 |
La Coupole
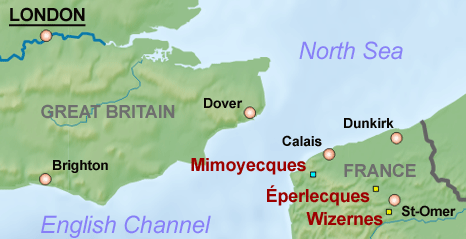
''La Coupole'' ( en, The Dome), also known as the ''Coupole d'Helfaut-Wizernes'' and originally codenamed ''Bauvorhaben'' 21 ('Building Project 21') or ''Schotterwerk Nordwest'' (Northwest Gravel Works), is a Second World War bunker complex in the Pas-de-Calais '' department'' of northern France, about from Saint-Omer, and some 14.4 kilometers (8.9 miles) south-southeast from the less developed Blockhaus d'Eperlecques V-2 launch installation in the same area. It was built by the forces of Nazi Germany between 1943 and 1944 to serve as a launch base for V-2 rockets directed against London and southern England, and is the earliest known precursor to modern underground missile silos still in existence. Constructed in the side of a disused chalk quarry, the most prominent feature of the complex is an immense concrete dome, to which its modern name refers. It was built above a network of tunnels housing storage areas, launch facilities and crew quarters. The facility was designed to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Wizernes
Wizernes (; vls, Wezerne) is a commune in the Pas-de-Calais department, northern France. It lies southwest of Saint-Omer on the banks of the river Aa at the D928 and D211 road junction. The commune is twinned with Ensdorf, Germany. Population History The village was named "Weserinium" in 844 and was damaged by the Allies of World War II during Operation Crossbow bombings of the German V-weapon bunker complex known as La Coupole ''La Coupole'' ( en, The Dome), also known as the ''Coupole d'Helfaut-Wizernes'' and originally codenamed ''Bauvorhaben'' 21 ('Building Project 21') or ''Schotterwerk Nordwest'' (Northwest Gravel Works), is a Second World War bunker complex in the .... Places of interest * The church of St. Folquin, dating from the twentieth century. References Communes of Pas-de-Calais {{PasdeCalais-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
German Occupation Of France During World War II
The Military Administration in France (german: Militärverwaltung in Frankreich; french: Occupation de la France par l'Allemagne) was an interim occupation authority established by Nazi Germany during World War II to administer the occupied zone in areas of northern and western France. This so-called ' was established in June 1940, and renamed ' ("north zone") in November 1942, when the previously unoccupied zone in the south known as ' ("free zone") was also occupied and renamed ' ("south zone"). Its role in France was partly governed by the conditions set by the Second Armistice at after the success of the leading to the Fall of France; at the time both French and Germans thought the occupation would be temporary and last only until Britain came to terms, which was believed to be imminent. For instance, France agreed that its soldiers would remain prisoners of war until the cessation of all hostilities. The "French State" (') replaced the French Third Republic that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
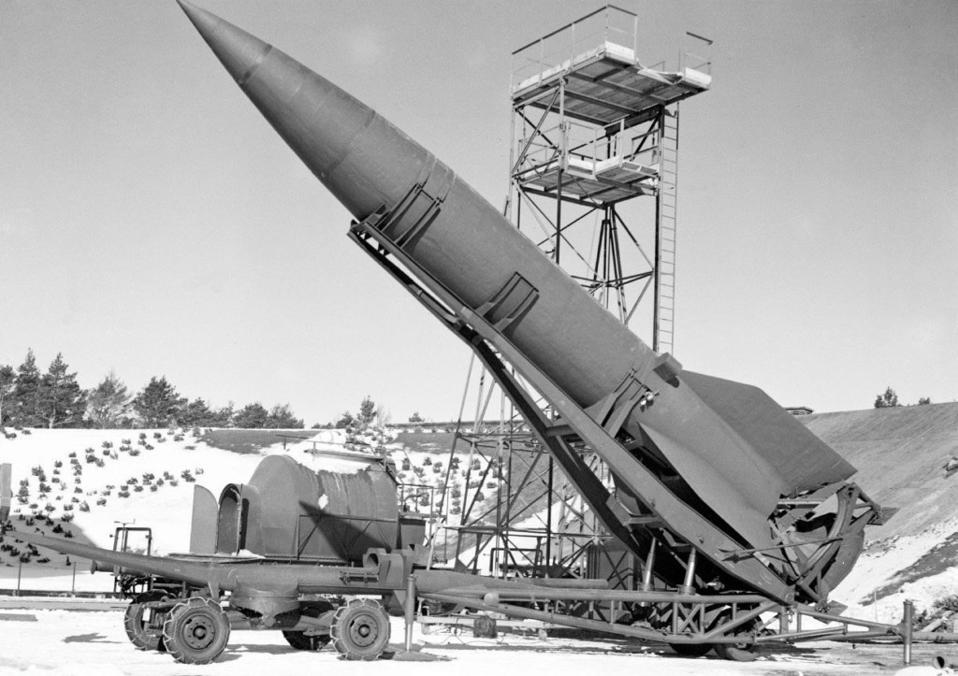 |
Meillerwagen
The ''Meillerwagen'' ( en, Meiller vehicle) was a German World War II trailer used to transport a V-2 rocket from the 'transloading point' of the Technical Troop Area to the launching point, to erect the missile on the ''Brennstand'' ( en, firing stand),) blast deflector shaped somewhat like a lemon juicer was used under the firing table. and to act as the service gantry for fuelling and launch preparation. The unofficial 'Meillerwagen' name was often used in official documents and refers to a parts supplier for the trailer, Meiller-Kipper GmbH of Munich, Germany (founded 1850). The Peenemünde Army Research Center designed the ''Meillerwagen'', and the Gollnow & Son company assembled the ''Meillerwagen'' from supplied components. The ''Meillerwagen'' was assembled with Italian and Russian prisoner laborers of the Lager Rebstock. The ''Meillerwagen'' was vehicle code number 102 of several vehicles in a V-2 launching battery, which included an 8 ton half-track launch contro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
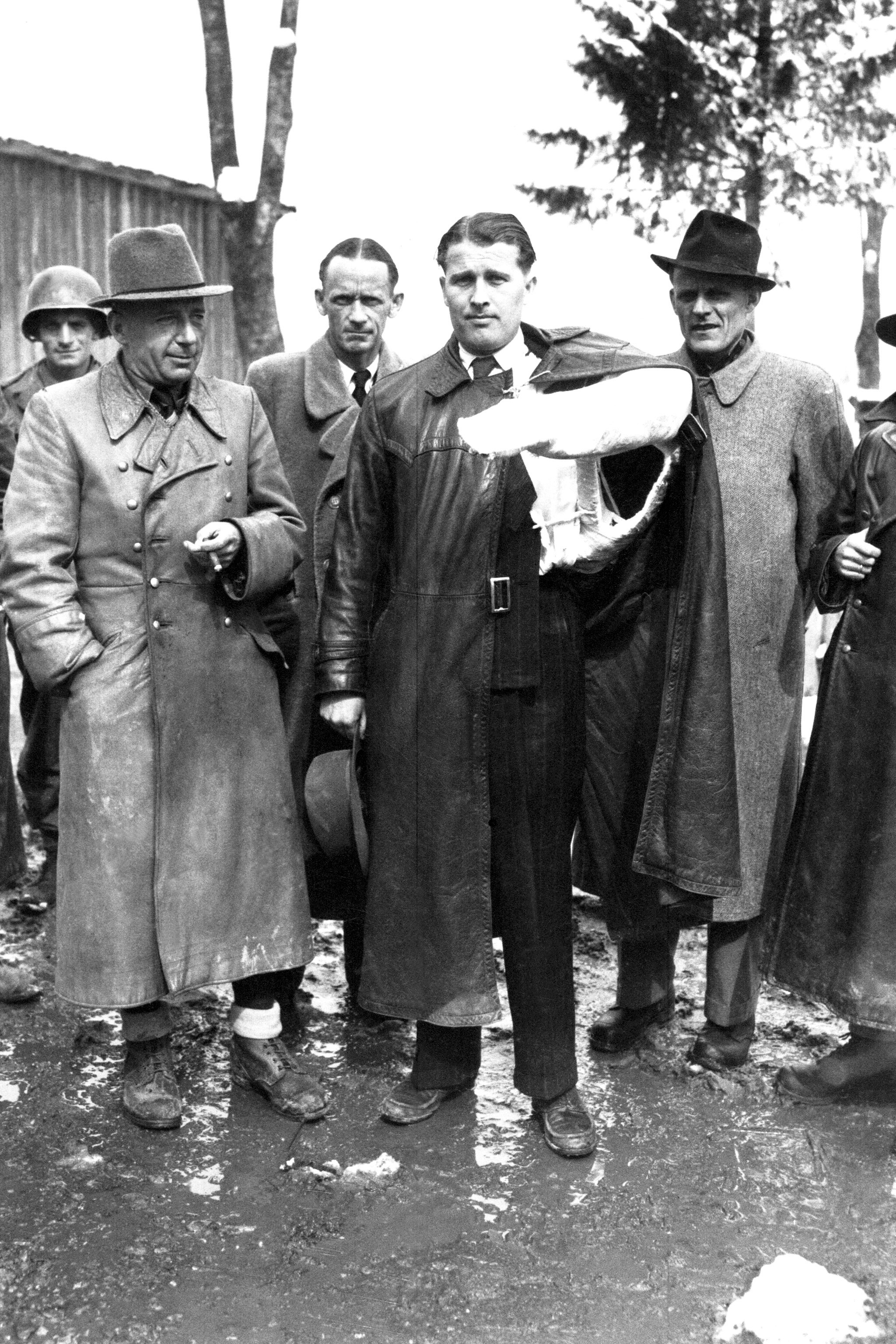 |
Walter Dornberger
Major-General Dr. Walter Robert Dornberger (6 September 1895 – 26 June 1980) was a German Army artillery officer whose career spanned World War I and World War II. He was a leader of Nazi Germany's V-2 rocket programme and other projects at the Peenemünde Army Research Centre. Dornberger was born in Gießen and enlisted in 1914. In October 1918, as an artillery lieutenant Dornberger was captured by United States Marines and spent two years in a French prisoner of war camp, mostly in solitary confinement because of repeated escape attempts. In the late 1920s, Dornberger completed an engineering course with distinction at the Berlin Technical Institute, and in the Spring of 1930,Dornberger's detailed account of the V2 project was one of the first to be published by a major participant. Dornberger graduated after five years with an MS degree in mechanical engineering from the '' Technische Hochschule Charlottenburg'' in Berlin. In 1935, Dornberger received an honorary d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
German Army (Wehrmacht)
The German Army (, "army") is the land component of the armed forces of Federal Republic of Germany, Germany. The present-day German Army was founded in 1955 as part of the newly formed West German ''Bundeswehr'' together with the German Navy, ''Marine'' (German Navy) and the German Air Force, ''Luftwaffe'' (German Air Force). , the German Army had a strength of 62,766 soldiers. History Overview A German army equipped, organized, and trained following a single doctrine and permanently unified under one command in 1871 during the unification of Germany under the leadership of Prussia. From 1871 to 1919, the title ''German Army (German Empire), Deutsches Heer'' (German Army) was the official name of the German land forces. Following the German defeat in World War I and the end of the German Empire, the main army was dissolved. From 1921 to 1935 the name of the German land forces was the ''Reichswehr, Reichsheer'' (Army of the Empire) and from 1935 to 1945 the name ''German Army (We ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Peenemünde Army Research Center
The Peenemünde Army Research Center (german: Heeresversuchsanstalt Peenemünde, HVP) was founded in 1937 as one of five military proving grounds under the German Army Weapons Office (''Heereswaffenamt''). Several German guided missiles and rockets of World War II were developed by the HVP, including the V-2 rocket. The works were attacked by the British in Operation Crossbow from August 1943, before falling to the Soviets in May 1945. History On April 2, 1936, the aviation ministry paid 750,000 reichsmarks to the town of Wolgast for the whole Northern peninsula of the Baltic island of Usedom. By the middle of 1938, the Army facility had been separated from the Luftwaffe facility and was nearly complete, with personnel moved from Kummersdorf. The Army Research Center (''Peenemünde Ost'') consisted of ''Werk Ost'' and ''Werk Süd'', while ''Werk West'' (Peenemünde West) was the Luftwaffe Test Site (), one of the four test and research facilities of the Luftwaffe, with i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian Sea in the north. It is more than long and wide, covering . It hosts key north European shipping lanes and is a major fishery. The coast is a popular destination for recreation and tourism in bordering countries, and a rich source of energy resources, including wind and wave power. The North Sea has featured prominently in geopolitical and military affairs, particularly in Northern Europe, from the Middle Ages to the modern era. It was also important globally through the power northern Europeans projected worldwide during much of the Middle Ages and into the modern era. The North Sea was the centre of the Vikings' rise. The Hanseatic League, the Dutch Republic, and the British each sought to gain command of the North Sea and access ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
English Channel
The English Channel, "The Sleeve"; nrf, la Maunche, "The Sleeve" ( Cotentinais) or (Jèrriais), ( Guernésiais), "The Channel"; br, Mor Breizh, "Sea of Brittany"; cy, Môr Udd, "Lord's Sea"; kw, Mor Bretannek, "British Sea"; nl, Het Kanaal, "The Channel"; german: Ärmelkanal, "Sleeve Channel" (French: ''la Manche;'' also called the British Channel or simply the Channel) is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that separates Southern England from northern France. It links to the southern part of the North Sea by the Strait of Dover at its northeastern end. It is the busiest shipping area in the world. It is about long and varies in width from at its widest to at its narrowest in the Strait of Dover."English Channel". ''The Columbia Encyclopedia'', 2004. It is the smallest of the shallow seas around the continental shelf of Europe, covering an area of some . The Channel was a key factor in Britain becoming a naval superpower and has been utilised by Britain as a natural d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Ethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl group linked to a hydroxyl group). Ethanol is a volatile, flammable, colorless liquid with a characteristic wine-like odor and pungent taste. It is a psychoactive recreational drug, the active ingredient in alcoholic drinks. Ethanol is naturally produced by the fermentation process of sugars by yeasts or via petrochemical processes such as ethylene hydration. It has medical applications as an antiseptic and disinfectant. It is used as a chemical solvent and in the synthesis of organic compounds, and as a fuel source. Ethanol also can be dehydrated to make ethylene, an important chemical feedstock. As of 2006, world production of ethanol was , coming mostly from Brazil and the U.S. Etymology ''Ethanol'' is the systematic name defined by the Interna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg) |
Liquid Oxygen
Liquid oxygen—abbreviated LOx, LOX or Lox in the aerospace, submarine and gas industries—is the liquid form of molecular oxygen. It was used as the oxidizer in the first liquid-fueled rocket invented in 1926 by Robert H. Goddard, an application which has continued to the present. Physical properties Liquid oxygen has a pale blue color and is strongly paramagnetic: it can be suspended between the poles of a powerful horseshoe magnet. Liquid oxygen has a density of , slightly denser than liquid water, and is cryogenic with a freezing point of and a boiling point of at . Liquid oxygen has an expansion ratio of 1:861 under and , and because of this, it is used in some commercial and military aircraft as a transportable source of breathing oxygen. Because of its cryogenic nature, liquid oxygen can cause the materials it touches to become extremely brittle. Liquid oxygen is also a very powerful oxidizing agent: organic materials will burn rapidly and energetically in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Nazi Germany, Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his death in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the leader of the Nazi Party, becoming the Chancellor of Germany, chancellor in 1933 and then taking the title of in 1934. During his dictatorship, he initiated European theatre of World War II, World War II in Europe by invasion of Poland, invading Poland on 1 September 1939. He was closely involved in military operations throughout the war and was central to the perpetration of the Holocaust: the genocide of Holocaust victims, about six million Jews and millions of other victims. Hitler was born in Braunau am Inn in Austria-Hungary and was raised near Linz. He lived in Vienna later in the first decade of the 1900s and moved to Germany in 1913. He was decorated during his Military career of Adolf Hitler, service in the German Army in Worl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
SRBM
A short-range ballistic missile (SRBM) is a ballistic missile with a range of about or less. In past and potential regional conflicts, these missiles have been and would be used because of the short distances between some countries and their relative low cost and ease of configuration. In modern terminology, SRBMs are part of the wider grouping of theatre ballistic missiles, which includes any ballistic missile with a range of less than 3,500 km. Models See also *Tactical ballistic missile *Medium-range ballistic missile (MRBM) *Intermediate-range ballistic missile (IRBM) *Intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) *Anti-ship ballistic missile (ASBM) *Hypersonic cruise missile A cruise missile is a guided missile used against terrestrial or naval targets that remains in the atmosphere and flies the major portion of its flight path at approximately constant speed. Cruise missiles are designed to deliver a large warhe ... References Missile types {{Mis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |