|
Lampropteryx Suffumata
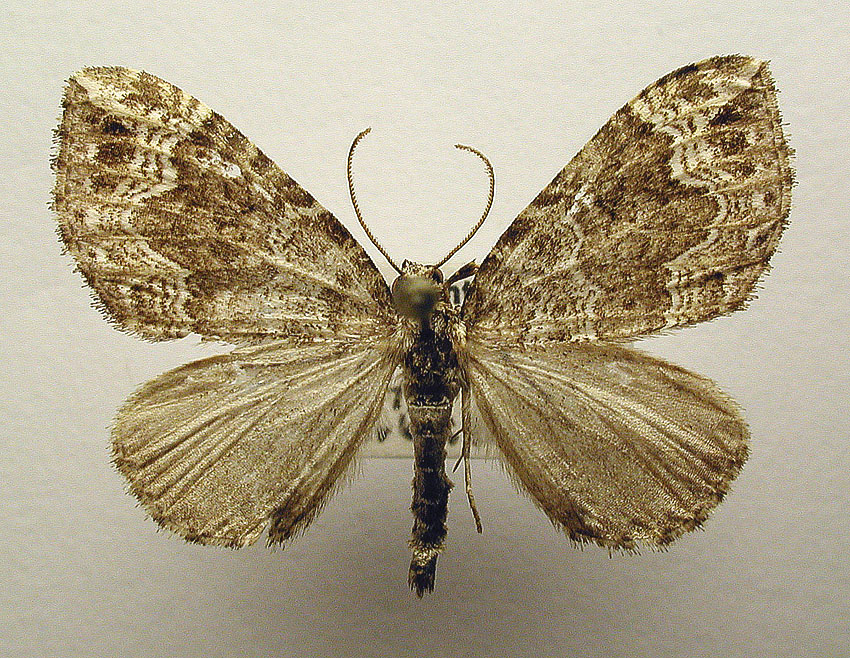
''Lampropteryx suffumata'', the water carpet, is a moth of the family Geometridae. It is found from Europe to the Altai Mountains, Khabarovsk Krai and the Kamchatka Peninsula in the far east of Russia, and Hokkaido, Japan. In 2000, the species was discovered in Alaska, USA, and then in 2008 DNA-barcoding analysis of museum specimens identified several Canadian specimens, thereby extending the geographical range from Ireland in the west, across Eurasia, to the west of North America. The habitat consists of damp woodland, grassy areas, chalk downland and scrubland. Description The wingspan is 25–32 mm. The ground colour is brownish. Between the wingbase and the midfield, as well as between the central and margin field is a whitish lateral band. The dark midfield is serrated on both sides. The outer cross-line limiting the midfield and shows a clearly protruding double wave. The margin field is heavily obscured below the apex. The hind wings are pale grey and have a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Denis
Johann Nepomuk Cosmas Michael Denis, also: ''Sined the Bard'', (27 September 1729 – 29 September 1800) was an Austrian Catholic priest and Jesuit, who is best known as a poet, bibliographer, and lepidopterist. Life Denis was born at Schärding, located on the Inn (river), Inn River, then ruled by the Electorate of Bavaria, in 1729, the son of Johann Rudolph Denis, who taught him Latin at an early age. At the age of ten, he was enrolled to be educated by the Society of Jesus, Jesuits at their college in Passau. After completing his studies in 1747, he entered the novitiate of the Society of Jesus in Vienna. In 1749, following this initial formation period, Denis was sent to carry his period of regency (Jesuit), Regency at Jesuit colleges in Graz and Klagenfurt. He was Holy Orders, ordained a Catholic priest, priest in 1757. Two years later, he was appointed professor at the Theresianum in Vienna, a Jesuit college. After the suppression of the Jesuits in 1773, and the subsequent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wingspan
The wingspan (or just span) of a bird or an airplane is the distance from one wingtip to the other wingtip. For example, the Boeing 777–200 has a wingspan of , and a wandering albatross (''Diomedea exulans'') caught in 1965 had a wingspan of , the official record for a living bird. The term wingspan, more technically extent, is also used for other winged animals such as pterosaurs, bats, insects, etc., and other aircraft such as ornithopters. In humans, the term wingspan also refers to the arm span, which is distance between the length from one end of an individual's arms (measured at the fingertips) to the other when raised parallel to the ground at shoulder height at a 90º angle. Former professional basketball player Manute Bol stood at and owned one of the largest wingspans at . Wingspan of aircraft The wingspan of an aircraft is always measured in a straight line, from wingtip to wingtip, independently of wing shape or sweep. Implications for aircraft design and anima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moths Of Europe
Moths are a paraphyletic group of insects that includes all members of the order Lepidoptera that are not butterflies, with moths making up the vast majority of the order. There are thought to be approximately 160,000 species of moth, many of which have yet to be described. Most species of moth are nocturnal, but there are also crepuscular and diurnal species. Differences between butterflies and moths While the butterflies form a monophyletic group, the moths, comprising the rest of the Lepidoptera, do not. Many attempts have been made to group the superfamilies of the Lepidoptera into natural groups, most of which fail because one of the two groups is not monophyletic: Microlepidoptera and Macrolepidoptera, Heterocera and Rhopalocera, Jugatae and Frenatae, Monotrysia and Ditrysia.Scoble, MJ 1995. The Lepidoptera: Form, function and diversity. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press; 404 p. Although the rules for distinguishing moths from butterflies are not well establis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moths Of Asia
Moths are a paraphyletic group of insects that includes all members of the order Lepidoptera that are not butterflies, with moths making up the vast majority of the order. There are thought to be approximately 160,000 species of moth, many of which have yet to be described. Most species of moth are nocturnal, but there are also crepuscular and diurnal species. Differences between butterflies and moths While the butterflies form a monophyletic group, the moths, comprising the rest of the Lepidoptera, do not. Many attempts have been made to group the superfamilies of the Lepidoptera into natural groups, most of which fail because one of the two groups is not monophyletic: Microlepidoptera and Macrolepidoptera, Heterocera Moths are a paraphyletic group of insects that includes all members of the order Lepidoptera that are not butterflies, with moths making up the vast majority of the order. There are thought to be approximately 160,000 species of moth, many of w ... and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moths Described In 1775
Moths are a paraphyletic group of insects that includes all members of the order Lepidoptera that are not butterflies, with moths making up the vast majority of the order. There are thought to be approximately 160,000 species of moth, many of which have yet to be described. Most species of moth are nocturnal, but there are also crepuscular and diurnal species. Differences between butterflies and moths While the butterflies form a monophyletic group, the moths, comprising the rest of the Lepidoptera, do not. Many attempts have been made to group the superfamilies of the Lepidoptera into natural groups, most of which fail because one of the two groups is not monophyletic: Microlepidoptera and Macrolepidoptera, Heterocera and Rhopalocera, Jugatae and Frenatae, Monotrysia and Ditrysia.Scoble, MJ 1995. The Lepidoptera: Form, function and diversity. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press; 404 p. Although the rules for distinguishing moths from butterflies are not well establishe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cidariini
The Cidariini are the largest tribe of geometer moths in the subfamily Larentiinae (possibly a distinct familyYoung (2008)). The Cidariini include many of the species known as "carpets" or, ambiguously, "carpet moths" (most other "carpets" are in the Xanthorhoini), and are among the few geometer moths that have been subject to fairly comprehensive cladistic study of their phylogeny. The tribe was described by Philogène Auguste Joseph Duponchel in 1845. Genera As several larentiine genera have not yet been assigned to a tribe, the genus list is still preliminary; for example the genus '' Almeria'' may well belong in the Cidariini.See references in Savela (2007) Several well-known species are also listed: Footnotes References * (2008)Family group names in Geometridae Retrieved 22 July 2008. * * (2008): Characterisation of the Australian Nacophorini using adult morphology, and phylogeny of the Geometridae based on morphological characters. ''Zootaxa ''Zootaxa'' is a peer- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lampropteryx Otregiata
''Lampropteryx otregiata'', the Devon carpet, is a moth of the family Geometridae. It is found from western Europe (from Scandinavia south to the Alps) to Japan and the Kuril Islands. The wingspan is 27–30 mm. There are two generations per year, with adults on wing in May and June and again in August and September. The larvae feed on ''Asperula'' and ''Galium'' species (including ''Galium palustre'' and ''Galium uliginosum''). Larvae can be found from July to August. It overwinters in the pupal stage. Subspecies *''Lampropteryx otregiata otregiata'' *''Lampropteryx otregiata dubitatrix'' (Bryk, 1942) Similar species *''Lampropteryx suffumata'' References External linksLepiforum.de Cidariini Moths described in 1917 Moths of Asia Moths of Europe {{Cidariini-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galium
''Galium'' is a large genus of annual and perennial herbaceous plants in the family Rubiaceae, occurring in the temperate zones of both the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. Some species are informally known as bedstraw. There are over 600 species of ''Galium'', with estimates of 629 to 650 The Jepson eFlora 2013. as of 2013. The field madder, '''', is a close relative and may be confused with a tiny bedstraw. '' Asperula
''Asperula'', commonly known as woodruff, is a genus of flowering plants in the family Rubiaceae. It contains 194 species and ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lampropteryx Suffumata
''Lampropteryx suffumata'', the water carpet, is a moth of the family Geometridae. It is found from Europe to the Altai Mountains, Khabarovsk Krai and the Kamchatka Peninsula in the far east of Russia, and Hokkaido, Japan. In 2000, the species was discovered in Alaska, USA, and then in 2008 DNA-barcoding analysis of museum specimens identified several Canadian specimens, thereby extending the geographical range from Ireland in the west, across Eurasia, to the west of North America. The habitat consists of damp woodland, grassy areas, chalk downland and scrubland. Description The wingspan is 25–32 mm. The ground colour is brownish. Between the wingbase and the midfield, as well as between the central and margin field is a whitish lateral band. The dark midfield is serrated on both sides. The outer cross-line limiting the midfield and shows a clearly protruding double wave. The margin field is heavily obscured below the apex. The hind wings are pale grey and have a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buckler W The Larvæ Of The British Butterflies And Moths PlateCXLIII
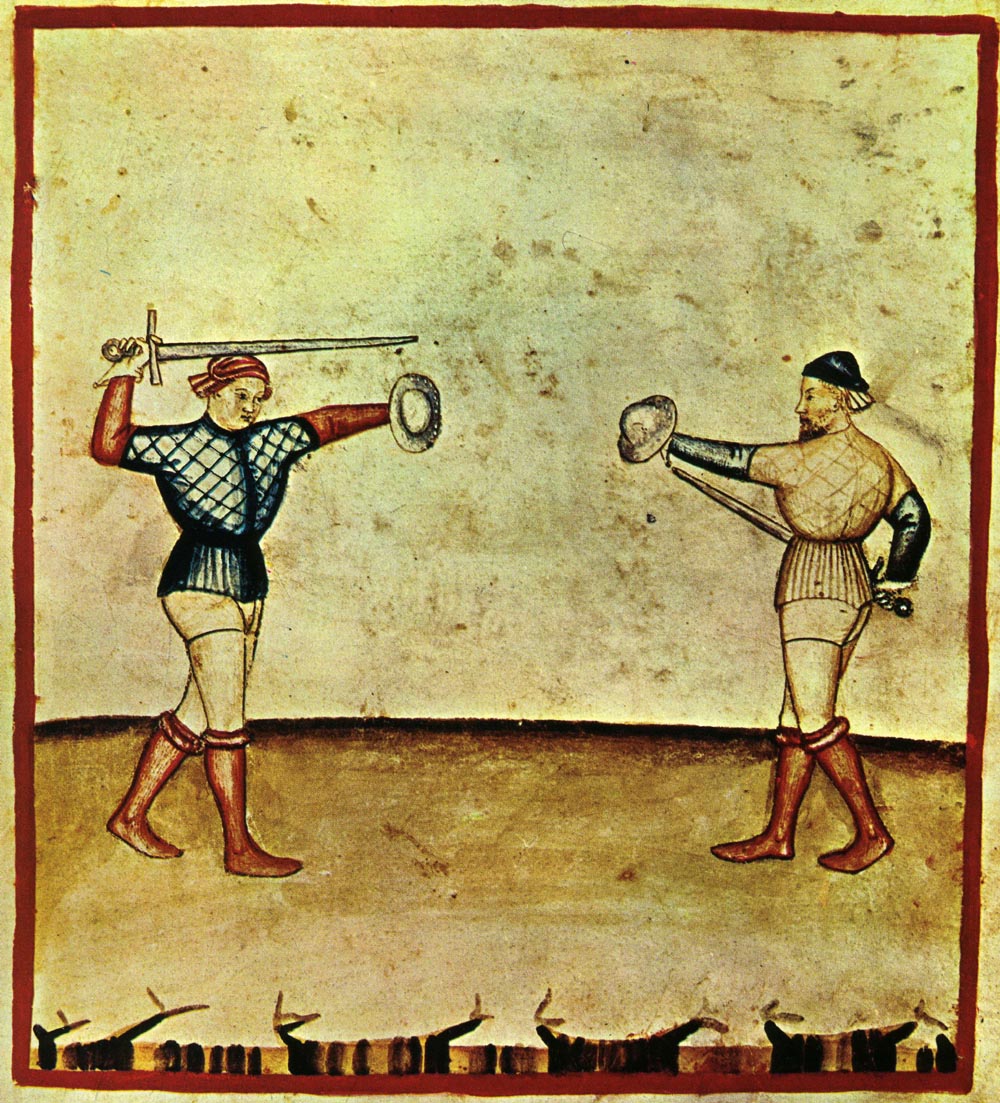
A buckler (French ''bouclier'' 'shield', from Old French ''bocle, boucle'' 'boss') is a small shield, up to 45 cm (up to 18 in) in diameter, gripped in the fist with a central handle behind the boss. While being used in Europe since antiquity, it became more common as a companion weapon in hand-to-hand combat during the Medieval and Renaissance periods. Its size made it poor protection against missile weapons (e.g., arrows) but useful in deflecting the blow of an opponent's weapons, binding his arms, hindering his movements, or punching him. MS I.33, considered the earliest extant armed-combat manual, (around 1300) contains an early description of a system of combat with buckler and sword. Typology According to the typology of Schmidt, there are three main types of buckler regarding their shape: *Type I: round *Type II: rectangular or trapezoid *Type III: oval or teardrop-shaped These types are combined with the cross sections: *Type a: flat *Type b: concave *Type ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
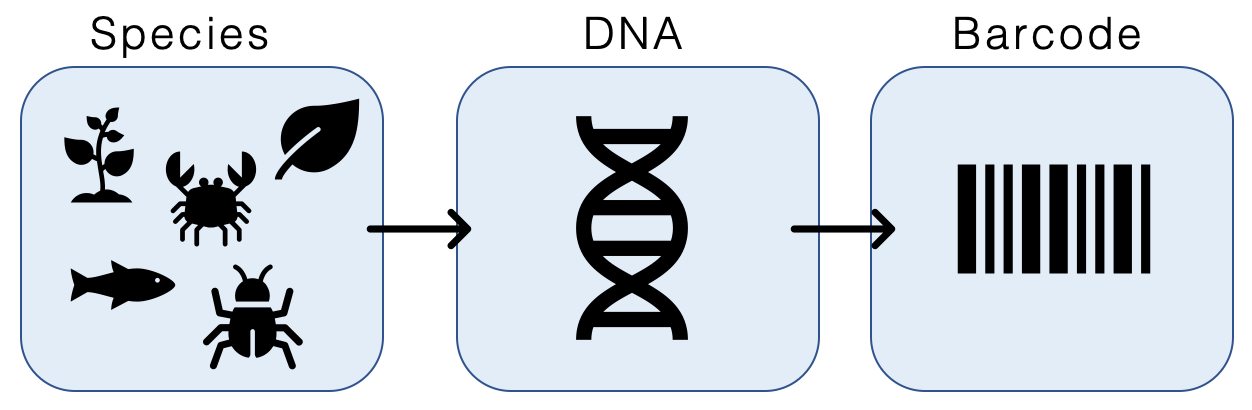
DNA Barcoding
DNA barcoding is a method of species identification using a short section of DNA from a specific gene or genes. The premise of DNA barcoding is that by comparison with a reference library of such DNA sections (also called "sequences"), an individual sequence can be used to uniquely identify an organism to species, just as a supermarket scanner uses the familiar black stripes of the UPC barcode to identify an item in its stock against its reference database. These "barcodes" are sometimes used in an effort to identify unknown species or parts of an organism, simply to catalog as many taxa as possible, or to compare with traditional taxonomy in an effort to determine species boundaries. Different gene regions are used to identify the different organismal groups using barcoding. The most commonly used barcode region for animals and some protists is a portion of the cytochrome ''c'' oxidase I (COI or COX1) gene, found in mitochondrial DNA. Other genes suitable for DNA barcoding ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ignaz Schiffermüller
Ignaz Schiffermüller (born 2 October 1727 in Hellmonsödt; died 21 June 1806 in Linz) was an Austrian naturalist mainly interested in Lepidoptera. Schiffermüller was a teacher at the Theresianum College in Vienna. His collection was presented to the old United Royal and Imperial Natural History Collections (Vereinigtes k.k. Naturalien-Cabinet) at the Hofburg where it burnt during the revolution in 1848. With Michael Denis, also a teacher at the Theresianum, he published the first index of the Lepidoptera of the Viennese region ''das Systematische Verzeichnis der Schmetterlinge der Wienergegend herausgegeben von einigen Lehrern am k. k. Theresianum'' (1775). His collection is in the ''Kaiserlichen Hof-Naturalienkabinett'' (now Naturhistorisches Museum Wien). Schiffermüller is also noteworthy for his work in developing a scientifically based colour nomenclature. In his ''Versuch eines Farbensystems'' (1772), Schiffermüller addressed the need for a standardised nomenclature wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |