|
LabelMe
LabelMe is a project created by the MIT Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL) which provides a dataset of digital images with annotations. The dataset is dynamic, free to use, and open to public contribution. The most applicable use of LabelMe is in computer vision research. As of October 31, 2010, LabelMe has 187,240 images, 62,197 annotated images, and 658,992 labeled objects. Motivation The motivation behind creating LabelMe comes from the history of publicly available data for computer vision researchers. Most available data was tailored to a specific research group's problems and caused new researchers to have to collect additional data to solve their own problems. LabelMe was created to solve several common shortcomings of available data. The following is a list of qualities that distinguish LabelMe from previous work. * Designed for recognition of a class of objects instead of single instances of an object. For example, a traditional dataset may hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labelme Polygons Words
LabelMe is a project created by the MIT Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL) which provides a dataset of digital images with annotations. The dataset is dynamic, free to use, and open to public contribution. The most applicable use of LabelMe is in computer vision research. As of October 31, 2010, LabelMe has 187,240 images, 62,197 annotated images, and 658,992 labeled objects. Motivation The motivation behind creating LabelMe comes from the history of publicly available data for computer vision researchers. Most available data was tailored to a specific research group's problems and caused new researchers to have to collect additional data to solve their own problems. LabelMe was created to solve several common shortcomings of available data. The following is a list of qualities that distinguish LabelMe from previous work. * Designed for recognition of a class of objects instead of single instances of an object. For example, a traditional dataset may h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labelme Part Labels
LabelMe is a project created by the MIT Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL) which provides a dataset of digital images with annotations. The dataset is dynamic, free to use, and open to public contribution. The most applicable use of LabelMe is in computer vision research. As of October 31, 2010, LabelMe has 187,240 images, 62,197 annotated images, and 658,992 labeled objects. Motivation The motivation behind creating LabelMe comes from the history of publicly available data for computer vision researchers. Most available data was tailored to a specific research group's problems and caused new researchers to have to collect additional data to solve their own problems. LabelMe was created to solve several common shortcomings of available data. The following is a list of qualities that distinguish LabelMe from previous work. * Designed for recognition of a class of objects instead of single instances of an object. For example, a traditional dataset may h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caltech 101
Caltech 101 is a data set of digital images created in September 2003 and compiled by Fei-Fei Li, Marco Andreetto, Marc 'Aurelio Ranzato and Pietro Perona at the California Institute of Technology. It is intended to facilitate Computer Vision research and techniques and is most applicable to techniques involving image recognition classification and categorization. Caltech 101 contains a total of 9,146 images, split between 101 distinct object categories (faces, watches, ants, pianos, etc.) and a background category. Provided with the images are a set of annotations describing the outlines of each image, along with a Matlab script for viewing. Purpose Most Computer Vision and Machine Learning algorithms function by training on example inputs. They require a large and varied set of training data to work effectively. For example, the real-time face detection method used by Paul Viola and Michael J. Jones was trained on 4,916 hand-labeled faces. Cropping, re-sizing and hand-marking ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Manual Image Annotation Tools
Manual image annotation is the process of manually defining regions in an image and creating a textual description of those regions. Such annotations can for instance be used to train machine learning algorithms for computer vision applications. This is a list of computer software Software is a set of computer programs and associated documentation and data. This is in contrast to hardware, from which the system is built and which actually performs the work. At the lowest programming level, executable code consists ... which can be used for manual annotation of images. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Manual image annotation tools Lists of software ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VoTT
VoTT (Visual Object Tagging Tool) is a free and open source electron app for image annotation and labeling developed by Microsoft. The software is written in the TypeScript programming language and used for building end to end object detection models from image and videos assets for computer vision algorithms. Overview VoTT is a React+ Redux web application that requires Node.js and npm. It is available as a stand-alone web application and can be used in any modern web browser. Notable features include the ability to label images or video frames, support for importing data from local or cloud storage providers, and support for exporting labeled data to local or cloud storage providers. Labeled assets can be exported into the following formats: * Comma-separated values (CSV) * Microsoft Azure Custom Vision Service * Microsoft Cognitive Toolkit (CNTK) * TensorFlow (Pascal VOC and TFRecords) * VoTT (generic JSON schema) The VoTT source code is licensed under MIT License and av ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
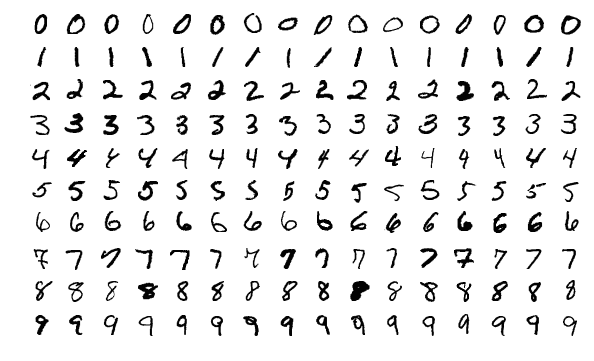
MNIST Database
The MNIST database (''Modified National Institute of Standards and Technology database'') is a large database of handwritten digits that is commonly used for training various image processing systems. The database is also widely used for training and testing in the field of machine learning. It was created by "re-mixing" the samples from NIST's original datasets. The creators felt that since NIST's training dataset was taken from American Census Bureau employees, while the testing dataset was taken from American high school students, it was not well-suited for machine learning experiments. Furthermore, the black and white images from NIST were normalized to fit into a 28x28 pixel bounding box and anti-aliased, which introduced grayscale levels. The MNIST database contains 60,000 training images and 10,000 testing images. Half of the training set and half of the test set were taken from NIST's training dataset, while the other half of the training set and the other half of the test ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Datasets For Machine Learning Research
These datasets are applied for machine learning research and have been cited in peer-reviewed academic journals. Datasets are an integral part of the field of machine learning. Major advances in this field can result from advances in learning algorithms (such as deep learning), computer hardware, and, less-intuitively, the availability of high-quality training datasets. High-quality labeled training datasets for supervised and semi-supervised machine learning algorithms are usually difficult and expensive to produce because of the large amount of time needed to label the data. Although they do not need to be labeled, high-quality datasets for unsupervised learning can also be difficult and costly to produce. Image data These datasets consist primarily of images or videos for tasks such as object detection, facial recognition, and multi-label classification. Facial recognition In computer vision, face images have been used extensively to develop facial recognition sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MIT Computer Science And Artificial Intelligence Laboratory
Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL) is a research institute at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) formed by the 2003 merger of the Laboratory for Computer Science (LCS) and the Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (AI Lab). Housed within the Ray and Maria Stata Center, CSAIL is the largest on-campus laboratory as measured by research scope and membership. It is part of the Schwarzman College of Computing but is also overseen by the MIT Vice President of Research. Research activities CSAIL's research activities are organized around a number of semi-autonomous research groups, each of which is headed by one or more professors or research scientists. These groups are divided up into seven general areas of research: * Artificial intelligence * Computational biology * Graphics and vision * Language and learning * Theory of computation * Robotics * Systems (includes computer architecture, databases, distributed systems, networks and networked sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
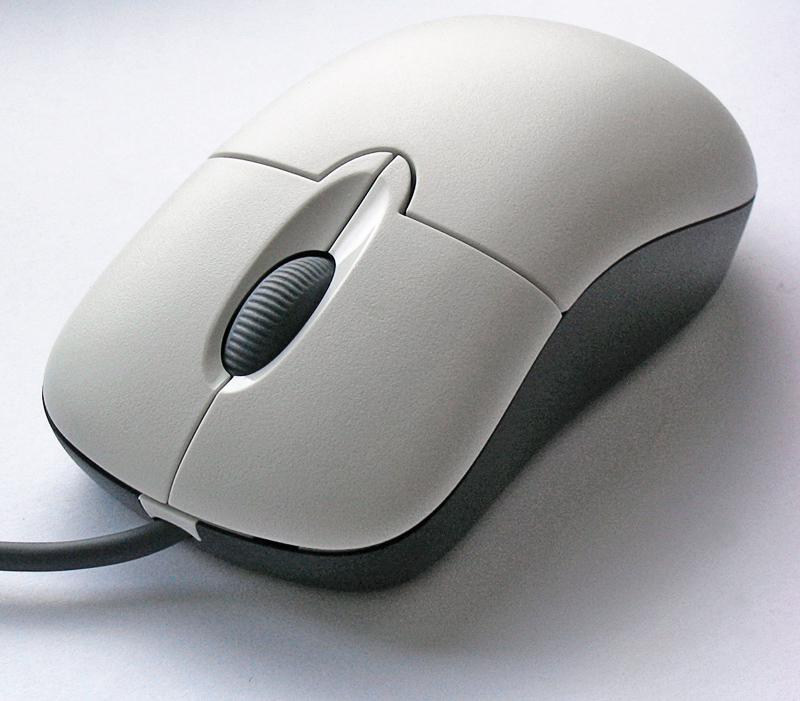
Mouse (computing)
A computer mouse (plural mice, sometimes mouses) is a hand-held pointing device that detects two-dimensional motion relative to a surface. This motion is typically translated into the motion of a pointer on a display, which allows a smooth control of the graphical user interface of a computer. The first public demonstration of a mouse controlling a computer system was in 1968. Mice originally used two separate wheels to track movement across a surface: one in the X-dimension and one in the Y. Later, the standard design shifted to utilize a ball rolling on a surface to detect motion. Most modern mice use optical sensors that have no moving parts. Though originally all mice were connected to a computer by a cable, many modern mice are cordless, relying on short-range radio communication with the connected system. In addition to moving a cursor, computer mice have one or more buttons to allow operations such as the selection of a menu item on a display. Mice often also feature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Histogram
In image processing and photography, a color histogram is a representation of the distribution of colors in an image. For digital images, a color histogram represents the number of pixels that have colors in each of a fixed list of color ranges, that span the image's color space, the set of all possible colors. The color histogram can be built for any kind of color space, although the term is more often used for three-dimensional spaces like RGB or HSV. For monochromatic images, the term intensity histogram may be used instead. For multi-spectral images, where each pixel is represented by an arbitrary number of measurements (for example, beyond the three measurements in RGB), the color histogram is ''N''-dimensional, with N being the number of measurements taken. Each measurement has its own wavelength range of the light spectrum, some of which may be outside the visible spectrum. If the set of possible color values is sufficiently small, each of those colors may be placed o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WordNet
WordNet is a lexical database of semantic relations between words in more than 200 languages. WordNet links words into semantic relations including synonyms, hyponyms, and meronyms. The synonyms are grouped into '' synsets'' with short definitions and usage examples. WordNet can thus be seen as a combination and extension of a dictionary and thesaurus. While it is accessible to human users via a web browser, its primary use is in automatic text analysis and artificial intelligence applications. WordNet was first created in the English language and the English WordNet database and software tools have been released under a BSD style license and are freely available for download from that WordNet website. History and team members WordNet was first created in English only in the Cognitive Science Laboratory of Princeton University under the direction of psychology professor George Armitage Miller starting in 1985 and was later directed by Christiane Fellbaum. The project was ini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algorithms
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequence of rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific problems or to perform a computation. Algorithms are used as specifications for performing calculations and data processing. More advanced algorithms can perform automated deductions (referred to as automated reasoning) and use mathematical and logical tests to divert the code execution through various routes (referred to as automated decision-making). Using human characteristics as descriptors of machines in metaphorical ways was already practiced by Alan Turing with terms such as "memory", "search" and "stimulus". In contrast, a heuristic is an approach to problem solving that may not be fully specified or may not guarantee correct or optimal results, especially in problem domains where there is no well-defined correct or optimal result. As an effective method, an algorithm can be expressed within a finite amount of space and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |