|
Lane Debates On Slavery
Lane Seminary, sometimes called Cincinnati Lane Seminary, and later renamed Lane Theological Seminary, was a Presbyterian theological college that operated from 1829 to 1932 in Walnut Hills, Ohio, today a neighborhood in Cincinnati. Its campus was bounded by today's Gilbert, Yale, Park, and Chapel Streets. Its board intended it to be "a great ''central theological institution'' at Cincinnati — soon to become the great Andover or Princeton of the West." However, the founding and first years of Lane were difficult and contentious, culminating in a mass student exodus over the issue of slavery, or more specifically whether students were permitted to discuss the topic publicly, the first major academic freedom incident in America. There was strong pro-slavery sentiment in Cincinnati, and the trustees immediately prohibited further discussion of the topic, to avoid repercussions. With the city being on the border of the South, a lot of fugitive slaves and freedmen went through Cin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lyman Beecher
Lyman Beecher (October 12, 1775 – January 10, 1863) was a Presbyterian minister, and the father of 13 children, many of whom became noted figures, including Harriet Beecher Stowe, Henry Ward Beecher, Charles Beecher, Edward Beecher, Isabella Beecher Hooker, Catharine Beecher, and Thomas K. Beecher. According to his son Henry Ward Beecher, his father was "largely engaged during his life-time in controversy". Early life Beecher was born in New Haven, Connecticut, to David Beecher, a blacksmith, and Esther Hawley Lyman. His mother died shortly after his birth, and he was committed to the care of his uncle Lot Benton, by whom he was adopted as a son, and with whom his early life was spent blacksmithing and farming. But it was soon found that he preferred study. He was fitted for college by the Rev. Thomas W. Bray, and at the age of eighteen entered Yale College, graduating in 1797. He spent 1798 in Yale Divinity School under the tutelage of his mentor Timothy Dwight. Ministry Mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allegheny Mountains
The Allegheny Mountain Range (; also spelled Alleghany or Allegany), informally the Alleghenies, is part of the vast Appalachian Mountain Range of the Eastern United States and Canada and posed a significant barrier to land travel in less developed eras. The Allegheny Mountains have a northeast–southwest orientation, running for about from north-central Pennsylvania, southward through western Maryland and eastern West Virginia. The Alleghenies comprise the rugged western-central portion of the Appalachians. They rise to approximately in northeastern West Virginia. In the east, they are dominated by a high, steep escarpment known as the Allegheny Front. In the west, they slope down into the closely associated Allegheny Plateau, which extends into Ohio and Kentucky. The principal settlements of the Alleghenies are Altoona, State College, and Johnstown, Pennsylvania; and Cumberland, Maryland. Name The name is derived from the Allegheny River, which drains only a small porti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodore D
Theodore may refer to: Places * Theodore, Alabama, United States * Theodore, Australian Capital Territory * Theodore, Queensland, a town in the Shire of Banana, Australia * Theodore, Saskatchewan, Canada * Theodore Reservoir, a lake in Saskatchewan People * Theodore (given name), includes the etymology of the given name and a list of people * Theodore (surname), a list of people Fictional characters * Theodore "T-Bag" Bagwell, on the television series ''Prison Break'' * Theodore Huxtable, on the television series ''The Cosby Show'' Other uses * Theodore (horse), a British Thoroughbred racehorse * Theodore Racing, a Formula One racing team See also * Principality of Theodoro, a principality in the south-west Crimea from the 13th to 15th centuries * Thoros (other), Armenian for Theodore * James Bass Mullinger James Bass Mullinger (1834 or 1843 – 22 November 1917), sometimes known by his pen name Theodorus, was a British author, historian, lecturer and scholar. A l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charisma
Charisma () is a personal quality of presence or charm that compels its subjects. Scholars in sociology, political science, psychology, and management reserve the term for a type of leadership seen as extraordinary; in these fields, the term "charisma" is used to describe a particular type of leader who uses "values-based, symbolic, and emotion-laden leader signaling". In Christian theology, the term appears as ''charism'', an endowment or extraordinary power given by the Holy Spirit."Spiritual gifts". ''A Dictionary of the Bible'' by W. R. F. Browning. Oxford University Press Inc. ''Oxford Reference Online''. Oxford University Press. Accessed 22 June 2011. Etymology The English term ''charisma'' is from the Greek (''khárisma''), which means "favor freely given" or "gift of grace". The term and its plural (''charismata'') derive from (''charis''), which means "grace" or indeed "charm" with which it shares the root. Some derivatives from that root (including "grace") have sim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lewis Tappan
Lewis Tappan (May 23, 1788 – June 21, 1873) was a New York abolitionist who worked to achieve freedom for the enslaved Africans aboard the '' Amistad''. Tappan was also among the founders of the American Missionary Association in 1846, which began more than 100 anti-slavery Congregational churches throughout the Midwest, and after the American Civil War, founded numerous schools and colleges to aid in the education of freedmen. Contacted by Connecticut abolitionists soon after the ''Amistad'' arrived in port, Tappan focused extensively on the captive Africans. He ensured the acquisition of high-quality lawyers for the captives, which led to their being set free after the case went to the United States Supreme Court. With his brother Arthur, Tappan not only gained legal help and acquittal for the Africans, but also managed to increase public support and fundraising. Finally, he organized the return trip home to Africa for surviving members of the group. Background Lewis Tapp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Tappan
Arthur Tappan (May 22, 1786 – July 23, 1865) was an American businessman, philanthropist and abolitionist. He was the brother of Ohio Senator Benjamin Tappan and abolitionist Lewis Tappan, and nephew of Harvard Divinity School theologian Rev. Dr. David Tappan. He was a great-grandfather of Thornton Wilder. Biography Arthur was born in Northampton, Massachusetts, to Benjamin Tappan (1747–1831) and Sarah Homes Tappan (1748–1826), the latter a great-niece of Benjamin Franklin. They were devout Calvinists. Tappan moved to Boston at the age of 15. In 1807 he established a dry goods business in Portland, Maine. After his death, Arthur was described thus by his friend and educational collaborator Theodore Dwight Weld, who called him one of humanity's "great benefactors": In 1826, a year after the Erie Canal was completed, Arthur and his brother Lewis moved to New York City, the new national center of business and retail trade, where they established a silk importing busi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
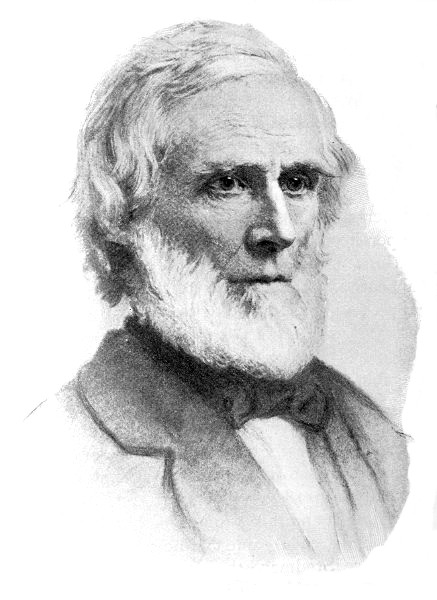
Theodore Dwight Weld, 1803-1895, Bust Portrait, Facing Slightly Left LCCN2006687237
Theodore may refer to: Places * Theodore, Alabama, United States * Theodore, Australian Capital Territory * Theodore, Queensland, a town in the Shire of Banana, Australia * Theodore, Saskatchewan, Canada * Theodore Reservoir, a lake in Saskatchewan People * Theodore (given name), includes the etymology of the given name and a list of people * Theodore (surname), a list of people Fictional characters * Theodore "T-Bag" Bagwell, on the television series ''Prison Break'' * Theodore Huxtable, on the television series ''The Cosby Show'' Other uses * Theodore (horse), a British Thoroughbred racehorse * Theodore Racing, a Formula One racing team See also * Principality of Theodoro, a principality in the south-west Crimea from the 13th to 15th centuries * Thoros (other), Armenian for Theodore * James Bass Mullinger James Bass Mullinger (1834 or 1843 – 22 November 1917), sometimes known by his pen name Theodorus, was a British author, historian, lecturer and scholar. A l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bellows Falls, Vermont
Bellows Falls is an incorporated village located in the town of Rockingham in Windham County, Vermont, United States. The population was 2,747 at the 2020 census. Bellows Falls is home to the Green Mountain Railroad, a heritage railroad; the annual Roots on the River Festival; and the No Film Film Festival. History The community was settled in 1753 by colonists of English descent, who called it Great Falls. Later the settlers renamed the town for Colonel Benjamin Bellows, a landowner, but kept the name Great Falls for the waterfall, a translation of their Abenaki name, "Kitchee pontegu." In 1785, Colonel Enoch Hale built at the falls the first bridge over the Connecticut River. It was the only bridge across the river until 1796, when another was built at Springfield, Massachusetts. The bridge was later replaced. Two bridges currently link Bellows Falls to New Hampshire: the New Arch Bridge (also called the Church Street Bridge), which replaced the Arch Bridge in 1982, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horace Bushnell
Horace Bushnell (April 14, 1802February 17, 1876) was an American Congregational minister and theologian. Life Bushnell was born in the village of Bantam, township of Litchfield, Connecticut. He attended Yale College where he roomed with future magazinist Nathaniel Parker Willis. Willis credited Bushnell with teaching him the proper technique for sharpening a razor. After graduating in 1827, he was literary editor of the ''New York Journal of Commerce'' from 1828–1829, and in 1829 became a tutor at Yale. Here he initially studied law, but in 1831 he entered the theology department of Yale College. In May, 1833 Bushnell was ordained pastor of the North Congregational church in Hartford, Connecticut. He married Mary Apthorp in 1833 and the couple had three children. Douglas, Ann. ''The Feminization of American Culture''. New York: Alfred A. Knopf, 1977: 342. Bushnell remained in Hartford until 1859 when, due to extended poor health he resigned his pastorate. Thereafter he held ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amos Dresser
Amos Dresser (December 17, 1812 – February 4, 1904) was an abolitionist and pacifist minister, one of the founders of Olivet College. His name was well known in the Antebellum period because of a well-publicized incident: in 1835 he was arrested, tried, convicted, and publicly whipped in Nashville, Tennessee, for the crime of possession of abolitionist publications. The incident was widely reported and became well known. Dresser published an account of it, and spoke of it frequently. Amos Dresser's early life Dresser was born in Peru, Massachusetts, and was a descendant of Robert Cushman, a Mayflower pilgrim. His father died when he was an infant; he lived with his mother Minerva Cushman and his mother's second husband, Henry Pierce, until his mother’s death in 1826, when he was 13. "He was for a time engaged in a store; he then taught a school." To prepare for the ministry, in 1830 he enrolled in the new Oneida Institute of Science and Industry, a manual labor school near Ut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Washington Gale
George Washington Gale (1789 – September 13, 1861) was a Presbyterian Church in the United States of America, Presbyterian minister who founded the Oneida Institute of Science and Industry. Early life Gale was born in Stanford, New York, Stanford, Dutchess County, New York, the youngest of nine siblings, and became a Presbyterian Church in the United States of America, Presbyterian minister in Western New York, Western New York State. At the time, the transportation center of Utica, New York, Utica was the intellectual capital of western New York. A graduate Latin honors, with honors from Union College in 1814, he attended Princeton Theological Seminary, but he withdrew because of poor health (dyspepsia). Although he briefly served at the Female Missionary Society, he received his ordination in the St. Laurence Presbytery. He settled down to preach in the Burned-over district. He was not a gifted speaker. Gale's first assignment was as missionary to settlements on the shore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oneida Institute
The Oneida Institute was a short-lived (1827–1843) but highly influential school that was a national leader in the emerging Abolitionism in the United States, abolitionist movement. It was the most radical school in the country, the first at which black men were just as welcome as whites. "Oneida was the seed of Lane Theological Seminary, Case Western Reserve University#Western Reserve College (1826–1882) and University (1882–1967), Western Reserve College, Oberlin College, Oberlin and Knox College (Illinois), Knox colleges." The Oneida Institute was located near Utica, New York, Utica, in the village of Whitesboro, New York, Administrative divisions of New York (state)#Town, town of Whitestown, New York, Whitestown, Oneida County, New York. It was founded in 1827 by George Washington Gale as the Oneida Institute of Science and Industry. His former teacher (in the Addison County Grammar School, Middlebury, Vermont, 1807–1808) John Frost, now a Presbyterian minister in Whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |