|
Land's End To John O' Groats
Land's End to John o' Groats is the traversal of the whole length of the island of Great Britain between two extremities, in the southwest and northeast. The traditional distance by road is and takes most cyclists 10 to 14 days; the record for running the route is nine days. Off-road walkers typically walk about and take two or three months for the expedition. Signposts indicate the traditional distance at each end. * Land's End is the traditionally acknowledged extreme western point of mainland England. It is in western Cornwall at the end of the Penwith peninsula. The O.S. Grid Reference of the road end is SW342250, Postcode TR19 7AA. In fact it, or strictly speaking Dr Syntax's Head, SW341253, a few hundred yards NW of the road end, is mainland England's most ''westerly'' point. The most southerly point is Lizard Point, about further south. Land's End is sometimes reckoned incorrectly as mainland Great Britain's most southwesterly point. This accolade belongs to Gwenna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A9 Road (Scotland)
The A9 is a major road in Scotland running from the Falkirk council area in central Scotland to Scrabster Harbour, Thurso in the far north, via Stirling, Bridge of Allan, Perth and Inverness. At 273 miles (439 km), it is the longest road in Scotland and the fifth-longest A-road in the United Kingdom. Historically it was the main road between Edinburgh and John o' Groats, and has been called ''the spine of Scotland''. It is one of the three major north–south trunk routes linking the Central Belt to the Highlands - the others being the A82 and the A90. The road's origins lie in the military roads building programme of the 18th century, further supplemented by the building of several bridges in later years. The A9 route was formally designated in 1923, and originally ran from Edinburgh to Inverness. The route was soon extended north from Inverness up to John O'Groats. By the 1970s the route was hampered by severe traffic congestion, and an extensive upgrading programm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tarporley
Tarporley is a large village and civil parish in Cheshire, England. The civil parish also contains the village of Rhuddall Heath. Tarporley is bypassed by the A49 and A51 roads. At the 2011 census, the population was 2,614. History Tarporley is near the site of a prehistoric settlement. Several prehistoric artefacts have been discovered within close proximity of the present-day village: a Neolithic stone axe, a flint scraper and a Bronze Age barbed and tanged arrow head. It is listed in the Domesday Book as ''Torpelei'', which has been translated as meaning “a pear wood near a hill called Torr”. For this reason, Tarporley Church of England Primary School has a pear tree for its emblem. However, the exact origins and meaning are unclear. The name has also been suggested to mean "a peasant's wood/clearing", derived from the Old English words ''þorpere'' (someone who lives at a thorp; a peasant) and ''lēah'' (a wood, forest, glade or clearing) In 1066, the settlement was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shrewsbury
Shrewsbury ( , also ) is a market town, civil parish, and the county town of Shropshire, England, on the River Severn, north-west of London; at the 2021 census, it had a population of 76,782. The town's name can be pronounced as either 'Shrowsbury' or 'Shroosbury', the correct pronunciation being a matter of longstanding debate. The town centre has a largely unspoilt medieval street plan and over 660 listed buildings, including several examples of timber framing from the 15th and 16th centuries. Shrewsbury Castle, a red sandstone fortification, and Shrewsbury Abbey, a former Benedictine monastery, were founded in 1074 and 1083 respectively by the Norman Earl of Shrewsbury, Roger de Montgomery. The town is the birthplace of Charles Darwin and is where he spent 27 years of his life. east of the Welsh border, Shrewsbury serves as the commercial centre for Shropshire and mid-Wales, with a retail output of over £299 million per year and light industry and distribution centre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
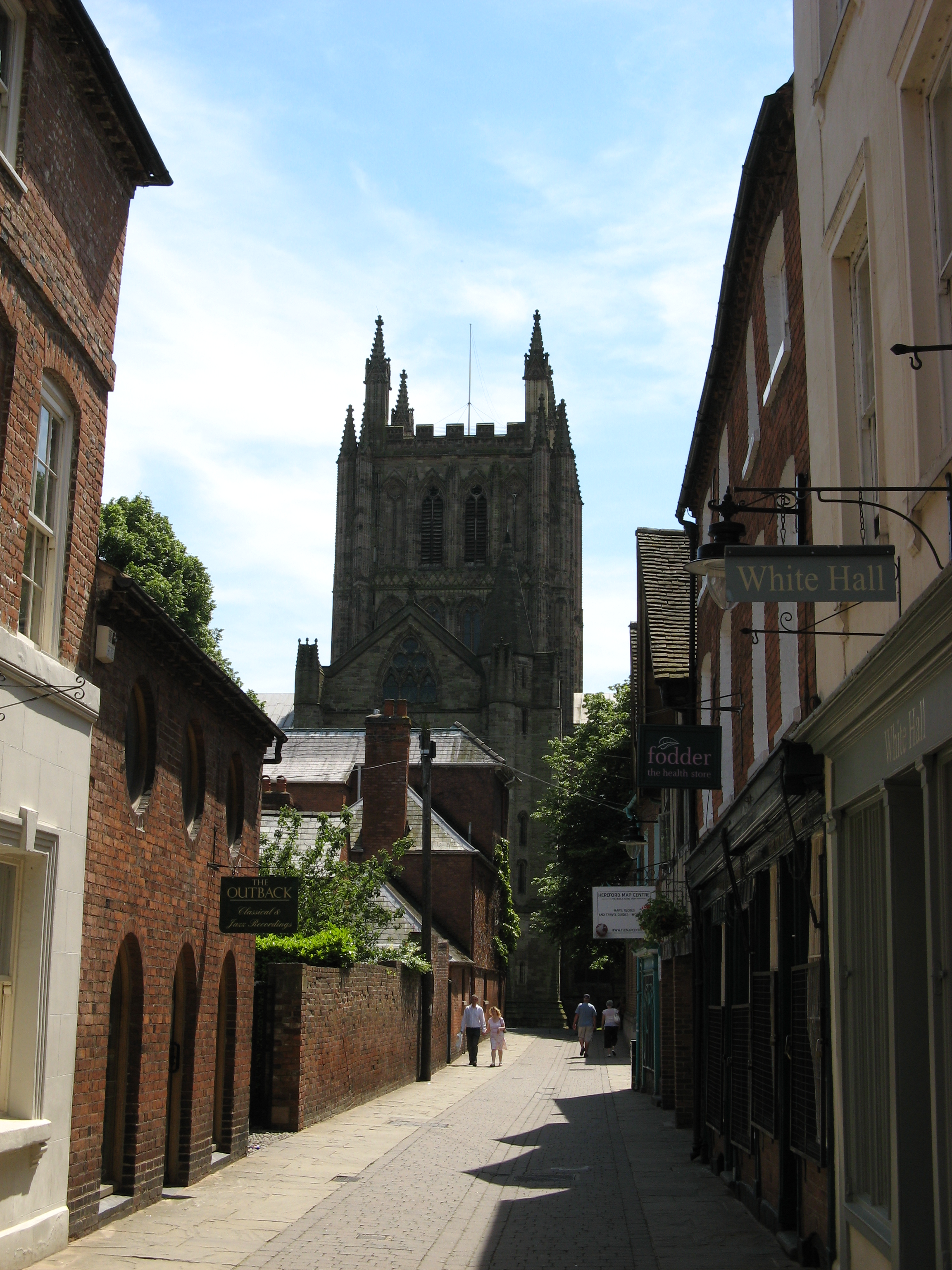
Hereford
Hereford () is a cathedral city, civil parish and the county town of Herefordshire, England. It lies on the River Wye, approximately east of the border with Wales, south-west of Worcester and north-west of Gloucester. With a population of 53,112 in 2021 it is by far the largest settlement in Herefordshire. An early town charter from 1189, granted by Richard I of England, describes it as "Hereford in Wales". Hereford has been recognised as a city since time immemorial, with the status being reconfirmed as recently as October 2000. It is now known chiefly as a trading centre for a wider agricultural and rural area. Products from Hereford include cider, beer, leather goods, nickel alloys, poultry, chemicals and sausage rolls, as well as the famous Hereford breed of cattle. Toponymy The Herefordshire edition of Cambridge County Geographies states "a Welsh derivation of Hereford is more probable than a Saxon one" but the name "Hereford" is also said to come from the Angl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monmouth
Monmouth ( , ; cy, Trefynwy meaning "town on the Monnow") is a town and community in Wales. It is situated where the River Monnow joins the River Wye, from the Wales–England border. Monmouth is northeast of Cardiff, and west of London. It is within the Monmouthshire local authority, and the parliamentary constituency of Monmouth. The population in the 2011 census was 10,508, rising from 8,877 in 2001. Monmouth is the historic county town of Monmouthshire although Abergavenny is now the county town. The town was the site of a small Roman fort, Blestium, and became established after the Normans built Monmouth Castle . The medieval stone gated bridge is the only one of its type remaining in Britain. The castle later came into the possession of the House of Lancaster, and was the birthplace of King Henry V in 1386. In 1536, it became the county town of Monmouthshire. A market town and a focus of educational and cultural activities for the surrounding rural area, Monmouth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Severn Bridge
The Severn Bridge ( cy, Pont Hafren) is a motorway suspension bridge that spans the River Severn between South Gloucestershire in England and Monmouthshire in South East Wales. It is the original Severn road crossing between England and Wales, and took three and a half years to build, at a cost of £8 million. It replaced the 137-year-old Aust Ferry. The bridge was opened in 1966 by Queen Elizabeth II. For thirty years, the bridge carried the M4 motorway. It was granted Grade I listed status in 1999. Following the completion of the Prince of Wales Bridge, the section of motorway from Olveston in England to Magor in Wales was designated the M48. History The first proposal for a bridge across the Severn, approximately in the same location as that eventually constructed, was in 1824 by Thomas Telford, who had been asked to advise on how to improve mail coach services between London and Wales. No action was taken, and over the next few decades the railways became the domina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
M48 Motorway
The M48 is a long motorway in Great Britain, which crosses the Severn near Chepstow, Monmouthshire, linking England with Wales via the Severn Bridge. This road used to be the M4, and as a result is anomalously numbered: as it lies to the north of the M4 and to the west of the M5, it is in the Motorway Zone 5. The M4, the M48 and the A48(M) motorway are the only motorways in Wales. Route Travelling from east to west, after leaving the M4 at Awkley, junction 21, near Olveston in England, the M48 begins by heading north-west towards Aust, junction 1. It crosses the Severn and Wye rivers. Entering Wales, the M48 heads south-west after junction 2, passing to the south of Chepstow, past Crick and continuing in a south-westerly direction, passing Caldicot and Rogiet. The motorway rejoins the M4 at Undy, junction 23 to the east of Magor. Junction 2 can be reached via the A466, which leads to the A48. The junction gives access to the Wye Valley, an Area of Outstanding Natural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avonmouth Bridge
The Avonmouth Bridge is a road bridge that carries the M5 motorway over the River Avon into Somerset near Bristol, England. The main span is long, and the bridge is long, with an air draught above mean high water level of . It also has a separate footpath and cycleway which connects the B4054 near Avonmouth station with the Royal Portbury Dock and the village of Pill. Construction The bridge was built with three lanes each way, with full hard shoulders. In 1995–2000, it was widened to four lanes each way, with the result that the hard shoulders are no longer of full width. The bridge was built to allow tall ships underneath. This gave the bridge steep gradients that cause heavy vehicles to slow down, resulting in congestion during rush hour and the summer tourist season: traffic can back up both on the bridge and on the approaches. The construction contract was let to Fairfield-Mabey and commenced in 1969; Fairfield-Mabey placed a sub-contract with Tarmac Civil Eng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bridgwater
Bridgwater is a large historic market town and civil parish in Somerset, England. Its population currently stands at around 41,276 as of 2022. Bridgwater is at the edge of the Somerset Levels, in level and well-wooded country. The town lies along both sides of the River Parrett; it has been a major inland port and trading centre since the industrial revolution. Most of its industrial bases still stand today. Its larger neighbour, Taunton, is linked to Bridgwater via a canal, the M5 motorway and the GWR railway line. Historically, the town had a politically radical tendency. The Battle of Sedgemoor, where the Monmouth Rebellion was finally crushed in 1685, was fought nearby. Notable buildings include the Church of St Mary and Blake Museum, which is a largely restored house in Blake Street and was the birthplace of Admiral Blake in 1598. The town has an arts centre and plays host to the annual Bridgwater Guy Fawkes Carnival. Etymology It is thought that the town was original ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taunton
Taunton () is the county town of Somerset, England, with a 2011 population of 69,570. Its thousand-year history includes a 10th-century monastic foundation, Taunton Castle, which later became a priory. The Normans built a castle owned by the Bishops of Winchester. Parts of the inner ward house were turned into the Museum of Somerset and Somerset Military Museum. For the Second Cornish uprising of 1497, Perkin Warbeck brought an army of 6,000; most surrendered to Henry VII on 4 October 1497. On 20 June 1685 the Duke of Monmouth crowned himself King of England here in a rebellion, defeated at the Battle of Sedgemoor. Judge Jeffreys led the Bloody Assizes in the Castle's Great Hall. The Grand Western Canal reached Taunton in 1839 and the Bristol and Exeter Railway in 1842. Today it hosts Musgrove Park Hospital, Somerset County Cricket Club, is the base of 40 Commando, Royal Marines, and is home to the United Kingdom Hydrographic Office on Admiralty Way. The popular Taunton flow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tiverton, Devon
Tiverton ( ) is a town and civil parish in Devon, England, and the commercial and administrative centre of the Mid Devon district. The population in 2019 was 20,587. History Early history The town's name is conjectured to derive from "Twy-ford-ton" or "Twyverton", meaning "the town on two fords", and was historically referred to as "Twyford". The town stands at the confluence of the rivers Exe and Lowman. Human occupation in the area dates back to the Stone Age, with many flint tools found in the area. An Iron Age hill fort, Cranmore Castle, stands at the top of Exeter Hill above the town, and a Roman fort or marching camp was discovered on the hillside below Knightshayes Court near Bolham, just to the north of the town. Tiverton formed part of the inheritance of Aethelweard, youngest son of King Alfred. Countess Gytha of Wessex controlled the town in 1066 and the Domesday Book indicates that William the Conqueror was its tenant-in-chief in 1086. Tiverton was also the se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |