|
Labeobarbus Sandersi
''Labeobarbus sandersi'' is a species of ray-finned fish in the genus ''Labeobarbus'' is found from southern Cameroon to the Chiloango River in Cabinda Province, Cabinda. References Labeobarbus, sandersi Taxa named by George Albert Boulenger Fish described in 1912 {{Labeobarbus-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Albert Boulenger
George Albert Boulenger (19 October 1858 – 23 November 1937) was a Belgian-British zoologist who described and gave scientific names to over 2,000 new animal species, chiefly fish, reptiles, and amphibians. Boulenger was also an active botanist during the last 30 years of his life, especially in the study of roses. Life Boulenger was born in Brussels, Belgium, the only son of Gustave Boulenger, a Belgian public notary, and Juliette Piérart, from Valenciennes. He graduated in 1876 from the Free University of Brussels with a degree in natural sciences, and worked for a while at the Royal Belgian Institute of Natural Sciences, Brussels, as an assistant naturalist studying amphibians, reptiles, and fishes. He also made frequent visits during this time to the ''Muséum national d'Histoire naturelle'' in Paris and the British Museum in London. In 1880, he was invited to work at the Natural History Museum, then a department of the British Museum, by Dr. Albert C. L. G. Günther a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ray-finned Fish
Actinopterygii (; ), members of which are known as ray-finned fishes, is a class of bony fish. They comprise over 50% of living vertebrate species. The ray-finned fishes are so called because their fins are webs of skin supported by bony or horny spines (rays), as opposed to the fleshy, lobed fins that characterize the class Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned fish). These actinopterygian fin rays attach directly to the proximal or basal skeletal elements, the radials, which represent the link or connection between these fins and the internal skeleton (e.g., pelvic and pectoral girdles). By species count, actinopterygians dominate the vertebrates, and they constitute nearly 99% of the over 30,000 species of fish. They are ubiquitous throughout freshwater and marine environments from the deep sea to the highest mountain streams. Extant species can range in size from ''Paedocypris'', at , to the massive ocean sunfish, at , and the long-bodied oarfish, at . The vast majority of Actinoptery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labeobarbus
''Labeobarbus'' is a mid-sized ray-finned fish genus in the family Cyprinidae. Its species are widely distributed throughout eastern Africa and especially southern Africa, but also in Lake Tana in Ethiopia. A common name, in particular for the southern species, is yellowfish. The scientific name refers to the fact that these large barbs remind of the fairly closely related " carps" in the genus ''Labeo'' in size and shape. As far as can be told, all ''Labeobarbus'' species are hexaploid.de Graaf ''et al.'' (2007), IUCN (2009) Systematics Like many other "barbs", it was long included in ''Barbus''. It appears to be a fairly close relative of the typical barbels and relatives – the genus ''Barbus'' proper –, but closer still to the large Near Eastern species nowadays separated in ''Carasobarbus''. ''Barbus'' has been split to account for the improved phylogenetic knowledge which indicated it was highly paraphyletic in its wide circumscription –, it may be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cameroon
Cameroon (; french: Cameroun, ff, Kamerun), officially the Republic of Cameroon (french: République du Cameroun, links=no), is a country in west-central Africa. It is bordered by Nigeria to the west and north; Chad to the northeast; the Central African Republic to the east; and Equatorial Guinea, Gabon and the Republic of the Congo to the south. Its coastline lies on the Bight of Biafra, part of the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean. Due to its strategic position at the crossroads between West Africa and Central Africa, it has been categorized as being in both camps. Its nearly 27 million people speak 250 native languages. Early inhabitants of the territory included the Sao civilisation around Lake Chad, and the Baka hunter-gatherers in the southeastern rainforest. Portuguese explorers reached the coast in the 15th century and named the area ''Rio dos Camarões'' (''Shrimp River''), which became ''Cameroon'' in English. Fulani soldiers founded the Adamawa Emirate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
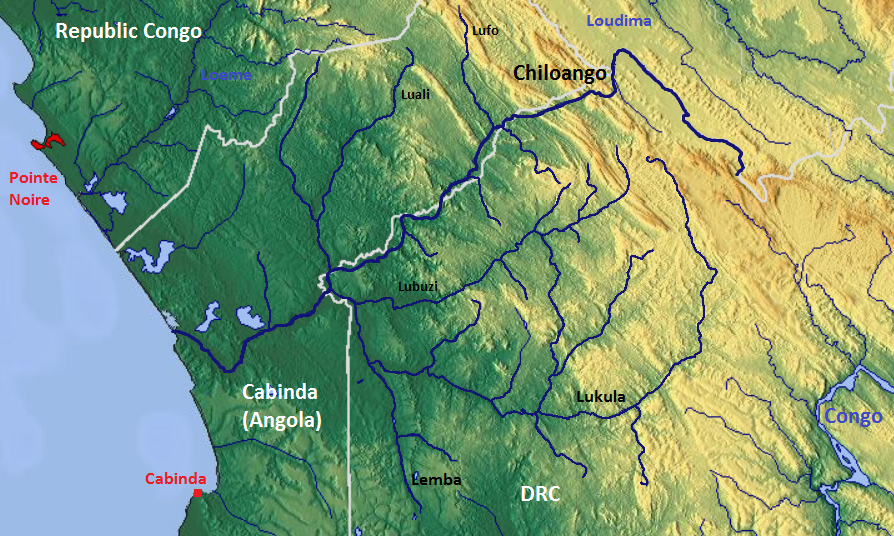
Chiloango River
The Chiloango River ( pt, Rio Chiluango, also known as Kakongo River, Louango, Shiloango and Rio Hi) is a river in western Central Africa. It forms the westernmost part of the border between the Democratic Republic of the Congo and the Republic of Congo, and then forms approximately half of the border between the DRC and Cabinda, Angola passing just south of the town of Necuto. The river then bisects Cabinda, making it the most important river in the province. It enters the Atlantic Ocean just north of the town of Cacongo Cacongo (Guilherme Capelo or Lândana) is a town, with a population of 15,000 (2014), in Cacongo municipality, Cabinda Province, in Angola , national_anthem = " Angola Avante"() , image_map = , map_caption ....United States. Hydrographic Office (1916) ''Africa Pilot: The southewest coast of Africa from Cape Palmas to the Cape of Good Hope, including the islands of St. Helena, Ascension, Tristan da Cunha, and neighboring ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cabinda Province
Cabinda (formerly called Portuguese Congo, kg, Kabinda) is an exclave and province of Angola in Africa, a status that has been disputed by several political organizations in the territory. The capital city is also called Cabinda, known locally as ''Tchiowa'', ''Tsiowa'' or ''Kiowa''. The province is divided into four municipalities—Belize, Buco-Zau, Cabinda and Cacongo. Modern Cabinda is the result of a fusion of three kingdoms: N'Goyo, Loango and Kakongo. It has an area of and a population of 716,076 at the 2014 census; the latest official estimate (as at mid 2019) is 824,143. According to 1988 United States government statistics, the total population of the province was 147,200, with a near even split between rural and urban populations. At one point an estimated one third of Cabindans were refugees living in the Democratic Republic of the Congo; however, after the 2007 peace agreement, refugees started returning to their homes. Cabinda is separated from the rest of An ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxa Named By George Albert Boulenger
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion. If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were set forth in Carl Linnaeus's system in ''Systema Naturae'', 10th edition (1758), as well as an unpublished work by Bernard and Antoine Laurent de Jussieu. The idea of a unit-based system of biological classification was first made widely available in 1805 in the intro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |