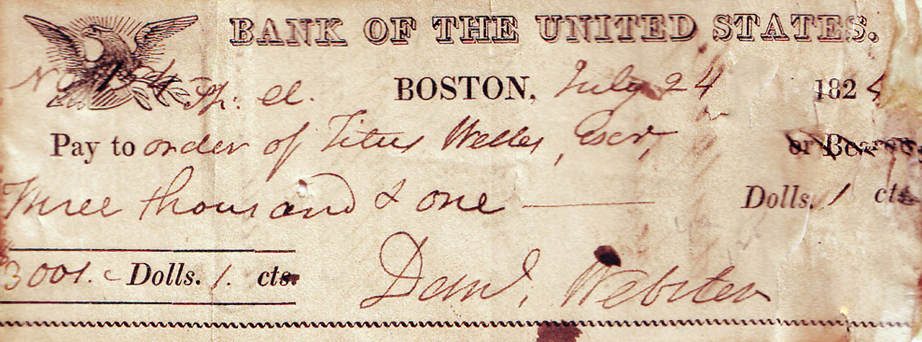|
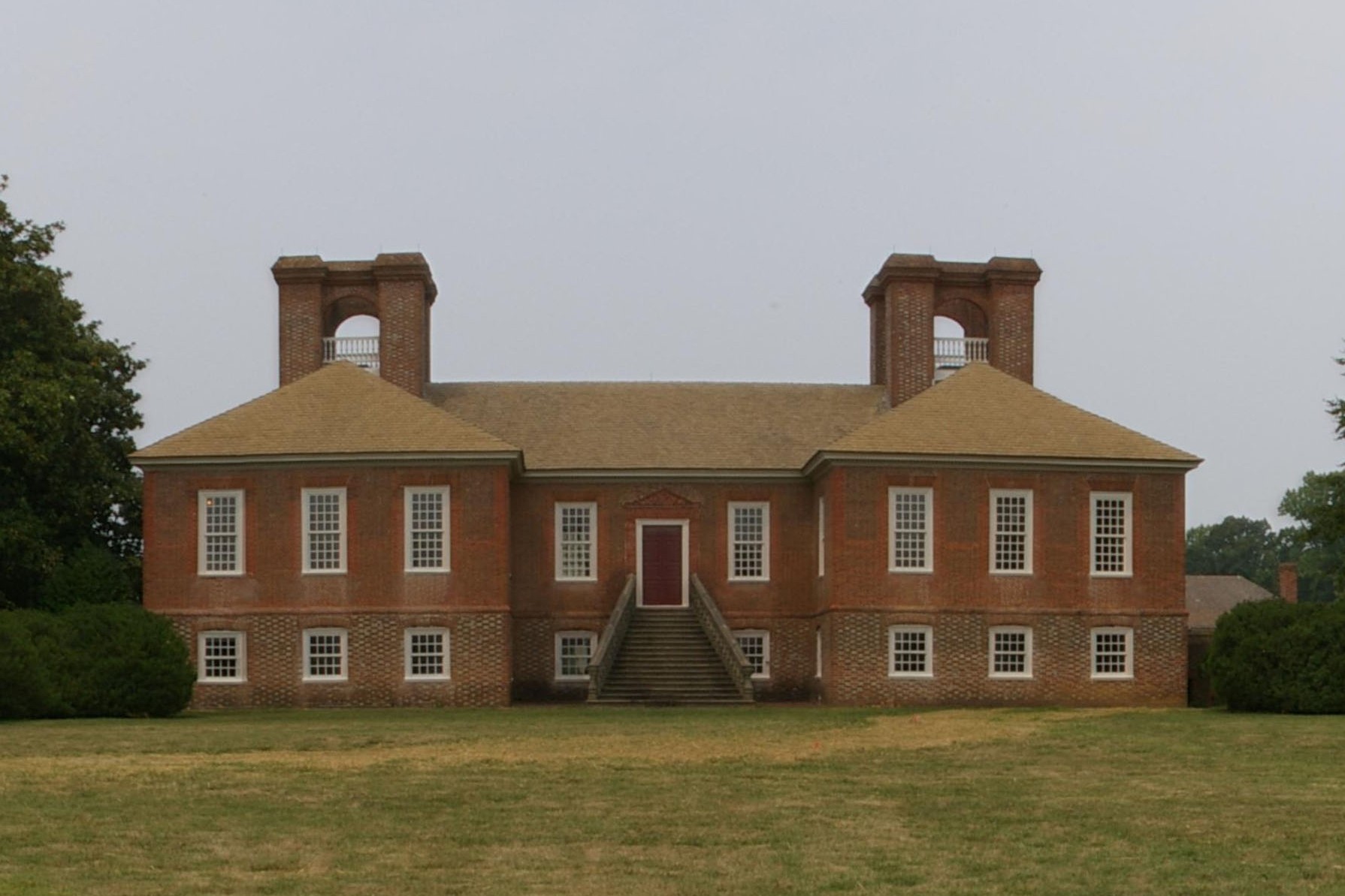
Lang Syne Plantation
Lang Syne Plantation is a historic plantation near St. Matthews, Calhoun County, South Carolina. The plantation was established in the 18th century by Ann Heatly Reid Lovell and her nephew Langdon Cheves, a prominent South Carolina politician and president of the Second Bank of the United States. The present Classical Revival plantation house was built in 1901. Julia Peterkin lived there with her planter husband and based many of her novels on the Gullah people of the Low Country. She won a 1929 Pulitzer Prize for her novel ''Scarlet Sister Mary.'' The plantation was listed in the National Register of Historic Places in 2014. See also *National Register of Historic Places listings in Calhoun County, South Carolina __NOTOC__ This is a list of the National Register of Historic Places listings in Calhoun County, South Carolina. This is intended to be a complete list of the properties on the National Register of Historic Places in Calhoun County, South Caroli ... References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plantations In The American South
A plantation complex in the Southern United States is the built environment (or complex) that was common on agricultural plantations in the American South from the 17th into the 20th century. The complex included everything from the main residence down to the pens for livestock. Until the abolition of slavery, such plantations were generally self-sufficient settlements that relied on the forced labor of enslaved people. Plantations are an important aspect of the history of the Southern United States, particularly the antebellum era (pre-American Civil War). The mild temperate climate, plentiful rainfall, and fertile soils of the southeastern United States allowed the flourishing of large plantations, where large numbers of enslaved Africans or African Americans were held captive and forced to produce crops to create wealth for a white elite. Today, as was also true in the past, there is a wide range of opinion as to what differentiated a plantation from a farm. Typically, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calhoun County, South Carolina
Calhoun County is a county in the U.S. state of South Carolina. As of the 2020 census, its population was 14,119, making it the third-least populous county in the state. Its county seat is St. Matthews. Located in a rural upland area long devoted to cotton plantations, part of the Black Belt of the South, the county was formed in 1908 from portions of Lexington and Orangeburg counties. It is named for John C. Calhoun, the former U.S. Vice-President, Senator, Representative and cabinet member from South Carolina, although Calhoun was from nearby Abbeville, South Carolina. Calhoun County is part of the Columbia, SC Metropolitan Statistical Area. It has an overall score of 52 including factors health, crime, equity, education, and housing. It is one of 11 counties with the same name in the United States. History Calhoun County was home to the Congaree Tribe. As early as 1715 maps show them living in the region. As well, arrowheads and other artifacts continue to be fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Langdon Cheves
Langdon Cheves ( September 17, 1776 – June 26, 1857) was an American politician, lawyer and businessman from South Carolina. He represented the city of Charleston in the United States House of Representatives from 1810 to 1815, where he played a key role on the home front of the War of 1812. Cheves was a leader among the War Hawk faction of the House. He served as chairman of the Committees on Naval Affairs and Ways and Means under Speaker of the House Henry Clay, then succeeded Clay as Speaker in the war's final stages. After leaving the House, he served as President of the Second Bank of the United States from 1819 to 1822. After leaving public office, Cheves was an active advocate for unified Southern resistance to protective tariffs and any attempt to abolish slavery, though an opponent of unilateral action by South Carolina or any one state. Originally, Cheves advocated for a convention of Southern states to pressure Congress into adopting these positions, but eventually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Bank Of The United States
The Second Bank of the United States was the second federally authorized Hamiltonian national bank in the United States. Located in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, the bank was chartered from February 1816 to January 1836.. The Bank's formal name, according to section 9 of its charter as passed by Congress, was "The President Directors and Company of the Bank of the United States". While other banks in the US were chartered by and only allowed to have branches in a single state, it was authorized to have branches in multiple states and lend money to the US government. A private corporation with public duties, the Bank handled all fiscal transactions for the U.S. Government, and was accountable to Congress and the U.S. Treasury. Twenty percent of its capital was owned by the federal government, the Bank's single largest stockholder.. Four thousand private investors held 80 percent of the Bank's capital, including three thousand Europeans. The bulk of the stocks were held by a few hundr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plantation House In The Southern United States
A plantation house is the main house of a plantation, often a substantial farmhouse, which often serves as a symbol for the plantation as a whole. Plantation complexes in the Southern United States, Plantation houses in the Southern United States and in other areas are known as quite grand and expensive architectural works today, though most were more utilitarian, working farmhouses. Antebellum American South In the Southern United States, American South, Antebellum South, antebellum plantations were centered on a "List of plantations in the United States, plantation house," the residence of the owner, where important business was conducted. Slavery in the United States, Slavery and plantations had different characteristics in different regions of the South. As the Upper South of the Chesapeake Bay colonies developed first, historians of the antebellum South defined planters as those who held 20 enslaved people. Major planters held many more, especially in the Deep South as i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julia Peterkin
Julia Peterkin (October 31, 1880 – August 10, 1961) was an American author from South Carolina. In 1929 she won the Pulitzer Prize for Novel/Literature for her novel ''Scarlet Sister Mary.'' She wrote several novels about the plantation South, especially the Gullah people of the Lowcountry. She was one of the few white authors who wrote about the African-American experience. Life and career Julia Mood was born in Laurens County, South Carolina. Her father was a physician, and she was the third of his four children. Her mother died soon after her birth, and her father later married Janie Brogdon. Janie was the mother of Henry Ashleigh Mood, Julia's half-brother and her father's fourth child. He became a doctor. In 1896, at age 16, Julia Mood graduated from Converse College in Spartanburg, South Carolina; she earned her master's degree there a year later. She taught at the public school in Fort Motte, South Carolina for a few years, then married William George Peterkin in 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gullah People
The Gullah () are an African American ethnic group who predominantly live in the Lowcountry region of the U.S. states of Georgia, Florida, South Carolina, and North Carolina, within the coastal plain and the Sea Islands. Their language and culture have preserved a significant influence of Africanisms as a result of their historical geographic isolation and the community's relation to their shared history and identity. Historically, the Gullah region extended from the Cape Fear area on North Carolina's coast south to the vicinity of Jacksonville on Florida's coast. The Gullah people and their language are also called Geechee, which may be derived from the name of the Ogeechee River near Savannah, Georgia. ''Gullah'' is a term that was originally used to designate the creole dialect of English spoken by Gullah and Geechee people. Over time, its speakers have used this term to formally refer to their creole language and distinctive ethnic identity as a people. The Georgia commun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulitzer Prize
The Pulitzer Prize () is an award for achievements in newspaper, magazine, online journalism, literature, and musical composition within the United States. It was established in 1917 by provisions in the will of Joseph Pulitzer, who had made his fortune as a newspaper publisher, and is administered by Columbia University. Prizes are awarded annually in twenty-one categories. In twenty of the categories, each winner receives a certificate and a US$15,000 cash award (raised from $10,000 in 2017). The winner in the public service category is awarded a gold medal. Entry and prize consideration The Pulitzer Prize does not automatically consider all applicable works in the media, but only those that have specifically been entered. (There is a $75 entry fee, for each desired entry category.) Entries must fit in at least one of the specific prize categories, and cannot simply gain entrance for being literary or musical. Works can also be entered only in a maximum of two categories, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scarlet Sister Mary
''Scarlet Sister Mary'' is a 1928 novel by Julia Peterkin. It won the Pulitzer Prize for the Novel in 1929. The book was called obscene and banned at the public library in Gaffney, South Carolina. ''The Gaffney Ledger'' newspaper, however, serially published the complete book. Dr. Richard S. Burton, the chairperson of Pulitzer's fiction-literature jury, recommended that the first prize go to the novel ''Victim and Victor'' by John Rathbone Oliver. His nomination was superseded by the School of Journalism's choice of Peterkin's book. Evidently in protest, Burton resigned from the jury. Ethel Barrymore had the dramatic rights to the novel, and in 1930 starred on Broadway in a blackface performance, whose cast included Estelle Winwood, Ted de Corsia, Marjorie Main and Barrymore's teenaged daughter, Ethel Barrymore Colt, in her stage debut. Synopsis ''Scarlet Sister Mary'' is set among the Gullah The Gullah () are an African American ethnic group who predominantly live in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Register Of Historic Places
The National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) is the United States federal government's official list of districts, sites, buildings, structures and objects deemed worthy of preservation for their historical significance or "great artistic value". A property listed in the National Register, or located within a National Register Historic District, may qualify for tax incentives derived from the total value of expenses incurred in preserving the property. The passage of the National Historic Preservation Act (NHPA) in 1966 established the National Register and the process for adding properties to it. Of the more than one and a half million properties on the National Register, 95,000 are listed individually. The remainder are contributing resources within historic districts. For most of its history, the National Register has been administered by the National Park Service (NPS), an agency within the U.S. Department of the Interior. Its goals are to help property owners and inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Register Of Historic Places Listings In Calhoun County, South Carolina
__NOTOC__ This is a list of the National Register of Historic Places listings in Calhoun County, South Carolina. This is intended to be a complete list of the properties on the National Register of Historic Places in Calhoun County, South Carolina, United States. The locations of National Register properties for which the latitude and longitude coordinates are included below, may be seen in a map. There are 18 properties listed on the National Register in the county. Current listings See also *List of National Historic Landmarks in South Carolina *National Register of Historic Places listings in South Carolina References {{Calhoun County, South Carolina Calhoun County Calhoun County is the name of several counties in the United States of America named after U.S. Vice President John C. Calhoun: * Calhoun County, Alabama * Calhoun County, Arkansas * Calhoun County, Florida * Calhoun County, Georgia * Calhoun Cou ... * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plantations In South Carolina
A plantation is an agricultural estate, generally centered on a plantation house, meant for farming that specializes in cash crops, usually mainly planted with a single crop, with perhaps ancillary areas for vegetables for eating and so on. The crops that are grown include cotton, coffee, tea, cocoa, sugar cane, opium, sisal, oil seeds, oil palms, fruits, rubber trees and forest trees. Protectionist policies and natural comparative advantage have sometimes contributed to determining where plantations are located. In modern use the term is usually taken to refer only to large-scale estates, but in earlier periods, before about 1800, it was the usual term for a farm of any size in the southern parts of British North America, with, as Noah Webster noted, "farm" becoming the usual term from about Maryland northwards. It was used in most British colonies, but very rarely in the United Kingdom itself in this sense. There, as also in America, it was used mainly for tree plantations, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |