|
Laestadius
Lars Levi Laestadius (; 10 January 1800 – 21 February 1861) was a Swedish Sami pastor and administrator of the Swedish state Lutheran church in Lapland who founded the Laestadian pietist revival movement to help his largely Sami congregations, who were being ravaged by alcoholism. Laestadius was also a noted botanist and an author. Laestadius himself became a teetotaller (except for his ongoing use of wine in holy Communion) in the 1840s, when he began successfully awakening his Sami parishioners to the misery and destruction alcohol was causing them. Early life Birth and education Laestadius was born in Swedish Lapland at Jäckvik near Arjeplog in a western mountainous part of Norrbotten County, the northernmost county in Sweden, to Carl Laestadius (1746-1832)—a Swedish hunter, fisherman, tar-maker, and one-time silver mine bailiff, who lost his job due to alcoholism—and Anna Magdalena (née Johansdotter) (1759-1824), who was the elder Laestadius's second wife. Both we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laestadius
Lars Levi Laestadius (; 10 January 1800 – 21 February 1861) was a Swedish Sami pastor and administrator of the Swedish state Lutheran church in Lapland who founded the Laestadian pietist revival movement to help his largely Sami congregations, who were being ravaged by alcoholism. Laestadius was also a noted botanist and an author. Laestadius himself became a teetotaller (except for his ongoing use of wine in holy Communion) in the 1840s, when he began successfully awakening his Sami parishioners to the misery and destruction alcohol was causing them. Early life Birth and education Laestadius was born in Swedish Lapland at Jäckvik near Arjeplog in a western mountainous part of Norrbotten County, the northernmost county in Sweden, to Carl Laestadius (1746-1832)—a Swedish hunter, fisherman, tar-maker, and one-time silver mine bailiff, who lost his job due to alcoholism—and Anna Magdalena (née Johansdotter) (1759-1824), who was the elder Laestadius's second wife. Both we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laestadian
Laestadianism, also known as Laestadian Lutheranism and Apostolic Lutheranism, is a pietistic Lutheran revival movement started in Sápmi in the middle of the 19th century. Named after Swedish Lutheran state church administrator and temperance movement leader Lars Levi Laestadius, it is the biggest pietistic revivalist movement in the Nordic countries. It has members mainly in Finland, Northern America, Norway, Russia and Sweden. There are also smaller congregations in Africa, South America and Central Europe. In addition Laestadians have missionaries in 23 countries. The number of Laestadians worldwide is estimated to be between 144,000 and 219,000. Organization in Finland and North America Most Laestadians in Finland are part of the national Lutheran Church of Finland (cf. ''Communion of Nordic Lutheran Dioceses''), but in America, where there is no official Lutheran church, they founded their own denomination, which split into several sub-groups in the mid-20th centu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milla Clementsdotter
Milla Clementsdotter (also known as, Milla Clemensdotter, Maria of Lappland (Finnish language, Lapin Maria; 1 November 1812 – 8 April 1892) was a Swedish Southern Sami woman who is remembered for guiding Lars Levi Laestadius in questions of Christian faith. She belonged to a revival movement marked by Pietistic and Moravian influences, a member of a group known as "Readers", a background shared by Laestadius' mother. Biography Milla Clementsdotter was born on 1 November 1812 in Orrnäsfjäll, Föllinge, Sweden. Her parents were Clemmens Andersson and Anna Larsdotter. Because the father was an alcoholic, the family lost all of its property. After her father's death in 1817, his mother remarried Torkel Jonsson. That led to Clementsdotter to having a half-sister, Sara Brita, who was born in 1825. At the age of six, she went to live with a family that farmed, before being removed to various foster families, where she received abusive treatment. She subsequently developed a deep be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fragments Of Lappish Mythology
''Fragments of Lappish Mythology'' is the detailed documented account of the Sami people, Sami Sami religion, religious beliefs and mythology during the mid-19th century. It was written between 1838–1845 by Sweden, Swedish Minister (Christianity), minister Lars Levi Laestadius, but was not published until 1997 in Swedish, 2000 in Finnish, and 2002 in English. The book was originally written for the France, French-funded La Recherche Expedition (1838–1840), La Recherche Expedition of 1838–1840, but was lost and forgotten for many decades thereafter. Laestadius describes the state of Sami religious beliefs held during his time, which had already long been passing into history by the Christianization of the Sami during this period. The condition of these stories is described as "fragments", as Laestadius himself admitted that there was a great deal of Sami religious beliefs that he knew little about because of the Sami peoples' secrecy concerning their beliefs. Loss and discover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pietism
Pietism (), also known as Pietistic Lutheranism, is a movement within Lutheranism that combines its emphasis on biblical doctrine with an emphasis on individual piety and living a holy Christian life, including a social concern for the needy and disadvantaged. It is also related to its non-Lutheran (but largely Lutheran-descended) Radical Pietism offshoot that either diversified or spread into various denominations or traditions, and has also had a contributing influence over the interdenominational Evangelical Christianity movement. Although the movement is aligned exclusively within Lutheranism, it had a tremendous impact on Protestantism worldwide, particularly in North America and Europe. Pietism originated in modern Germany in the late 17th century with the work of Philipp Spener, a Lutheran theologian whose emphasis on personal transformation through spiritual rebirth and renewal, individual devotion, and piety laid the foundations for the movement. Although Spener did not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pietistic
Pietism (), also known as Pietistic Lutheranism, is a movement within Lutheranism that combines its emphasis on biblical doctrine with an emphasis on individual piety and living a holy Christian life, including a social concern for the needy and disadvantaged. It is also related to its non-Lutheran (but largely Lutheran-descended) Radical Pietism offshoot that either diversified or spread into various denominations or traditions, and has also had a contributing influence over the interdenominational Evangelical Christianity movement. Although the movement is aligned exclusively within Lutheranism, it had a tremendous impact on Protestantism worldwide, particularly in North America and Europe. Pietism originated in modern Germany in the late 17th century with the work of Philipp Spener, a Lutheran theologian whose emphasis on personal transformation through spiritual rebirth and renewal, individual devotion, and piety laid the foundations for the movement. Although Spener did not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karesuando
Karesuando (; fi, Kaaresuvanto or ; Sami: , or ) is the northernmost locality in Sweden. It is situated in Kiruna Municipality, Norrbotten County, Sweden, with 303 inhabitants in 2010 and 350 in 2011. It is a church village, located alongside the Muonio River on the border with Finland. The Finnish village of Karesuvanto (population about 140) is located on the Finnish side of the river. According to Finnish tradition, they are one and the same village (with a combined population of about 470), but are usually considered to be separate villages since there is a national border between them (although both are called Karesuvanto in Finnish). The village's buildings were built in 1670, when Måns Mårtensson Karesuando, called "Hyvä Maunu Martinpoika" in Finnish and "Good Maunu, Son of Martin" in English, bought land from Sami Henrik Nilsson Nikkas. The Lutheran vicar and botanist Lars Levi Laestadius served in Karesuando from 1826 to 1849. It was here that he founded the re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pajala
Pajala () is a locality and the seat of Pajala Municipality in Norrbotten County, Sweden, with 1,958 inhabitants in 2010. It is located in Swedish Lapland. Pajala is in the Torne Valley and was dominated by people speaking a Finnish dialect until Eastern Sweden (Finland) got annexed by Russia in the 1800s and Pajala ended on the Swedish side of the river that marked the border. Today the town is nearly unilingually Swedish although the Meänkieli name for the locality remains in use and is a minority language. Even so, Pajala has belonged to Sweden since the country's inception as a political unit. History Lars Levi Laestadius, a botanist, Lutheran minister, and founder of the revivalist movement Laestadianism, lived and worked in Pajala municipality in the mid-19th century. He lived in Kengis, but in 1869 his house and grave and the whole church of Kengis were moved to Pajala. The town was mistakenly bombed by Soviet airplanes during the Finnish/Soviet Winter War, in spring 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jämtland
Jämtland (; no, Jemtland or , ; Jamtish: ''Jamtlann''; la, Iemptia) is a historical province () in the centre of Sweden in northern Europe. It borders Härjedalen and Medelpad to the south, Ångermanland to the east, Lapland to the north and Trøndelag and Norway to the west. Jämtland covers an area of 34,009 square kilometres, 8.3% of Sweden's total area and is the second largest province in Sweden. It has a population of 115,331, the majority of whom live in , the area surrounding lake Storsjön. Östersund is Jämtland's only city and is the 24th most populous city in Sweden. The historical province is one of the least densely populated. Jämtland was originally an autonomous republic,Ekerwald, Carl-Göran (2004). ''Jämtarnas historia'' (in Swedish), 124. "Svaret är att Jämtland före 1178 var ett självständigt bondesamfund, "dei vart verande ein nasjon för seg sjöl", för att nu citera Halfdan Koht.. Jämtland var en bonderepublik.." its own nation with its o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krokom
Krokom (from Old Norse ''krókar'', dat. ''krókum'', 'bends Indalsälven.html"_;"title="f_the_Indalsälven">f_the_Indalsälven_river)_is_a_Urban_areas_in_Sweden.html" "title="Indalsälven_river.html" ;"title="Indalsälven.html" ;"title="f the Indalsälven">f the Indalsälven river">Indalsälven.html" ;"title="f the Indalsälven">f the Indalsälven river) is a Urban areas in Sweden">locality Locality may refer to: * Locality (association), an association of community regeneration organizations in England * Locality (linguistics) * Locality (settlement) * Suburbs and localities (Australia), in which a locality is a geographic subdivis ... and the seat of Krokom Municipality in Jämtland County, Sweden with 2,277 inhabitants in 2010. Krokom is situated about 20 km northwest of Östersund along European route E14 (E14). It is located at the junction where E14, County Road 340 / County Road 339 and County Road 615 meet. Railroad service passage through Krokom started in 1882. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Åsele
Åsele () is a locality and the seat of Åsele Municipality in Västerbotten County, province of Lapland, Sweden with 1,798 inhabitants in 2010. Its elevation The elevation of a geographic location is its height above or below a fixed reference point, most commonly a reference geoid, a mathematical model of the Earth's sea level as an equipotential gravitational surface (see Geodetic datum § Vert ... is 313 m (1027 ft). References Populated places in Västerbotten County Populated places in Åsele Municipality Municipal seats of Västerbotten County Swedish municipal seats Lapland (Sweden) {{Västerbotten-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
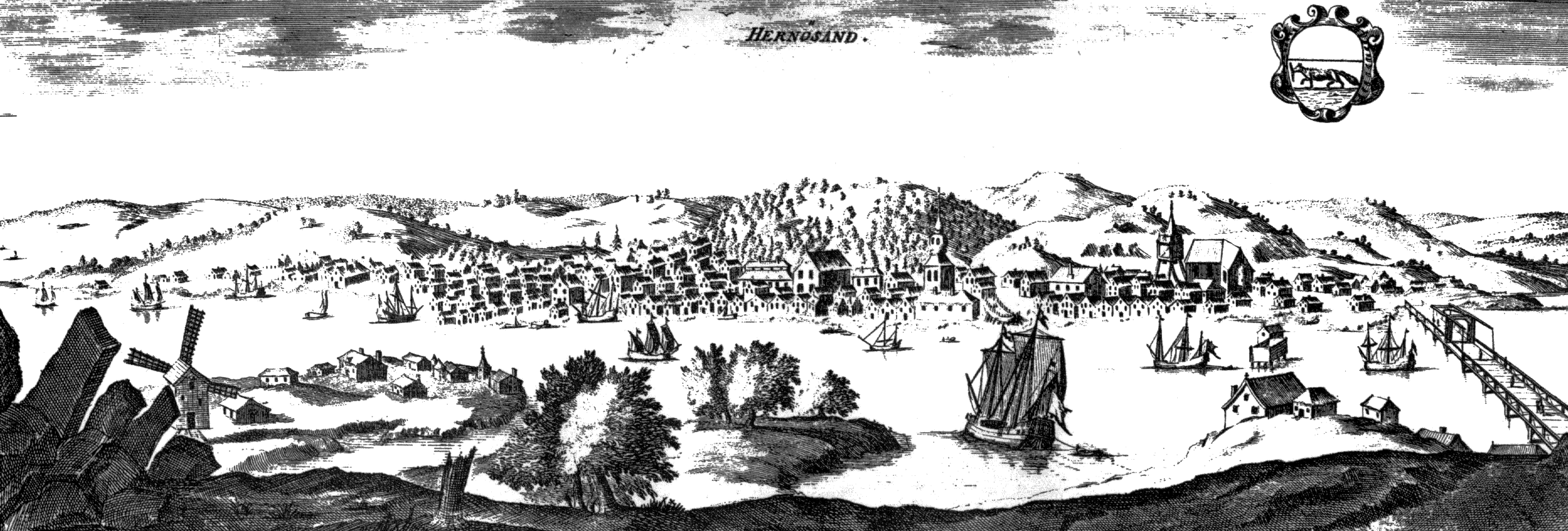
Härnösand
Härnösand () is a locality and the seat of Härnösand Municipality in Västernorrland County, Sweden with 17,556 inhabitants in 2010. It is called "the gate to the High Coast" because of the world heritage landscape just a few miles north of Härnösand. Härnösand is the seat of the Diocese of Härnösand. History On 10 December 1885, Härnösand became the first town in Sweden with electric street lighting, following the Gådeå power station being taken into use. Education Härnösand is the seat of The National Agency for Special Needs Education and Schools (''Specialpedagogiska skolmyndigheten''). The Swedish International Development Cooperation Agency (Sida) operates its training programme Sida Partnership Forum in Härnösand. Industry One of the biggest employers in Härnösand is the cable-TV and Cable internet service provider Com Hem. Sports The women's team of the bandy club Härnösands AIK plays in the highest division and the men's team has don ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |