|
Lake Mojave
Lake Mojave is an ancient former lake fed by the Mojave River that, through the Holocene, occupied the Silver Lake and Soda Lake basins in the Mojave Desert of San Bernardino County, California. Its outlet may have ultimately emptied into the Colorado River north of Blythe. Geography Lake Mojave existed in San Bernardino County. The city of Las Vegas lies northeast of Lake Mojave. On the western side, Lake Mojave was bordered by mountains that steeply rise from the basin. The eastern side is more gentle, featuring alluvial fans and pediment. The lake At its maximum stand, Lake Mojave had a surface area of and a volume of . Lake Mojave had two separate lake level stands, the A stand and the B stand. The A stand lies at an altitude of above sea level and the B stand at an altitude of . The lake was about deep. 15 alluvial fans abut the shores of Lake Mojave that face the Soda Mountains. A present-day bay exists on the northwestern side of the Silver Lake basin and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mojave Desert
The Mojave Desert ( ; mov, Hayikwiir Mat'aar; es, Desierto de Mojave) is a desert in the rain shadow of the Sierra Nevada mountains in the Southwestern United States. It is named for the indigenous Mojave people. It is located primarily in southeastern California and southwestern Nevada, with small portions extending into Arizona and Utah. The Mojave Desert, together with the Sonoran, Chihuahuan, and Great Basin deserts, forms a larger North American Desert. Of these, the Mojave is the smallest and driest. The Mojave Desert displays typical basin and range topography, generally having a pattern of a series of parallel mountain ranges and valleys. It is also the site of Death Valley, which is the lowest elevation in North America. The Mojave Desert is often colloquially called the "high desert", as most of it lies between . It supports a diversity of flora and fauna. The desert supports a number of human activities, including recreation, ranching, and military training. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beach Ridge
A beach ridge is a wave-swept or wave-deposited ridge running parallel to a shoreline. It is commonly composed of sand as well as sediment worked from underlying beach material. The movement of sediment by wave action is called ''littoral transport''. Movement of material parallel to the shoreline is called ''longshore transport''. Movement perpendicular to the shore is called ''on-offshore transport''. A beach ridge may be capped by, or associated with, sand dunes. The height of a beach ridge is affected by wave size and energy. A fall in water level (or an uplift of land) can isolate a beach ridge from the body of water that created it. Isolated beach ridges may be found along dry lakes in the western United States and inland of the Great Lakes of North America, where they formed at the end of the last ice age when lake levels were much higher due to glacial melting and obstructed outflow caused by glacial ice. Some isolated beach ridges are found in parts of Scandinavia, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Dumont
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the ocean, although, like the much larger oceans, they do form part of the Earth's water cycle. Lakes are distinct from lagoons, which are generally coastal parts of the ocean. Lakes are typically larger and deeper than ponds, which also lie on land, though there are no official or scientific definitions. Lakes can be contrasted with rivers or streams, which usually flow in a channel on land. Most lakes are fed and drained by rivers and streams. Natural lakes are generally found in mountainous areas, rift zones, and areas with ongoing glaciation. Other lakes are found in endorheic basins or along the courses of mature rivers, where a river channel has widened into a basin. Some parts of the world have many lakes formed by the chaotic drainage patterns left over from the last ic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in 2009 by the International Union of Geological Sciences, the cutoff of the Pleistocene and the preceding Pliocene was regarded as being 1.806 million years Before Present (BP). Publications from earlier years may use either definition of the period. The end of the Pleistocene corresponds with the end of the last glacial period and also with the end of the Paleolithic age used in archaeology. The name is a combination of Ancient Greek grc, label=none, πλεῖστος, pleīstos, most and grc, label=none, καινός, kainós (latinized as ), 'new'. At the end of the preceding Pliocene, the previously isolated North and South American continents were joined by the Isthmus of Panama, causing Great American Interchang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dry Lake
A dry lake bed, also known as a playa, is a basin or depression that formerly contained a standing surface water body, which disappears when evaporation processes exceeds recharge. If the floor of a dry lake is covered by deposits of alkaline compounds, it is known as an alkali flat. If covered with salt, it is known as a '' salt flat.'' Terminology If its basin is primarily salt, then a dry lake bed is called a '' salt pan'', ''pan'', or ''salt flat'' (the latter being a remnant of a salt lake). ''Hardpan'' is the dry terminus of an internally drained basin in a dry climate, a designation typically used in the Great Basin of the western United States. Another term for dry lake bed is ''playa''. The Spanish word ''playa'' () literally means "beach". Dry lakes are known by this name in some parts of Mexico and the western United States. This term is used e.g. on the Llano Estacado and other parts of the Southern High Plains and is commonly used to address paleolake sediments ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
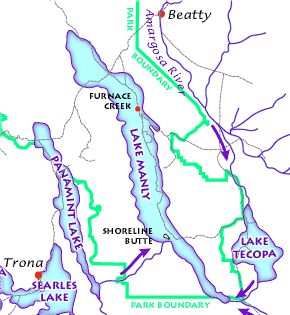
Lake Manly
Lake Manly was a pluvial lake in Death Valley, California, covering much of Death Valley with a surface area of during the so-called "Blackwelder stand". Water levels varied through its history, and the chronology is further complicated by active tectonic processes that have modified the elevations of the various shorelines of Lake Manly; during the Blackwelder stage they reached above sea level. The lake received water mainly from the Amargosa River and at various points from the Mojave River and Owens River. The lake and its substantial catchment favoured the spread of a number of aquatic species, including some lizards, pupfish and springsnails. The lake probably supported a substantial ecosystem, and a number of diatoms developed there. In Death Valley, lakes existed during different times in the geological past. After some poorly defined lake stages during the Miocene, Pliocene and early Pleistocene, the first large lake stage occurred about 185,000–128,000 years ago ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Manix
Lake Manix is a former lake fed by the Mojave River in the Mojave Desert. It lies within San Bernardino County, California. Located close to Barstow, this lake had the shape of a cloverleaf and covered four basins named Coyote, Cady/Manix, Troy and Afton. It covered a surface area of and reached an altitude of at highstands, although poorly recognizable shorelines have been found at altitudes of . The lake was fed by increased runoff during the Pleistocene and overflowed into the Lake Mojave basin and from there to Lake Manly in Death Valley, or less likely into the Bristol Lake basin and from there to the Colorado River. The lake formed about 500,000 years before present, when the Mojave River left the Victorville area and started to drain into Manix and Lake Harper. The lake did not immediately include the Afton basin; its integration occurred only about 190,000 years ago, most likely due to a catastrophic flood. Lake Manix lasted until 25,000–13,800 years ago, when Afton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Harper
Harper Lake is a dry lake located in the Mojave Desert near the small community of Lockhart, California, in northwestern San Bernardino County of Southern California. The lake is accessible from Harper Lake Road, which runs north off of State Route 58 midway between Boron and Barstow. General Lake Harper during its highstand reached an elevation of above sea level, had a surface area of and was inhabited by cyprinid minnow, molluscs and ostracods. Ostracods found in Lake Harper are species of '' Candona'', ''Cypridopsis'', '' Heterocypris'' and '' Limnocythere''. These species indicate a freshwater lake with seasonal inflow and some shallower environments. An elongated peninsula jutted into the lake from the western shore and smaller peninsulas existed on the northern and southern shores towards the eastern side of the lake. Blue clays in boreholes and fine grained mud and sand on the former shores testify to the existence of a lake there. History The highest shorelines ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transverse Ranges
The Transverse Ranges are a group of mountain ranges of southern California, in the Pacific Coast Ranges physiographic region in North America. The Transverse Ranges begin at the southern end of the California Coast Ranges and lie within Santa Barbara, Ventura, Los Angeles, San Bernardino, Riverside and Kern counties. The Peninsular Ranges lie to the south. The name Transverse Ranges is due to their east–west orientation, making them transverse to the general northwest–southeast orientation of most of California's coastal mountains.Dibblee Jr, T.W., 1982. Regional geology of the Transverse Ranges Province of southern California. ''Geology and mineral wealth of the California Transverse Ranges'', ''10'', pp.7-26. The ranges extend from west of Point Conception eastward approximately 500 kilometers into the Mojave and Colorado Desert. The geology and topography of the ranges express three distinct segments that have contrasting elevations, rock types, and vegetation. The wes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polar Jet Stream
Jet streams are fast flowing, narrow, meandering air currents in the atmospheres of some planets, including Earth. On Earth, the main jet streams are located near the altitude of the tropopause and are westerly winds (flowing west to east). Jet streams may start, stop, split into two or more parts, combine into one stream, or flow in various directions including opposite to the direction of the remainder of the jet. Overview The strongest jet streams are the polar jets around the polar vortices, at above sea level, and the higher altitude and somewhat weaker subtropical jets at . The Northern Hemisphere and the Southern Hemisphere each have a polar jet and a subtropical jet. The northern hemisphere polar jet flows over the middle to northern latitudes of North America, Europe, and Asia and their intervening oceans, while the southern hemisphere polar jet mostly circles Antarctica, both all year round. Jet streams are the product of two factors: the atmospheric heating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Bernardino Mountains
The San Bernardino Mountains are a high and rugged mountain range in Southern California in the United States. Situated north and northeast of San Bernardino and spanning two California counties, the range tops out at at San Gorgonio Mountain – the tallest peak in all of Southern California. The San Bernardinos form a significant region of wilderness and are popular for hiking and skiing. The mountains were formed about eleven million years ago by tectonic activity along the San Andreas Fault, and are still actively rising. Many local rivers originate in the range, which receives significantly more precipitation than the surrounding desert. The range's unique and varying environment allows it to maintain some of the greatest biodiversity in the state. For over 10,000 years, the San Bernardinos and their surroundings have been inhabited by indigenous peoples, who used the mountains as a summer hunting ground. Spanish explorers first encountered the San Bernardinos in the late ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kelso Dunes
Kelso Dunes, also known as the Kelso Dune Field, is the largest field of Aeolian processes, aeolian sand deposits in the Mojave Desert. The region is protected by the Mojave National Preserve and is located near the town of Baker, California, Baker, San Bernardino County, California, San Bernardino County, California, and the Kelso Depot, Preserve Visitor Center. The dune, dune field covers and includes migrating dunes, Sand dune stabilization, vegetation-stabilized dunes, sand sheets, and sand ramps. The tallest dunes rise up to above the surrounding terrain. Geology The dunes are composed predominantly of light-colored quartz and feldspar, most likely erosion, eroded from the granite, granitics of the San Bernardino Mountains to the southwest. Magnetite and amphibole can also be found, often accumulating at the dune crests. Kelso Dunes represent part of a much larger sand transport system, which includes the nearby Devils Playground region. The composition and morphology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |