|
Lampriformes
Lampriformes is an order of ray-finned fish. Members are collectively called lamprids (which is more properly used for the Lampridae) or lampriforms, and unite such open-ocean and partially deep-sea Teleostei as the crestfishes, oarfish, opahs, and ribbonfishes. A synonym for this order is Allotriognathi, while an often-seen, but apparently incorrect, spelling variant is Lampridiformes. They contain seven extant families which are generally small but highly distinct, and a mere 12 lampriform genera with some 20 species altogether are recognized. The scientific name literally means "shaped (like the) bright (one)", as "lampr-", meaning bright, comes from ''lampris'', the generic name for the opah. In contrast, most other living lampriforms are actually ribbon-like and not very similar to the disc-shaped opahs in habitus. They are, however, quite distinctly united by their anatomy, and the family's phylogeny, as well as the most ancient fossils of this order suggest the origi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oarfish
Oarfish are huge, greatly elongated, pelagic lampriform fish belonging to the small family Regalecidae. Found in areas spanning from temperate ocean zones to tropical ones, yet rarely seen, the oarfish family contains three species in two genera. One of these, the giant oarfish (''Regalecus glesne''), is the longest bony fish alive, growing up to in length. The common name ''oarfish'' is thought to be in reference either to their highly compressed and elongated bodies, or to the now discredited belief that the fish "row" themselves through the water with their pelvic fins. The family name Regalecidae is derived from the Latin ''regalis'', meaning "royal". The occasional beachings of oarfish after storms, and their habit of lingering at the surface when sick or dying, make oarfish a probable source of many sea serpent tales. Although the larger species are considered game fish and are fished commercially to a minor extent, oarfish are rarely caught alive; their flesh is not w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
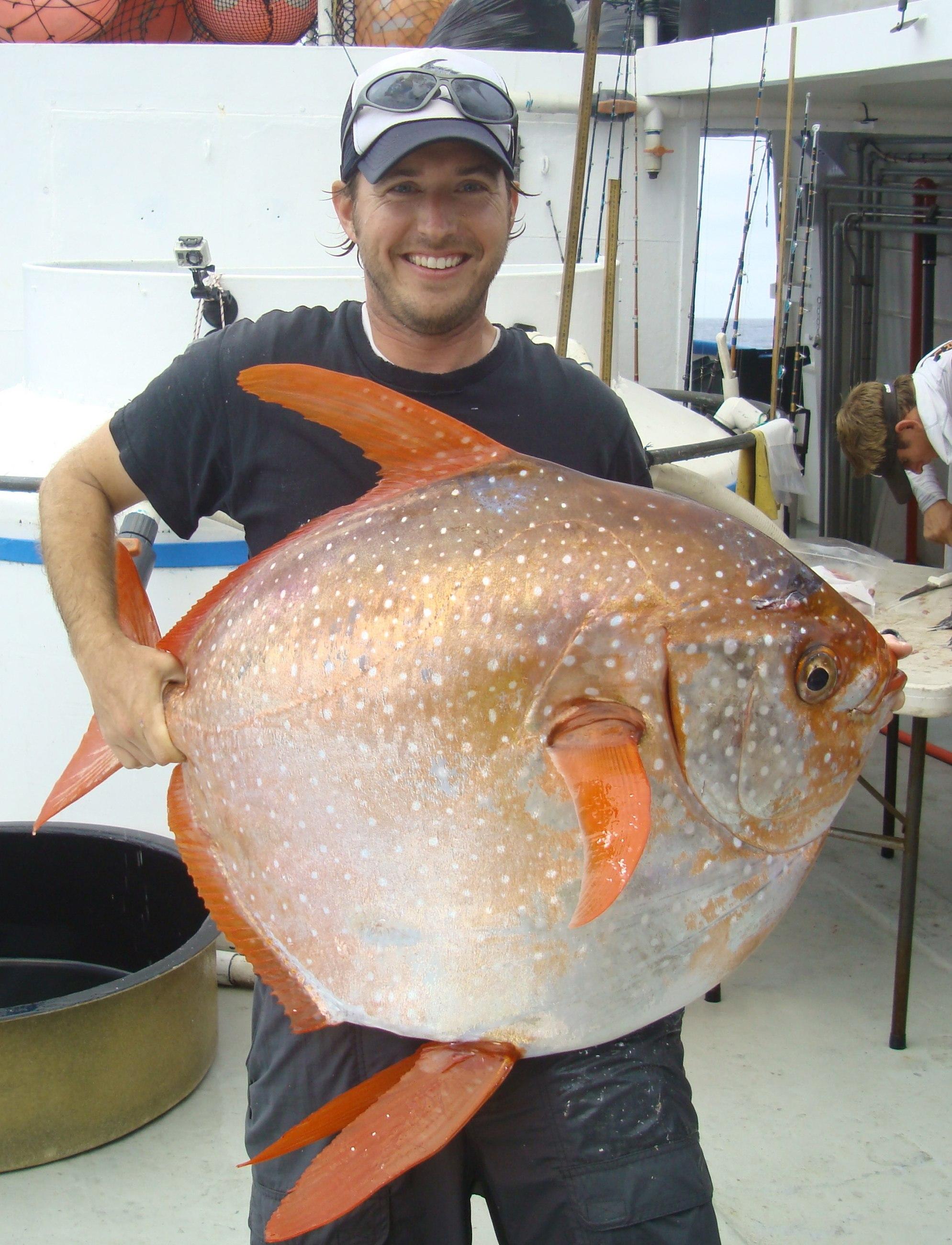
Lampris Guttatus
''Lampris guttatus'', commonly known as the opah, cravo, moonfish, kingfish, and Jerusalem haddock, is a large, colorful, deep-bodied pelagic zone, pelagic Lampriformes, lampriform fish belonging to the family (biology), family Lampridae, which comprises the genus ''Lampris''. It is a pelagic fish with a worldwide distribution. While it is common to locations such as Hawaii and west Africa, it remains uncommon in others, including the Mediterranean. In the places where ''L. guttatus'' is prevalent, it is not a target of fishing, though it does represent an important commercial component of bycatch. It is common in restaurants in Hawaii. In Longline bycatch in Hawaii, Hawaiian longline fisheries, it is generally caught in deep nets targeting bigeye tuna. In 2005, the fish caught numbered 13,332. In areas where the fish is uncommon, such as the Mediterranean, its prevalence is increasing. Some researchers believe this a result of climate change. Much is still unknown about the dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
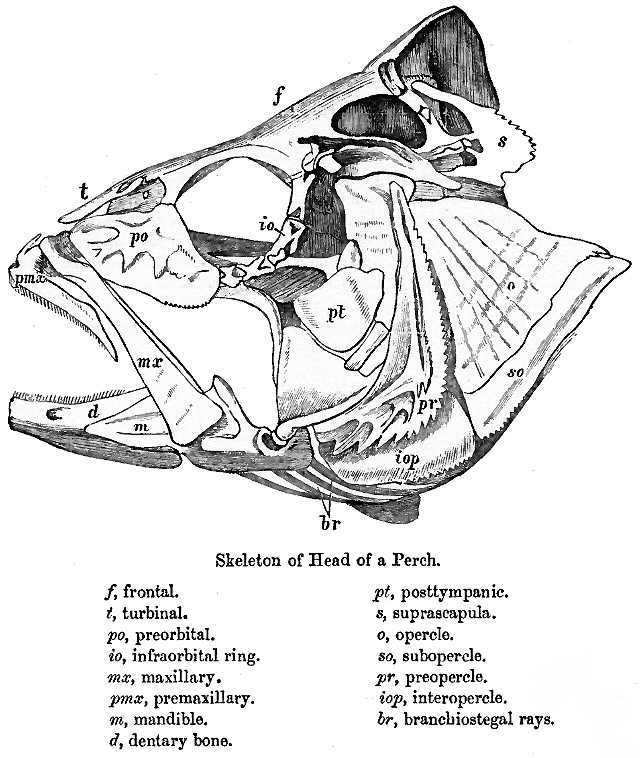
Teleost
Teleostei (; Greek ''teleios'' "complete" + ''osteon'' "bone"), members of which are known as teleosts ), is, by far, the largest infraclass in the class Actinopterygii, the ray-finned fishes, containing 96% of all extant species of fish. Teleosts are arranged into about 40 orders and 448 family (biology), families. Over 26,000 species have been described. Teleosts range from giant oarfish measuring or more, and ocean sunfish weighing over , to the minute male anglerfish ''Photocorynus spiniceps'', just long. Including not only torpedo-shaped fish built for speed, teleosts can be flattened vertically or horizontally, be elongated cylinders or take specialised shapes as in anglerfish and seahorses. The difference between teleosts and other bony fish lies mainly in their jaw bones; teleosts have a movable premaxilla and corresponding modifications in the jaw musculature which make it possible for them to cranial kinesis, protrude their jaws outwards from the mouth. This is of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lophotidae
Crestfishes, family Lophotidae, are lampriform fishes found in most oceans. It consists of two extant and four extinct genera. They are elongated, ribbon-like fishes, silver in color, found in deep tropical and subtropical waters worldwide. Their scientific name is from Greek ''lophos'' meaning "crest" and refer to the crest (part of the dorsal fin) that emerges from the snout and head; this structure gives them their other name of unicorn fishes. The extant genera all possess ink sacs that open into their cloacae from which they can produce a cloud of black ink when threatened (as in many cephalopod A cephalopod is any member of the molluscan class Cephalopoda (Greek plural , ; "head-feet") such as a squid, octopus, cuttlefish, or nautilus. These exclusively marine animals are characterized by bilateral body symmetry, a prominent head ...s). References Lophotidae {{Lampriformes-stub Animal families ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Actinopterygii
Actinopterygii (; ), members of which are known as ray-finned fishes, is a class of bony fish. They comprise over 50% of living vertebrate species. The ray-finned fishes are so called because their fins are webs of skin supported by bony or horny spines (rays), as opposed to the fleshy, lobed fins that characterize the class Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned fish). These actinopterygian fin rays attach directly to the proximal or basal skeletal elements, the radials, which represent the link or connection between these fins and the internal skeleton (e.g., pelvic and pectoral girdles). By species count, actinopterygians dominate the vertebrates, and they constitute nearly 99% of the over 30,000 species of fish. They are ubiquitous throughout freshwater and marine environments from the deep sea to the highest mountain streams. Extant species can range in size from ''Paedocypris'', at , to the massive ocean sunfish, at , and the long-bodied oarfish, at . The vast majority of Actinopt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crestfish
Crestfishes, family Lophotidae, are lampriform fishes found in most oceans. It consists of two extant and four extinct genera. They are elongated, ribbon-like fishes, silver in color, found in deep tropical and subtropical waters worldwide. Their scientific name is from Greek ''lophos'' meaning "crest" and refer to the crest (part of the dorsal fin A dorsal fin is a fin located on the back of most marine and freshwater vertebrates within various taxa of the animal kingdom. Many species of animals possessing dorsal fins are not particularly closely related to each other, though through c ...) that emerges from the snout and head; this structure gives them their other name of unicorn fishes. The extant genera all possess ink sacs that open into their cloacae from which they can produce a cloud of black ink when threatened (as in many cephalopods). References Lophotidae {{Lampriformes-stub Animal families ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crested Oarfish
The crested oarfish (''Lophotus lacepede'') is a species of crestfish in the family Lophotidae. It is an oceanodromous fish ranging from waters 0–92 meters deep, but may get stranded in shallow waters. Distribution and habitat The crested oarfish lives in warm seas near areas such as the Western Atlantic, Western Indian Ocean, Eastern Atlantic, and the Eastern Pacific within the oceanic and mesopelagic zone. Description and ecology The crested oarfish has maximum length of 200 centimeters, but are often are only found at 100 centimeters in length. It has an ink sack near the cloaca, and discharges ink out of it when it feels alarmed. Its prey consists of squids and fishes such as anchovies. It is oviparous, and lays planktonic eggs. Conservation The crested oarfish are likely found in marine protected areas, and has no known major threats towards it. No specific conservation measures have been made, and IUCN Red List has classified the fish as a 'least concern' species ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomy
Anatomy () is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having its beginnings in prehistoric times. Anatomy is inherently tied to developmental biology, embryology, comparative anatomy, evolutionary biology, and phylogeny, as these are the processes by which anatomy is generated, both over immediate and long-term timescales. Anatomy and physiology, which study the structure and function (biology), function of organisms and their parts respectively, make a natural pair of related disciplines, and are often studied together. Human anatomy is one of the essential basic research, basic sciences that are applied in medicine. The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic scale, macroscopic and microscopic scale, microscopic. Gross anatomy, Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phylogenetic Tree
A phylogenetic tree (also phylogeny or evolutionary tree Felsenstein J. (2004). ''Inferring Phylogenies'' Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA.) is a branching diagram or a tree showing the evolutionary relationships among various biological species or other entities based upon similarities and differences in their physical or genetic characteristics. All life on Earth is part of a single phylogenetic tree, indicating common ancestry. In a ''rooted'' phylogenetic tree, each node with descendants represents the inferred most recent common ancestor of those descendants, and the edge lengths in some trees may be interpreted as time estimates. Each node is called a taxonomic unit. Internal nodes are generally called hypothetical taxonomic units, as they cannot be directly observed. Trees are useful in fields of biology such as bioinformatics, systematics, and phylogenetics. ''Unrooted'' trees illustrate only the relatedness of the leaf nodes and do not require the ancestral root to b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lampris
Opahs, also commonly known as moonfish, sunfish (not to be confused with Molidae), kingfish, redfin ocean pan are large, colorful, deep-bodied pelagic lampriform fishes comprising the small family Lampridae (also spelled Lamprididae). The family comprises two genera: ''Lampris'' (from the Ancient Greek ''λαμπρός'' : lamprós, "brilliant" or "clear") and the monotypic ''Megalampris'' (known only from fossil remains). The extinct family, Turkmenidae, from the Paleogene of Central Asia, is closely related, though much smaller. In 2015, ''Lampris guttatus'' was discovered to have near-whole-body endothermy in which the entire core of the body is maintained at around 5 °C above the surrounding water. This is unique among fish as most fish are entirely cold blooded or are capable of warming only some parts of their bodies. Species Two living species were traditionally recognized, but a taxonomic review in 2018 found that more should be recognized (the result of splitti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitatively measure the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binomial Nomenclature
In taxonomy, binomial nomenclature ("two-term naming system"), also called nomenclature ("two-name naming system") or binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, both of which use Latin grammatical forms, although they can be based on words from other languages. Such a name is called a binomial name (which may be shortened to just "binomial"), a binomen, name or a scientific name; more informally it is also historically called a Latin name. The first part of the name – the '' generic name'' – identifies the genus to which the species belongs, whereas the second part – the specific name or specific epithet – distinguishes the species within the genus. For example, modern humans belong to the genus ''Homo'' and within this genus to the species ''Homo sapiens''. ''Tyrannosaurus rex'' is likely the most widely known binomial. The ''formal'' introduction of this system of naming species is credit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |