|
Lake Amara
Lake Amara ( ro, Lacul Amara) is a Seawater, saltwater Liman (landform), fluvial liman lake located on the Slobozia - Buzău road near Amara, Romania, Amara in Ialomița County, Romania. The lake has a surface area of , a water volume of , a length of and a width between and while the maximum depth reaches . The lake is situated in a Depression (geology), depression having no links to the Ialomița River. Because of the lack of a year-round constant fresh water supply and because of the evaporation process triggered by the dry climate, the concentration of salts in the lake is quite high. The Tonicity, hypertonic water is rich in Sulfate, sulphate salts, bicarbonate, chlorides, iodides, bromides and Magnesium, magnesium salts which led to the formation of a therapeutic mud used to treat different illnesses. The general mineral concentration of the water is around 9.8g/L. The Sapropel, sapropelic mud contains around 40% organic and 41% mineral substances. The mud is recommended t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amara, Romania
Amara is a town in Ialomița County, Muntenia, Romania. It is located in Bărăgan Plain, Bărăgan on the shores of Lake Amara, at 7 km kilometers north of the county capital, Slobozia. Amara was elevated to town status in 2004. Demographics At the census from 2011, Amara, Romania have a total of 7080 residents, 3507 males, and 3573 females. References Towns in Romania, Amara Populated places in Ialomița County, Amara Localities in Muntenia Spa towns in Romania {{Ialomiţa-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iodide
An iodide ion is the ion I−. Compounds with iodine in formal oxidation state −1 are called iodides. In everyday life, iodide is most commonly encountered as a component of iodized salt, which many governments mandate. Worldwide, iodine deficiency affects two billion people and is the leading preventable cause of intellectual disability. Structure and characteristics of inorganic iodides Iodide is one of the largest monatomic anions. It is assigned a radius of around 206 picometers. For comparison, the lighter halides are considerably smaller: bromide (196 pm), chloride (181 pm), and fluoride (133 pm). In part because of its size, iodide forms relatively weak bonds with most elements. Most iodide salts are soluble in water, but often less so than the related chlorides and bromides. Iodide, being large, is less hydrophilic compared to the smaller anions. One consequence of this is that sodium iodide is highly soluble in acetone, whereas sodium chloride is not. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lakes Of Romania
This is a list of lakes of Romania. Notable lakes include Lake Sfânta Ana, the only crater lake in Romania, and Lake Razelm, the largest liman in the country. Major natural lakes Glacial lakes In volcanic craters Karstic lakes Behind natural dams In depressions On river banks On river-maritime banks Lagoons In river valleys In Danube Delta Major reservoirs Major mountain lakes Other (minor) mountain lakes Other lakes * Lake Sărat: "Sărat" = "Salty"; at its bottom is still a crust of salt. Near Brăila. A small beach. *Lake Someșu Rece: it is located in Cluj County See also * List of lakes in Bucharest * Ocna Sibiului mine#Lakes of the salt mine References External links * Paul Decei, ''Lacuri de munte'', Editura Sport–Turism, 1981 * Anuarul 2004 al Institutului Naţional de Statistică {{Romania topics * Romania Lakes A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infectious Disease
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable disease, is an illness resulting from an infection. Infections can be caused by a wide range of pathogens, most prominently bacteria and viruses. Hosts can fight infections using their immune system. Mammalian hosts react to infections with an innate response, often involving inflammation, followed by an adaptive response. Specific medications used to treat infections include antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals, antiprotozoals, and antihelminthics. Infectious diseases resulted in 9.2 million deaths in 2013 (about 17% of all deaths). The branch of medicine that focuses on infections is referred to as infectious disease. Types Infections are caused by infectious agents (pathogens) including: * Bacteria (e.g. '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asthma
Asthma is a long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath. These may occur a few times a day or a few times per week. Depending on the person, asthma symptoms may become worse at night or with exercise. Asthma is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Environmental factors include exposure to air pollution and allergens. Other potential triggers include medications such as aspirin and beta blockers. Diagnosis is usually based on the pattern of symptoms, response to therapy over time, and spirometry lung function testing. Asthma is classified according to the frequency of symptoms, forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1), and peak expiratory flow rate. It may also be classified as atopic or non-atopic, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graves' Disease
Graves' disease (german: Morbus Basedow), also known as toxic diffuse goiter, is an autoimmune disease that affects the thyroid. It frequently results in and is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism. It also often results in an enlarged thyroid. Signs and symptoms of hyperthyroidism may include irritability, muscle weakness, sleeping problems, a fast heartbeat, poor tolerance of heat, diarrhea and unintentional weight loss. Other symptoms may include thickening of the skin on the shins, known as pretibial myxedema, and eye bulging, a condition caused by Graves' ophthalmopathy. About 25 to 30% of people with the condition develop eye problems. The exact cause of the disease is unclear; however, it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. A person is more likely to be affected if they have a family member with the disease. If one twin is affected, a 30% chance exists that the other twin will also have the disease. The onset of disease may be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiovascular Disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels. CVD includes coronary artery diseases (CAD) such as angina and myocardial infarction (commonly known as a heart attack). Other CVDs include stroke, heart failure, hypertensive heart disease, rheumatic heart disease, cardiomyopathy, abnormal heart rhythms, congenital heart disease, valvular heart disease, carditis, aortic aneurysms, peripheral artery disease, thromboembolic disease, and venous thrombosis. The underlying mechanisms vary depending on the disease. It is estimated that dietary risk factors are associated with 53% of CVD deaths. Coronary artery disease, stroke, and peripheral artery disease involve atherosclerosis. This may be caused by high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes mellitus, lack of exercise, obesity, high blood cholesterol, poor diet, excessive alcohol consumption, and poor sleep, among other things. High blood pressure is estimated to account for approximat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skin Disease
A skin condition, also known as cutaneous condition, is any medical condition that affects the integumentary system—the organ system that encloses the body and includes skin, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this system is as a barrier against the external environment. Conditions of the human integumentary system constitute a broad spectrum of diseases, also known as dermatoses, as well as many nonpathologic states (like, in certain circumstances, melanonychia and racquet nails). While only a small number of skin diseases account for most visits to the physician, thousands of skin conditions have been described. Classification of these conditions often presents many nosological challenges, since underlying causes and pathogenetics are often not known. Therefore, most current textbooks present a classification based on location (for example, conditions of the mucous membrane), morphology ( chronic blistering conditions), cause (skin conditions result ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infertility
Infertility is the inability of a person, animal or plant to reproduce by natural means. It is usually not the natural state of a healthy adult, except notably among certain eusocial species (mostly haplodiploid insects). It is the normal state of a human child or other young offspring, because they have not undergone puberty, which is the body's start of reproductive capacity. In humans, infertility is the inability to become pregnant after one year of unprotected and regular sexual intercourse involving a male and female partner.Chowdhury SH, Cozma AI, Chowdhury JH. Infertility. Essentials for the Canadian Medical Licensing Exam: Review and Prep for MCCQE Part I. 2nd edition. Wolters Kluwer. Hong Kong. 2017. There are many causes of infertility, including some that medical intervention can treat. Estimates from 1997 suggest that worldwide about five percent of all heterosexual couples have an unresolved problem with infertility. Many more couples, however, experience involu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gynaecology
Gynaecology or gynecology (see spelling differences) is the area of medicine that involves the treatment of women's diseases, especially those of the reproductive organs. It is often paired with the field of obstetrics, forming the combined area of obstetrics and gynecology (OB-GYN). The term comes from Greek and means "the science of women". Its counterpart is andrology, which deals with medical issues specific to the male reproductive system. Etymology The word "gynaecology" comes from the oblique stem (γυναικ-) of the Greek word γυνή (''gyne)'' semantically attached to "woman", and ''-logia'', with the semantic attachment "study". The word gynaecology in Kurdish means "jinekolojî", separated word as "jin-ekolojî", so the Kurdish "jin" called like "gyn" and means in Kurdish "woman". History Antiquity The Kahun Gynaecological Papyrus, dated to about 1800 BC, deals with gynaecological diseases, fertility, pregnancy, contraception, etc. The text is divided into th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
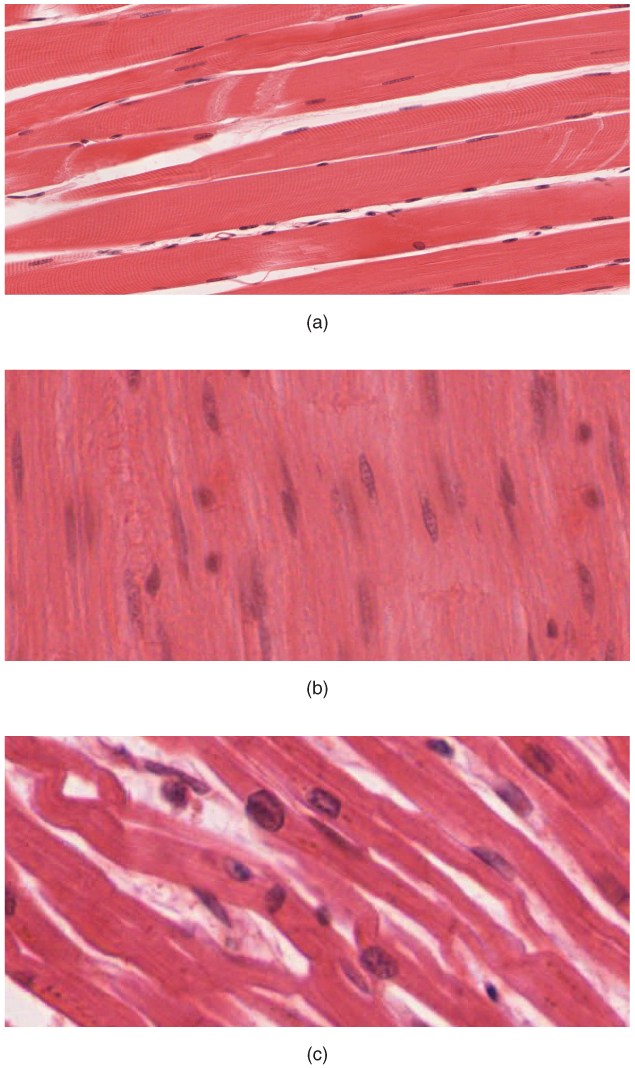
Human Musculoskeletal System
The human musculoskeletal system (also known as the human locomotor system, and previously the activity system) is an organ system that gives humans the ability to move using their muscular and skeletal systems. The musculoskeletal system provides form, support, stability, and movement to the body. It is made up of the bones of the skeleton, muscles, cartilage, tendons, ligaments, joints, and other connective tissue that supports and binds tissues and organs together. The musculoskeletal system's primary functions include supporting the body, allowing motion, and protecting vital organs. The skeletal portion of the system serves as the main storage system for calcium and phosphorus and contains critical components of the hematopoietic system. This system describes how bones are connected to other bones and muscle fibers via connective tissue such as tendons and ligaments. The bones provide stability to the body. Muscles keep bones in place and also play a role in the movement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sapropel
Sapropel (a contraction of ancient Greek words ''sapros'' and ''pelos'', meaning putrefaction and mud (or clay), respectively) is a term used in marine geology to describe dark-coloured sediments that are rich in organic matter. Organic carbon concentrations in sapropels commonly exceed 2 wt.% in weight. The term sapropel events may also refer to cyclic oceanic anoxic event (OAE), in particular those affecting the Mediterranean Sea with a periodicity of about 21,000 years. Formation Sapropels have been recorded in the Mediterranean sediments since the closure of the Eastern Tethys Ocean 13.5 million years ago. The formation of sapropel events in the Mediterranean Sea occurs approximately every 21,000 years and last between 3,000 and 5,000 years. The first identification of these events occurred in the mid-20th century. Since then, their formulative conditions of have been investigated. The occurrence of sapropels has been related to the Earth's orbital parameters (Milankovitc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)

.jpg)