|
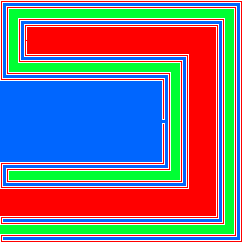
Lakes Of Wada
In mathematics, the are three disjoint connected open sets of the plane or open unit square with the counterintuitive property that they all have the same boundary. In other words, for any point selected on the boundary of ''one'' of the lakes, the other two lakes' boundaries also contain that point. More than two sets with the same boundary are said to have the Wada property; examples include Wada basins in dynamical systems. This property is rare in real-world systems. The lakes of Wada were introduced by , who credited the discovery to Takeo Wada. His construction is similar to the construction by of an indecomposable continuum, and in fact it is possible for the common boundary of the three sets to be an indecomposable continuum. Construction of the lakes of Wada The Lakes of Wada are formed by starting with a closed unit square of dry land, and then digging 3 lakes according to the following rule: *On day ''n'' = 1, 2, 3,... extend lake ''n'' mod 3 (=0, 1, 2) so that i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lakes Of Wada
In mathematics, the are three disjoint connected open sets of the plane or open unit square with the counterintuitive property that they all have the same boundary. In other words, for any point selected on the boundary of ''one'' of the lakes, the other two lakes' boundaries also contain that point. More than two sets with the same boundary are said to have the Wada property; examples include Wada basins in dynamical systems. This property is rare in real-world systems. The lakes of Wada were introduced by , who credited the discovery to Takeo Wada. His construction is similar to the construction by of an indecomposable continuum, and in fact it is possible for the common boundary of the three sets to be an indecomposable continuum. Construction of the lakes of Wada The Lakes of Wada are formed by starting with a closed unit square of dry land, and then digging 3 lakes according to the following rule: *On day ''n'' = 1, 2, 3,... extend lake ''n'' mod 3 (=0, 1, 2) so that i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newton Fractal
The Newton fractal is a boundary set in the complex plane which is characterized by Newton's method applied to a fixed polynomial or transcendental function. It is the Julia set of the meromorphic function which is given by Newton's method. When there are no attractive cycles (of order greater than 1), it divides the complex plane into regions , each of which is associated with a root of the polynomial, . In this way the Newton fractal is similar to the Mandelbrot set, and like other fractals it exhibits an intricate appearance arising from a simple description. It is relevant to numerical analysis because it shows that (outside the region of quadratic convergence) the Newton method can be very sensitive to its choice of start point. Almost all points of the complex plane are associated with one of the roots of a given polynomial in the following way: the point is used as starting value for Newton's iteration , yielding a sequence of points If the sequence converges to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Notices Of The American Mathematical Society
''Notices of the American Mathematical Society'' is the membership journal of the American Mathematical Society (AMS), published monthly except for the combined June/July issue. The first volume appeared in 1953. Each issue of the magazine since January 1995 is available in its entirety on the journal web site. Articles are peer-reviewed by an editorial board of mathematical experts. Since 2019, the editor-in-chief is Erica Flapan. The cover regularly features mathematical visualization Mathematical phenomena can be understood and explored via visualization. Classically this consisted of two-dimensional drawings or building three-dimensional models (particularly plaster models in the 19th and early 20th century), while today it ...s. The ''Notices'' is self-described to be the world's most widely read mathematical journal. As the membership journal of the American Mathematical Society, the ''Notices'' is sent to the approximately 30,000 AMS members worldwide, one-third of whom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tôhoku Mathematical Journal
The ''Tohoku Mathematical Journal'' is a mathematical research journal published by Tohoku University in Japan. It was founded in August 1911 by Tsuruichi Hayashi. History Due to World War II the publication of the journal stopped in 1943 with volume 49. Publication was resumed in 1949 with the volume numbering starting again at 1. In order to distinguish between the identical numbered volumes, volumes in the first publishing period are referred to as the ''first series'' whereas the later volumes are called ''second series''. Before volume 51 of the second series the journal was called ''Tôhoku Mathematical Journal'', with a circumflex over the second letter of ''Tohoku''. Selected papers *. The first publication of the Sprague–Grundy theorem, the basis for much of combinatorial game theory, later independently rediscovered by P. M. Grundy. *. This paper describes Weiszfeld's algorithm for finding the geometric median. *. This paper, often referred to as " The Tohoku pape ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematische Annalen
''Mathematische Annalen'' (abbreviated as ''Math. Ann.'' or, formerly, ''Math. Annal.'') is a German mathematical research journal founded in 1868 by Alfred Clebsch and Carl Neumann. Subsequent managing editors were Felix Klein, David Hilbert, Otto Blumenthal, Erich Hecke, Heinrich Behnke, Hans Grauert, Heinz Bauer, Herbert Amann, Jean-Pierre Bourguignon, Wolfgang Lück, and Nigel Hitchin. Currently, the managing editor of Mathematische Annalen is Thomas Schick. Volumes 1–80 (1869–1919) were published by Teubner. Since 1920 (vol. 81), the journal has been published by Springer. In the late 1920s, under the editorship of Hilbert, the journal became embroiled in controversy over the participation of L. E. J. Brouwer on its editorial board, a spillover from the foundational Brouwer–Hilbert controversy. Between 1945 and 1947 the journal briefly ceased publication. References External links''Mathematische Annalen''homepage at Springer''Mathematische Annalen''archive (1869� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miguel Angel Fernández Sanjuán
--> Miguel is a given name and surname, the Portuguese and Spanish form of the Hebrew name Michael (given name), Michael. It may refer to: Places *Pedro Miguel, a parish in the municipality of Horta and the island of Faial in the Azores Islands *São Miguel (other), various locations in Azores, Portugal, Brazil and Cape Verde People * Miguel (surname) Arts, entertainment, and media *Miguel (singer) (born 1985), Miguel Jontel Pimentel, American recording artist *Miguel Bosé (born 1956), Spanish pop new wave musician and actor *Miguel Calderón (born 1971), artist and writer *Miguel Cancel (born 1968), former American singer *Miguel Córcega (1929–2008), Mexican actor and director *Miguel de Cervantes (1547–1616), Spanish author *Miguel Delibes (1920–2010), Spanish novelist *Miguel Ferrer (1955–2017), American actor *Miguel Galván (1957–2008), Mexican actor *Miguel Gómez (photographer) (born 1974), Colombian / American photographer. *Miguel Ángel Landa (bor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamiltonian System
A Hamiltonian system is a dynamical system governed by Hamilton's equations. In physics, this dynamical system describes the evolution of a physical system such as a planetary system or an electron in an electromagnetic field. These systems can be studied in both Hamiltonian mechanics and dynamical systems theory. Overview Informally, a Hamiltonian system is a mathematical formalism developed by Hamilton to describe the evolution equations of a physical system. The advantage of this description is that it gives important insights into the dynamics, even if the initial value problem cannot be solved analytically. One example is the planetary movement of three bodies: while there is no closed-form solution to the general problem, Poincaré showed for the first time that it exhibits deterministic chaos. Formally, a Hamiltonian system is a dynamical system characterised by the scalar function H(\boldsymbol,\boldsymbol,t), also known as the Hamiltonian. The state of the system, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dissipative System
A dissipative system is a thermodynamically open system which is operating out of, and often far from, thermodynamic equilibrium in an environment with which it exchanges energy and matter. A tornado may be thought of as a dissipative system. Dissipative systems stand in contrast to conservative systems. A dissipative structure is a dissipative system that has a dynamical regime that is in some sense in a reproducible steady state. This reproducible steady state may be reached by natural evolution of the system, by artifice, or by a combination of these two. Overview A dissipative structure is characterized by the spontaneous appearance of symmetry breaking (anisotropy) and the formation of complex, sometimes chaotic, structures where interacting particles exhibit long range correlations. Examples in everyday life include convection, turbulent flow, cyclones, hurricanes and living organisms. Less common examples include lasers, Bénard cells, droplet cluster, and the Belousov� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaos Theory
Chaos theory is an interdisciplinary area of scientific study and branch of mathematics focused on underlying patterns and deterministic laws of dynamical systems that are highly sensitive to initial conditions, and were once thought to have completely random states of disorder and irregularities. Chaos theory states that within the apparent randomness of chaotic complex systems, there are underlying patterns, interconnection, constant feedback loops, repetition, self-similarity, fractals, and self-organization. The butterfly effect, an underlying principle of chaos, describes how a small change in one state of a deterministic nonlinear system can result in large differences in a later state (meaning that there is sensitive dependence on initial conditions). A metaphor for this behavior is that a butterfly flapping its wings in Brazil can cause a tornado in Texas. Small differences in initial conditions, such as those due to errors in measurements or due to rounding errors i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cubic Polynomial
In mathematics, a cubic function is a function of the form f(x)=ax^3+bx^2+cx+d where the coefficients , , , and are complex numbers, and the variable takes real values, and a\neq 0. In other words, it is both a polynomial function of degree three, and a real function. In particular, the domain and the codomain are the set of the real numbers. Setting produces a cubic equation of the form :ax^3+bx^2+cx+d=0, whose solutions are called roots of the function. A cubic function has either one or three real roots (which may not be distinct); all odd-degree polynomials have at least one real root. The graph of a cubic function always has a single inflection point. It may have two critical points, a local minimum and a local maximum. Otherwise, a cubic function is monotonic. The graph of a cubic function is symmetric with respect to its inflection point; that is, it is invariant under a rotation of a half turn around this point. Up to an affine transformation, there are only t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newton's Method
In numerical analysis, Newton's method, also known as the Newton–Raphson method, named after Isaac Newton and Joseph Raphson, is a root-finding algorithm which produces successively better approximations to the roots (or zeroes) of a real-valued function. The most basic version starts with a single-variable function defined for a real variable , the function's derivative , and an initial guess for a root of . If the function satisfies sufficient assumptions and the initial guess is close, then :x_ = x_0 - \frac is a better approximation of the root than . Geometrically, is the intersection of the -axis and the tangent of the graph of at : that is, the improved guess is the unique root of the linear approximation at the initial point. The process is repeated as :x_ = x_n - \frac until a sufficiently precise value is reached. This algorithm is first in the class of Householder's methods, succeeded by Halley's method. The method can also be extended to complex functions an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |