|
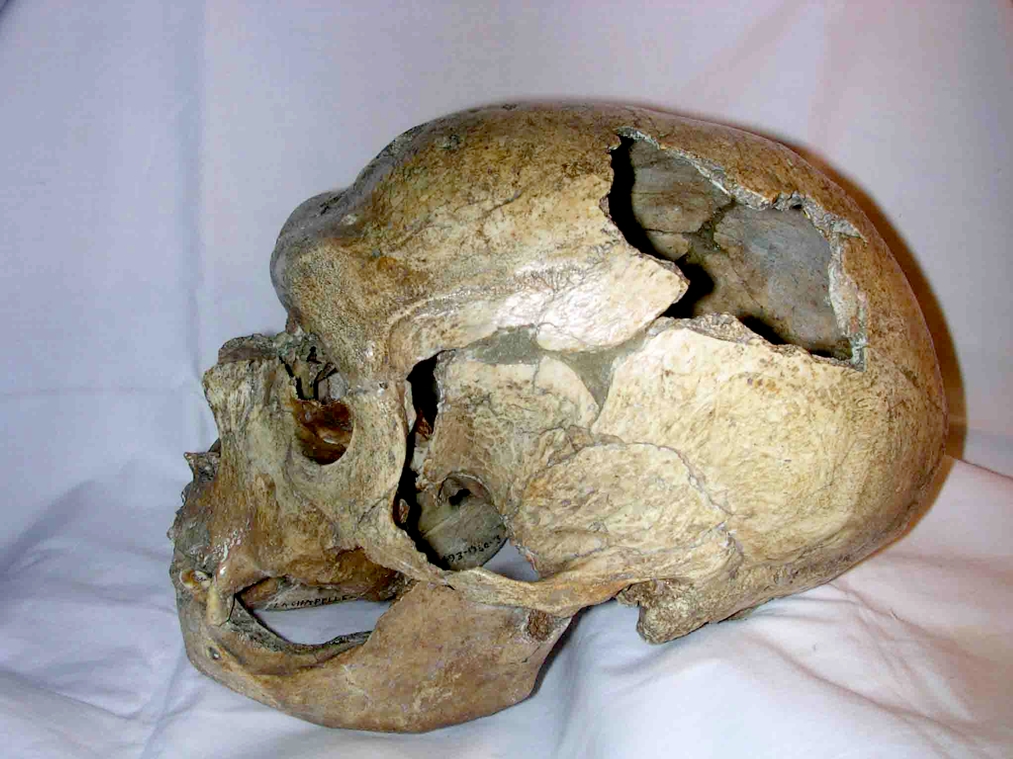
La Chapelle-aux-Saints 1
La Chapelle-aux-Saints 1 ("The Old Man") is an almost-complete male Neanderthal skeleton discovered in La Chapelle-aux-Saints, France by A. and J. Bouyssonie, and L. Bardon in 1908. The individual was about 40 years of age at the time of his death. He was in bad health, having lost most of his teeth and suffering from bone resorption in the mandible and advanced arthritis. It is the most convincing example of a possible Neanderthal deliberate burial, but like all claimed Neanderthal burials, this isn't generally accepted. The remains were first studied by Marcellin Boule, whose reconstruction of Neanderthal anatomy based on la Chapelle-aux-Saints material shaped popular perceptions of the Neanderthals for over thirty years. The La Chapelle-aux-Saints specimen is typical of "classic" Western European Neanderthal anatomy. It is estimated to be about 60,000 years old. Boule's reconstruction of La Chapelle-aux-Saints 1, published during 1911–1913, depicted Neanderthals with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homo Neanderthalensis
Neanderthals (, also ''Homo neanderthalensis'' and erroneously ''Homo sapiens neanderthalensis''), also written as Neandertals, are an Extinction, extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Eurasia until about 40,000 years ago. While the "causes of Neanderthal disappearance about 40,000 years ago remain highly contested," demographic factors such as small population size, inbreeding and genetic drift, are considered probable factors. Other scholars have proposed competitive replacement, assimilation into the modern human genome (bred into extinction), great climate change, climatic change, disease, or a combination of these factors. It is unclear when the line of Neanderthals split from that of Early modern human, modern humans; studies have produced various intervals ranging from 315,000 to more than 800,000 years ago. The date of divergence of Neanderthals from their ancestor ''Homo heidelbergensis, H. heidelbergensis'' is also unclear. The oldest potential ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Chapelle-aux-Saints
La Chapelle-aux-Saints (; oc, La Chapela daus Sents) is a commune in the Corrèze department in central France. History Neanderthal skeleton The La Chapelle-aux-Saints cave, bordering the Sourdoire valley, revealed many archeological artifacts belonging to the late Mousterian techno-complex,BINANT P., 1991 - ''Les sépultures du Paléolithique''. Paris : Errance including the first ever recognized Neanderthal burial discovered on August 3, 1908. Jean and Amédée Bouyssonie, as well as L. Bardon, led archaeological digs in the cave from 1905 to 1908, discovering over 1,000 pieces of stone industry (mainly flint), bones of different fauna including reindeer, bovid, horse, fox, wolf and even a rhinoceros’ tooth. The most spectacular discovery was that of a very well preserved skeleton of an adult Neanderthal man who appears to have been intentionally buried in a rectangular pit deep, long and wide.NOUGIER L.-R., 1963, ''La préhistoire : essai de paléosociologie religieuse'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its Metropolitan France, metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea; overseas territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and many islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean. Due to its several coastal territories, France has the largest exclusive economic zone in the world. France borders Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany, Switzerland, Monaco, Italy, Andorra, and Spain in continental Europe, as well as the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Netherlands, Suriname, and Brazil in the Americas via its overseas territories in French Guiana and Saint Martin (island), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neanderthal
Neanderthals (, also ''Homo neanderthalensis'' and erroneously ''Homo sapiens neanderthalensis''), also written as Neandertals, are an extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Eurasia until about 40,000 years ago. While the "causes of Neanderthal disappearance about 40,000 years ago remain highly contested," demographic factors such as small population size, inbreeding and genetic drift, are considered probable factors. Other scholars have proposed competitive replacement, assimilation into the modern human genome (bred into extinction), great climatic change, disease, or a combination of these factors. It is unclear when the line of Neanderthals split from that of modern humans; studies have produced various intervals ranging from 315,000 to more than 800,000 years ago. The date of divergence of Neanderthals from their ancestor ''H. heidelbergensis'' is also unclear. The oldest potential Neanderthal bones date to 430,000 years ago, but the classification ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bone Resorption
Bone resorption is resorption of bone tissue, that is, the process by which osteoclasts break down the tissue in bones and release the minerals, resulting in a transfer of calcium from bone tissue to the blood. The osteoclasts are multi-nucleated cells that contain numerous mitochondria and lysosomes. These are the cells responsible for the resorption of bone. Osteoblasts are generally present on the outer layer of bone, just beneath the periosteum. Attachment of the osteoclast to the osteon begins the process. The osteoclast then induces an infolding of its cell membrane and secretes collagenase and other enzymes important in the resorption process. High levels of calcium, magnesium, phosphate and products of collagen will be released into the extracellular fluid as the osteoclasts tunnel into the mineralized bone. Osteoclasts are prominent in the tissue destruction found in psoriatic arthritis and rheumatological disorders. The human body is in a constant state of bone remod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthritis
Arthritis is a term often used to mean any disorder that affects joints. Symptoms generally include joint pain and stiffness. Other symptoms may include redness, warmth, swelling, and decreased range of motion of the affected joints. In some types of arthritis, other organs are also affected. Onset can be gradual or sudden. There are over 100 types of arthritis. The most common forms are osteoarthritis (degenerative joint disease) and rheumatoid arthritis. Osteoarthritis usually occurs with age and affects the fingers, knees, and hips. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder that often affects the hands and feet. Other types include gout, lupus, fibromyalgia, and septic arthritis. They are all types of rheumatic disease. Treatment may include resting the joint and alternating between applying ice and heat. Weight loss and exercise may also be useful. Recommended medications may depend on the form of arthritis. These may include pain medications such as ibuprofen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neanderthal Burial
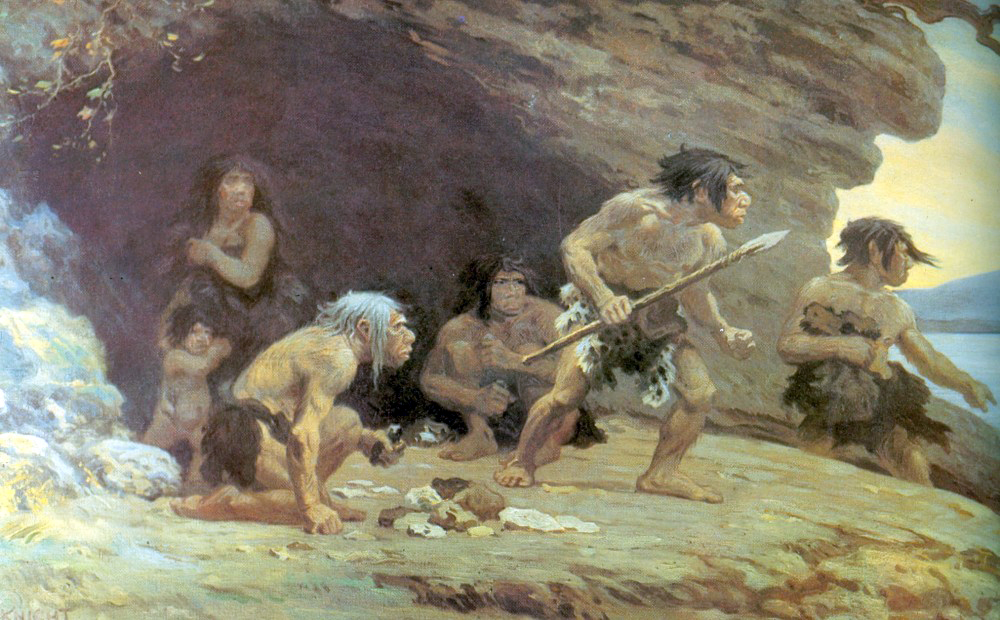
Almost everything about Neanderthal behaviour remains controversial. From their physiology, Neanderthals are presumed to have been omnivores, but animal protein formed the majority of their dietary protein, showing them to have been carnivorous apex predators and not scavengers. Although very little is known of their social organization, it appears patrilines would make up the nucleus of the tribe, and women would seek out partners in neighbouring tribes once reaching adolescence, presumably to avoid inbreeding. The men would pass knowledge and customs down from fathers to sons. Neanderthal women appear to heavily skew physically impressive neanderthal men, hinting that neanderthal men would compete with each other and polyamorous relationships would emerge. The quality of stone tools at archaeological sites suggests Neanderthals were good at "expert" cognition, a form of observational learning and practice – acquired through apprenticeship – that relies heavily on long-term pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neandertal Skull From La Chapelle Aux Saints
Neanderthals (, also ''Homo neanderthalensis'' and erroneously ''Homo sapiens neanderthalensis''), also written as Neandertals, are an extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Eurasia until about 40,000 years ago. While the "causes of Neanderthal disappearance about 40,000 years ago remain highly contested," demographic factors such as small population size, inbreeding and genetic drift, are considered probable factors. Other scholars have proposed competitive replacement, assimilation into the modern human genome (bred into extinction), great climatic change, disease, or a combination of these factors. It is unclear when the line of Neanderthals split from that of modern humans; studies have produced various intervals ranging from 315,000 to more than 800,000 years ago. The date of divergence of Neanderthals from their ancestor ''H. heidelbergensis'' is also unclear. The oldest potential Neanderthal bones date to 430,000 years ago, but the classification r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marcellin Boule
Pierre-Marcellin Boule (1 January 1861 – 4 July 1942), better known as merely Marcellin Boule, was a French palaeontologist, geologist, and anthropologist. Early life and education Pierre-Marcellin Boule was born in Montsalvy, France. Career Boule was a professor at the Muséum National d’Histoire Naturelle, Paris (1902–36) and "for many years director of the Institut de Paléontologie Humaine, Paris." He was an editor (1893–1940) of the journal ''L’Anthropologie'' (and contributed articles to it) and was the founder of two other scientific journals. Boule studied and published in 1910 the first analysis of a complete Neanderthal specimen. The fossil discovered in La Chapelle-aux-Saints was an old man, and Boule characterized it as brutish, bent-kneed and not a fully erect biped. In an illustration Boule commissioned, the Neanderthal was characterized as a hairy gorilla-like figure with opposable toes, according to a skeleton which was already distorted with arthri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neanderthal Anatomy
Neanderthal anatomy differed from modern humans in that they had a more robust build and distinctive morphological features, especially on the cranium, which gradually accumulated more derived aspects, particularly in certain isolated geographic regions. This robust build was an effective adaptation for Neanderthals, as they lived in the cold environments of Europe. In which they also had to operate in Europe's dense forest landscape that was extremely different from the environments of the African grassland plains that ''Homo sapiens'' adapted to with a different anatomical build. Anatomical evidence suggests they were much stronger than modern humans while they were 12-14cm shorter on average than post World War II Europeans, but as tall or slightly taller than Europeans of 20 KYA: based on 45 long bones from at most 14 males and 7 females, height estimates using different methods yielded averages in the range of for males and for females. Samples of 26 specimens in 2010 fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shanidar
Shanidar Cave ( ku, Zewî Çemî Şaneder ,ئەشکەوتی شانەدەر, ) is an archaeological site located on Bradost Mountain, within the Zagros Mountains, in the Erbil Governorate of Kurdistan Region in northern Iraq. It is known for the discovery of Neanderthal remains at the site, most notably Shanidar 1, who survived several injuries during his life, possibly due to care from others in his group, and Shanidar 4, the famed 'flower burial'."Shanidar Cave." ''Shanidar Cave , Unbelievable Kurdistan – Official Tourism Site of Kurdistan'', http://bot.gov.krd/erbil-province-mirgasor/history-and-heritage/shanidar-cave Until this discovery, Cro-Magnons, the earliest known ''H. sapiens'' in Europe, were the only individuals known for purposeful, ritualistic burials. Archaeology The site, 1/2 mile from the Great Zab river and near Rowanduz, lies at 2100 feet above sea level. The cave entrance is triangular, 82 feet wide by 26 high. Its dimensions are, at maximum, 175 feet wid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Neanderthal Fossils
This is a list of Neanderthal fossils. Some important European Neanderthals Remains of more than 300 European Neanderthals have been found. This is a list of the most notable. Southwest Asian Neanderthals As of 2017, this list of Southwest Asian Neanderthals may be considered essentially complete. Central and North Asian Neanderthals Central Asian Neanderthals were found in Uzbekistan and North Asian Neanderthals in Asian Russia. See also *List of Southwest Asian Neanderthals *Neanderthal Museum *List of fossil sites *List of human fossils The following tables give an overview of notable finds of hominin fossils and remains relating to human evolution, beginning with the formation of the tribe Hominini (the divergence of the human and chimpanzee lineages) in the late Miocene, roug ... Notes References Further reading * * * * * External links * {{Homo neanderthalensis, state=expanded Human evolution ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |