|
Lands End Nunataks
The Lands End Nunataks () are two rock nunataks north-northwest of Airdrop Peak at the north end of Ebony Ridge, Antarctica. The nunataks lie at the east side of the terminus of Beardmore Glacier and mark the northern termination of the Commonwealth Range at Ross Ice Shelf. The descriptive name was recommended to the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names by John Gunner of the Ohio State University The Ohio State University, commonly called Ohio State or OSU, is a public land-grant research university in Columbus, Ohio. A member of the University System of Ohio, it has been ranked by major institutional rankings among the best publ ... Institute of Polar Studies, who, with Henry H. Brecher, measured a geological section here on January 16, 1970. References Nunataks of Antarctica Dufek Coast {{DufekCoast-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nunatak
A nunatak (from Inuit ''nunataq'') is the summit or ridge of a mountain that protrudes from an ice field or glacier that otherwise covers most of the mountain or ridge. They are also called glacial islands. Examples are natural pyramidal peaks. When rounded by glacial action, smaller rock promontories may be referred to as rognons. The word is of Greenlandic origin and has been used in English since the 1870s. Description The term is typically used in areas where a permanent ice sheet is present and the nunataks protrude above the sheet.J. J. Zeeberg, ''Climate and Glacial History of the Novaya Zemlya Archipelago, Russian Arctic''. pp. 82–84 Nunataks present readily identifiable landmark reference points in glaciers or ice caps and are often named. While some nunataks are isolated, sometimes they form dense clusters, such as Queen Louise Land in Greenland. Nunataks are generally angular and jagged, which hampers the formation of glacial ice on their tops, although snow can a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airdrop Peak
Airdrop Peak is a twin- peaked mountain high at the north end of Commonwealth Range, Antarctica. It is the first prominent feature in Ebony Ridge when approached from the northwest. When New Zealand surveyors were making observations from the higher of the two peaks on December 11, 1959, an R4D aircraft of U.S. Navy Squadron VX-6 flew overhead to drop a spare radio to the expedition whose original one had broken down. So named because of this incident by the New Zealand Alpine Club The New Zealand Alpine Club (NZAC) was founded in 1891 and is one of the oldest alpine clubs in the world. The NZAC is the national climbing organisation in New Zealand and is a member of the Union Internationale des Associations d'Alpinisme. It ... Antarctic Expedition, 1959–60. References Mountains of the Ross Dependency Shackleton Coast Dufek Coast {{DufekCoast-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ebony Ridge
Ebony and Ivory Ridge () is a coastal ridge long between Airdrop Peak and Mount Robert Scott at the northern end of the Commonwealth Range in Antarctica. It consists of dark metamorphosed greywacke contrasting sharply with the predominant brown ochre of the weathered surface of the granitic intrusions forming nearby Mount Kyffin and Mount Harcourt. It was descriptively named by the New Zealand Alpine Club Antarctic Expedition New is an adjective referring to something recently made, discovered, or created. New or NEW may refer to: Music * New, singer of K-pop group The Boyz Albums and EPs * ''New'' (album), by Paul McCartney, 2013 * ''New'' (EP), by Regurgitator ..., 1959–60. References Ridges of the Ross Dependency Dufek Coast {{DufekCoast-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beardmore Glacier
The Beardmore Glacier in Antarctica is one of the largest valley glaciers in the world, being long and having a width of . It descends about from the Antarctic Plateau to the Ross Ice Shelf and is bordered by the Commonwealth Range of the Queen Maud Mountains on the eastern side and the Queen Alexandra Range of the Central Transantarctic Mountains on the western. The glacier is one of the main passages through the Transantarctic Mountains to the great polar plateau beyond, and was one of the early routes to the South Pole despite its steep upward incline. The glacier was discovered and climbed by Ernest Shackleton during his ''Nimrod'' Expedition of 1908. Although Shackleton turned back at latitude 88° 23' S, just from the South Pole, he established the first proven route towards the pole and, in doing so, became the first person to set foot upon the polar plateau. In 1911–1912, Captain Scott and his ''Terra Nova'' Expedition team reached the South Pole by simi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commonwealth Range
The Commonwealth Range is a north-south trending range of rugged mountains, long, located within the Queen Maud Mountains on the Dufek Coast of the continent of Antarctica. The range borders the eastern side of Beardmore Glacier from the Ross Ice Shelf to Keltie Glacier. The range was discovered by the British Antarctic Expedition (1907–09) and named by the expedition after the Commonwealth of Australia, which gave much assistance to the expedition. Key features Its highest peak is Flat Top at 4000 meters or 13,123 feet. Other peaks within the range include: * |
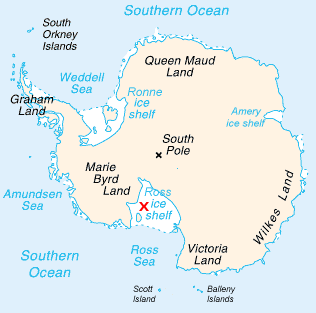
Ross Ice Shelf
The Ross Ice Shelf is the largest ice shelf of Antarctica (, an area of roughly and about across: about the size of France). It is several hundred metres thick. The nearly vertical ice front to the open sea is more than long, and between high above the water surface. Ninety percent of the floating ice, however, is below the water surface. Most of Ross Ice Shelf is in the Ross Dependency claimed by New Zealand. It floats in, and covers, a large southern portion of the Ross Sea and the entire Roosevelt Island located in the east of the Ross Sea. The ice shelf is named after Sir James Clark Ross, who discovered it on 28 January 1841. It was originally called "The Barrier", with various adjectives including "Great Ice Barrier", as it prevented sailing further south. Ross mapped the ice front eastward to 160° W. In 1947, the U.S. Board on Geographic Names applied the name "Ross Shelf Ice" to this feature and published it in the original U.S. Antarctic Gazetteer. In Januar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advisory Committee On Antarctic Names
The Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (ACAN or US-ACAN) is an advisory committee of the United States Board on Geographic Names responsible for recommending commemorative names for features in Antarctica. History The committee was established in 1943 as the Special Committee on Antarctic Names (SCAN). It became the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names in 1947. Fred G. Alberts was Secretary of the Committee from 1949 to 1980. By 1959, a structured nomenclature was reached, allowing for further exploration, structured mapping of the region and a unique naming system. A 1990 ACAN gazeeter of Antarctica listed 16,000 names. Description The United States does not recognise territorial boundaries within Antarctica, so ACAN assigns names to features anywhere within the continent, in consultation with other national nomenclature bodies where appropriate, as defined by the Antarctic Treaty System. The research and staff support for the ACAN is provided by the United States Geologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Gunner (geologist)
John Hugh Gunner (17 May 1884 — 9 August 1918) was an English first-class cricketer and British Army officer. The son of the cricketer Charles Gunner, he was born at Bishops Waltham in May 1884. He was educated at Marlborough College, where he played for a captained the college cricket team. From there he matriculated to Trinity College, Oxford. He represented Trinity College at cricket, but did not progress to play for Oxford University Cricket Club, but did gain a half blue in field hockey. After graduating from Oxford, Gunner became a solicitor and joined the family firm, Gunner & Sons Solicitors, the fifth generation of the family to do so. Gunner was commissioned into the Hampshire Yeomanry as a second lieutenant in May 1905. Gunner played first-class cricket for Hampshire, making his debut against the touring West Indians at Southampton in 1906. He made five further first-class appearances for Hampshire, with three matches in 1906 and two in 1907. He scored 65 runs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ohio State University
The Ohio State University, commonly called Ohio State or OSU, is a public land-grant research university in Columbus, Ohio. A member of the University System of Ohio, it has been ranked by major institutional rankings among the best public universities in the United States. Founded in 1870 as the state's land-grant university and the ninth university in Ohio with the Morrill Act of 1862, Ohio State was originally known as the Ohio Agricultural and Mechanical College and focused on various agricultural and mechanical disciplines, but it developed into a comprehensive university under the direction of then-Governor and later U.S. president Rutherford B. Hayes, and in 1878, the Ohio General Assembly passed a law changing the name to "the Ohio State University" and broadening the scope of the university. Admission standards tightened and became greatly more selective throughout the 2000s and 2010s. Ohio State's political science department and faculty have greatly contri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry H
Henry may refer to: People *Henry (given name) *Henry (surname) * Henry Lau, Canadian singer and musician who performs under the mononym Henry Royalty * Portuguese royalty ** King-Cardinal Henry, King of Portugal ** Henry, Count of Portugal, Henry of Burgundy, Count of Portugal (father of Portugal's first king) ** Prince Henry the Navigator, Infante of Portugal ** Infante Henrique, Duke of Coimbra (born 1949), the sixth in line to Portuguese throne * King of Germany **Henry the Fowler (876–936), first king of Germany * King of Scots (in name, at least) ** Henry Stuart, Lord Darnley (1545/6–1567), consort of Mary, queen of Scots ** Henry Benedict Stuart, the 'Cardinal Duke of York', brother of Bonnie Prince Charlie, who was hailed by Jacobites as Henry IX * Four kings of Castile: **Henry I of Castile **Henry II of Castile **Henry III of Castile **Henry IV of Castile * Five kings of France, spelt ''Henri'' in Modern French since the Renaissance to italianize the name and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nunataks Of Antarctica
A nunatak (from Inuit ''nunataq'') is the summit or ridge of a mountain that protrudes from an ice field or glacier that otherwise covers most of the mountain or ridge. They are also called glacial islands. Examples are natural pyramidal peaks. When rounded by glacial action, smaller rock promontories may be referred to as rognons. The word is of Greenlandic origin and has been used in English since the 1870s. Description The term is typically used in areas where a permanent ice sheet is present and the nunataks protrude above the sheet.J. J. Zeeberg, ''Climate and Glacial History of the Novaya Zemlya Archipelago, Russian Arctic''. pp. 82–84 Nunataks present readily identifiable landmark reference points in glaciers or ice caps and are often named. While some nunataks are isolated, sometimes they form dense clusters, such as Queen Louise Land in Greenland. Nunataks are generally angular and jagged, which hampers the formation of glacial ice on their tops, although snow can a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)