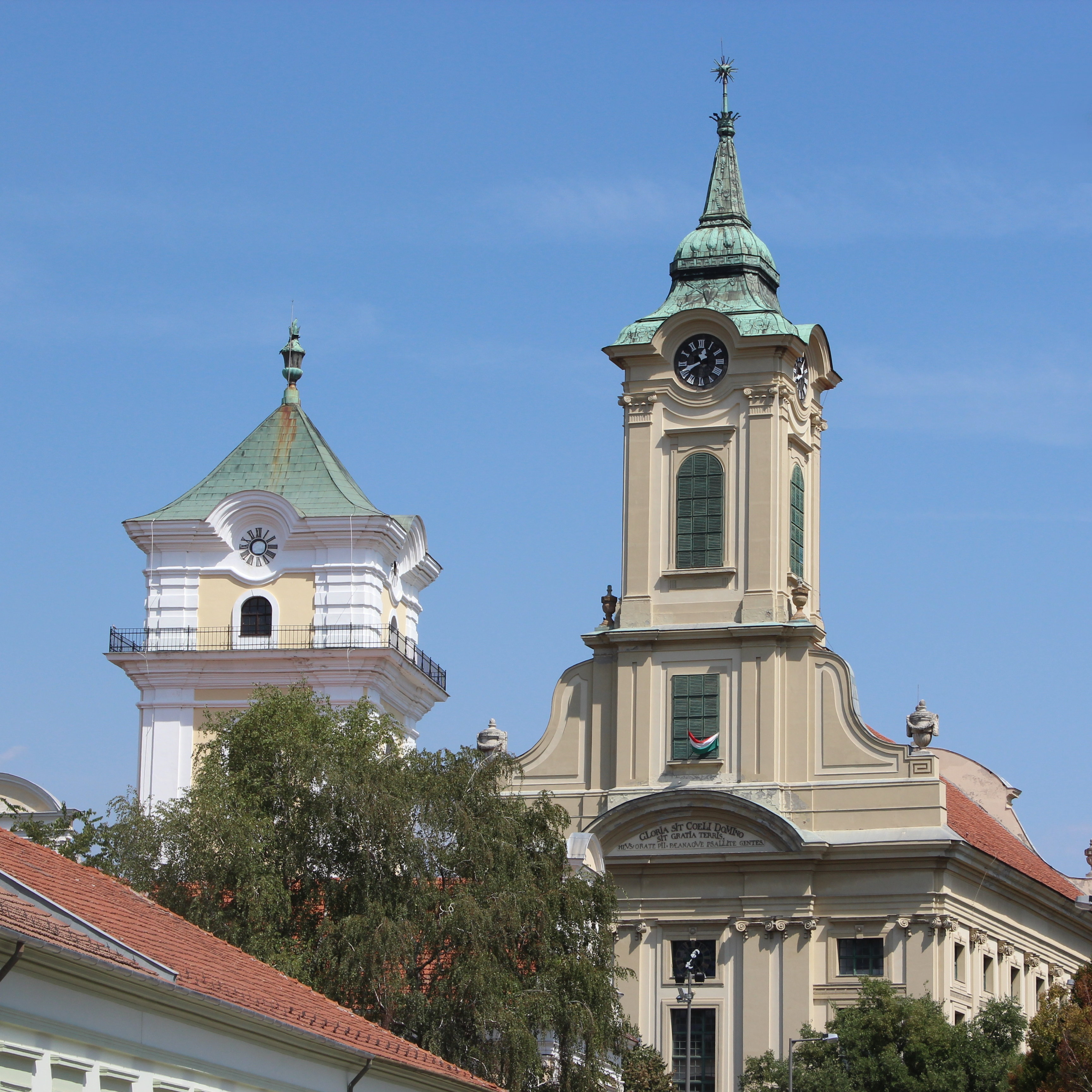
Békéscsaba
Békéscsaba (; sk, Békešská Čaba; see also other alternative names) is a city with county rights in southeast Hungary, the capital of Békés County. Geography Békéscsaba is located in the Great Hungarian Plain, southeast from Budapest. Highway 44, 47, Békéscsaba beltway (around the city) and Budapest-Szolnok-Békéscsaba-Lökösháza high speed () railway line also cross the city. Highway 44 is a four-lane expressway between Békéscsaba and Gyula. According to the 2011 census, the city has a total area of . Name '' Csaba'' is a popular Hungarian given name for boys of Turkic origin, while the prefix ''Békés'' refers to the county named Békés, which means peaceful in Hungarian. Other names derived from the Hungarian one include german: Tschabe, ro, Bichișciaba, and sk, Békešská Čaba. History The area has been inhabited since the ancient times. In the Iron Age the area had been conquered by the Scythians, by the Celts, then by the Huns. After th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Hungarian Mountains
The North Hungarian Mountains ( hu, Északi-középhegység), sometimes also referred to as the Northeast Hungarian Mountains, Northeast Mountains, North Hungarian Highlands, North Hungarian Mid-Mountains or North Hungarian Range, is the northern, mountainous part of Hungary. It forms a geographical unity with the Mátra-Slanec Area, the adjacent parts of Slovakia. It is a separate geomorphological area within the Western Carpathians. The mountains run along the northeastern border of Hungary as well as eastern parts of the Hungarian–Slovak border in broadband from the Danube Bend to the town of Prešov. Subdivisions The area consists of the following geomorphological units: * Börzsöny Regional Map Series of Hungary ( hu, Börzsöny + Burda (mountains), Burda (SK) * Gödöllő Hills ( hu, Gödöllői-dombság) * Cserh� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swabian German
Swabian (german: Schwäbisch ) is one of the dialect groups of Alemannic German that belong to the High German dialect continuum. It is mainly spoken in Swabia, which is located in central and southeastern Baden-Württemberg (including its capital Stuttgart and the Swabian Jura region) and the southwest of Bavaria ( Bavarian Swabia). Furthermore, Swabian German dialects are spoken by Caucasus Germans in Transcaucasia. The dialects of the Danube Swabian population of Hungary, the former Yugoslavia and Romania are only nominally Swabian and can be traced back not only to Swabian but also to Franconian, Bavarian and Hessian dialects, with locally varying degrees of influence of the initial dialects. Description Swabian can be difficult to understand for speakers of Standard German due to its pronunciation and partly differing grammar and vocabulary. For example, the Standard German term for "strawberry jam" is ''Erdbeermarmelade'' whereas in Swabian it is called ''Bräschd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mecsek
Mecsek (; hr, Meček; Serbian: ''Meček'' or Мечек; german: Metscheck) is a mountain range in southern Hungary. It is situated in the Baranya region, in the north of the city of Pécs. Etymology The Hungarian toponym "Mecsek" derives from the sobriquet version of the name Mihály (Michael). Originally applied only to the hills adjacent to Pécs, the name Mecsek was first mentioned in 16th century. Geography The mountains cover an area of approximately 500 km2. The highest peak in the mountain range is Zengő (literally translates to 'resonant'), which has an elevation of 682 metres (2238 feet). The Mecsek Hills consist of plateau-like block mountains of a broken, folded structure. Its basis is crystalline rock of Variscan origin surmounted by Triassic and Jurassic limestone and dolomite and Tertiary formations that form the main block. The mountains are divided by a structural fault running NW to SE. The eastern part consist mainly of high ridges of sedimentary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-European Languages
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutch, and Spanish, have expanded through colonialism in the modern period and are now spoken across several continents. The Indo-European family is divided into several branches or sub-families, of which there are eight groups with languages still alive today: Albanian, Armenian, Balto-Slavic, Celtic, Germanic, Hellenic, Indo-Iranian, and Italic; and another nine subdivisions that are now extinct. Today, the individual Indo-European languages with the most native speakers are English, Hindi–Urdu, Spanish, Bengali, French, Russian, Portuguese, German, and Punjabi, each with over 100 million native speakers; many others are small and in danger of extinction. In total, 46% of the world's population (3.2 billion people) speaks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Language
A first language, native tongue, native language, mother tongue or L1 is the first language or dialect that a person has been exposed to from birth or within the critical period. In some countries, the term ''native language'' or ''mother tongue'' refers to the language or dialect of one's ethnic group rather than one's first language. The first language of a child is part of that child's personal, social and cultural identity. Another impact of the first language is that it brings about the reflection and learning of successful social patterns of acting and speaking. Research suggests that while a non-native speaker may develop fluency in a targeted language after about two years of immersion, it can take between five and seven years for that child to be on the same working level as their native speaking counterparts. On 17 November 1999, UNESCO designated 21 February as International Mother Language Day. Definitions One of the more widely accepted definitions of native ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uralic Languages
The Uralic languages (; sometimes called Uralian languages ) form a language family of 38 languages spoken by approximately 25million people, predominantly in Northern Eurasia. The Uralic languages with the most native speakers are Hungarian (which alone accounts for more than half of the family's speakers), Finnish, and Estonian. Other significant languages with fewer speakers are Erzya, Moksha, Mari, Udmurt, Sami, Komi, and Vepsian, all of which are spoken in northern regions of Scandinavia and the Russian Federation. The name "Uralic" derives from the family's original homeland (''Urheimat'') commonly hypothesized to have been somewhere in the vicinity of the Ural Mountains. Finno-Ugric is sometimes used as a synonym for Uralic, though Finno-Ugric is widely understood to exclude the Samoyedic languages. Scholars who do not accept the traditional notion that Samoyedic split first from the rest of the Uralic family may treat the terms as synonymous. History Homelan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Council Of Europe
The Council of Europe (CoE; french: Conseil de l'Europe, ) is an international organisation founded in the wake of World War II to uphold human rights, democracy and the rule of law in Europe. Founded in 1949, it has 46 member states, with a population of approximately 675 million; it operates with an annual budget of approximately 500 million euros. The organisation is distinct from the European Union (EU), although it is sometimes confused with it, partly because the EU has adopted the original European flag, created for the Council of Europe in 1955, as well as the European anthem. No country has ever joined the EU without first belonging to the Council of Europe. The Council of Europe is an official United Nations Observer. Being an international organization, the Council of Europe cannot make laws, but it does have the ability to push for the enforcement of select international agreements reached by member states on various topics. The best-known body of the Counci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Charter For Regional Or Minority Languages
The European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages (ECRML) is a European treaty (CETS 148) adopted in 1992 under the auspices of the Council of Europe to protect and promote historical regional and minority languages in Europe. However, the charter does not provide any criterion or definition for an idiom to be a minority or a regional language, and the classification stays in the hands of the national state. The preparation for the charter was undertaken by the predecessor to the current Congress of Local and Regional Authorities, the Standing Conference of Local and Regional Authorities of Europe because involvement of local and regional government was essential. The actual charter was written in the Parliamentary Assembly based on the Congress' Recommendations. It only applies to languages traditionally used by the nationals of the State Parties (thus excluding languages used by recent immigrants from other states, see immigrant languages), which significantly diffe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minority Languages
A minority language is a language spoken by a minority of the population of a territory. Such people are termed linguistic minorities or language minorities. With a total number of 196 sovereign states recognized internationally (as of 2019) and an estimated number of roughly 5,000 to 7,000 languages spoken worldwide, the vast majority of languages are minority languages in every country in which they are spoken. Some minority languages are simultaneously also official languages, such as Irish in Ireland or the numerous indigenous languages of Bolivia. Likewise, some national languages are often considered minority languages, insofar as they are the national language of a stateless nation. Definitions There is no scholarly consensus on what a "minority language" is, because various different standards have been applied in order to classify languages as "minority language" or not. According to Owens (2013), attempts to define minority languages generally fall into several cate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.png)
